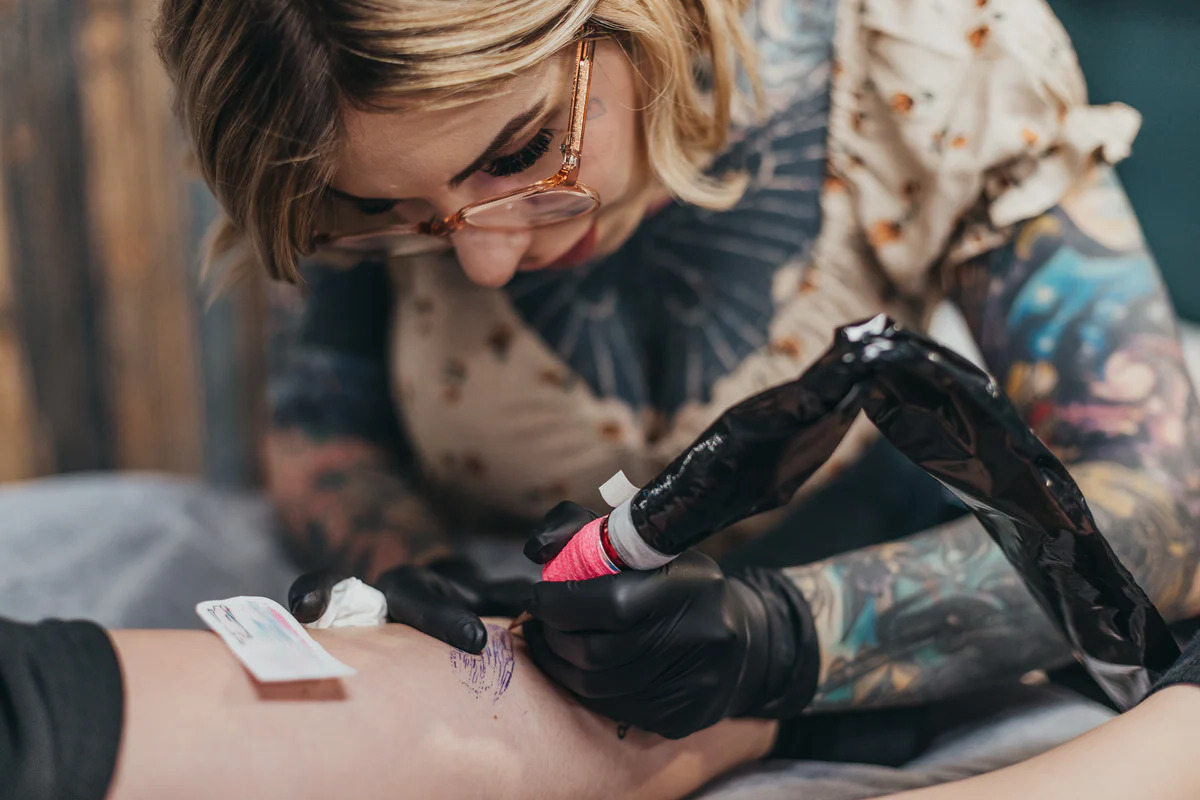
Tattooing has been a part of human culture for thousands of years, evolving from ancient rituals to modern art. The word "tattoo" comes from the Samoan term "tatau," meaning to mark or puncture the skin. Evidence of tattooing dates back to 12,000 years BC, with Ötzi the Iceman, discovered in 1991, showcasing over 60 tattoos from around 3370 to 3100 BC. Cultures worldwide, from Egypt to Polynesia, have embraced tattooing for various reasons, including status, protection, and punishment. The practice has seen significant changes, especially with the invention of the electric tattoo machine in 1891, making it faster and less painful. Today, tattoos are a global phenomenon, reflecting personal stories, cultural heritage, and artistic expression.
Key Takeaways:
- Tattooing has been around for over 12,000 years, with evidence found on mummified skin dating back to 4th millennium BC. It has been a significant part of various cultures, from Egypt to Polynesia.
- The evolution of tattooing has been fascinating, from its ancient origins to the introduction of the electric tattoo machine in the 19th century. The future of tattooing holds exciting possibilities, from bio-hacking to advanced removal technologies.
The Ancient Roots of Tattooing
Tattooing is an ancient art form that has been a part of human culture for thousands of years. Its origins are diverse, spanning multiple civilizations and continents. Let's explore some fascinating facts about the early history of tattooing.
-
Origin of the Word "Tattoo"
The word "tattoo" comes from the Samoan word "tatau," meaning to mark or puncture the skin. -
Ancient Origins
Tattooing has existed since 12,000 years BC, making it one of the oldest forms of body modification. -
Early Evidence
Physical evidence of tattooing on mummified human skin dates back to the 4th millennium BC. -
Ötzi the Iceman
Ötzi the Iceman, discovered in 1991, had over 60 tattoos on his body, dating to between 3370 and 3100 BC. -
Global Presence
Tattooed mummies have been found in at least 49 archaeological sites, including Greenland, Alaska, and Egypt.
Cultural Significance of Tattoos
Throughout history, tattoos have held various meanings and served different purposes in different cultures. Here are some intriguing facts about the cultural significance of tattoos.
-
Upper-Class Egyptian Tattoos
Around 2000 BC, upper-class Egyptian women and priestesses had tattoos believed to protect them during pregnancy. -
Roman Emperor Constantine
In AD 316, Roman Emperor Constantine banned facial tattooing, believing it defiled the divine image of man. -
Japanese Body Art
In Japan, tattoos were used to punish criminals around 720 AD but later became fashionable again. -
Arab Diplomat Ahmad Ibn Fadlan
In 922, Ahmad Ibn Fadlan described heavily tattooed traders from northern Europe with dark green lines and pictures. -
Tattooing in Polynesia
In Polynesian culture, tattoos were significant, with rituals involving pain to signify status and masculinity.
Tattoos in the West
The introduction of tattoos to the Western world brought about a new wave of fascination and adoption. Here are some key moments in the history of Western tattooing.
-
Captain Cook and the West
Captain Cook and his crew introduced tattoos to the West after their 1769 voyage to Polynesia. -
Historical Use of Tattoos
Tattoos have been used to signify status, skill, and even to ward off illness throughout history. -
Sailor Tattoos
Sailor tattoos often carried specific meanings, like a pig and rooster to protect against drowning. -
Fashionable Tattoos
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, tattoos became fashionable among aristocrats. -
Signs of Faith
Early Christians often had the sign of the cross tattooed on their bodies as a mark of faith.
Technological Advancements in Tattooing
The evolution of tattooing technology has significantly impacted the practice, making it more accessible and less painful. Here are some important milestones.
-
First Tattooed Man in England
The first tattooed man publicly shown in England was a Pacific islander known as Prince Joely in 1691. -
Holystoning
European missionaries in the Cook Islands tried to remove tattoos by scrubbing them off with sandstone. -
Collection of Tattooed Heads
In the late 18th and early 19th centuries, collecting tattooed Maori heads became popular in Europe. -
Tattoo Machine Technology
Samuel O’Reilly patented the first electric tattoo machine in 1891, inspired by Thomas Edison’s electric pen. -
Percy Waters’ Design
Percy Waters patented a tattoo machine design closer to modern models, featuring two electromagnetic coils.
Hygiene and Tattoo Ink
Hygiene and the composition of tattoo ink have always been crucial aspects of tattooing. Here are some interesting facts about these elements.
-
Hygiene Standards
Hygiene-conscious tattoo artists prevent cross-contamination by using single-use containers and sterilized equipment. -
Tattoo Ink Ingredients
Ancient tattoo ink sometimes included urine for its antiseptic properties, while modern ink uses pigments and carriers. -
Skin Piercing
A tattoo machine pierces the skin 50 to 3000 times per minute, inserting ink into the dermis layer. -
Tattoo Ink Placement
Tattoo ink is placed in the dermis, the second layer of skin, beneath the epidermis.
Religious and Philosophical Views on Tattoos
Religious and philosophical views on tattoos have varied widely across different cultures and eras. Here are some notable perspectives.
-
Religious Views
While many religions oppose tattooing, Buddhism and Hinduism use tattoos to further spirituality. -
Confucius’ Stance
Confucius opposed tattooing, believing the human body is a gift that should not be altered. -
Black Ink Removal
Black ink is the easiest color to remove during laser tattoo removal procedures.
Modern Tattooing and Its Evolution
Modern tattooing has come a long way from its ancient roots, with significant advancements and cultural shifts. Here are some key developments.
-
Martin Hildebrandt’s Parlor
Martin Hildebrandt opened the first US tattoo parlor in New York City in 1846. -
Royal Tattoos
Many royals, including King Harold II and King Edward VII, had tattoos, often for identification or symbolic reasons. -
Tattooing in Ancient China
Ancient Chinese stone sculptures depict men with facial tattoos, used both for acceptance and punishment. -
Tattooing in Japan
Japanese tattooing evolved from criminal punishment to a fashionable art form, even used by samurai warriors. -
Tattooing in Polynesia
In Polynesian societies, the pain of tattooing was integral, signifying status and masculinity. -
Tattooing in Europe
Tattooing became popular in Europe during the 18th and 19th centuries, initially among sailors and travelers. -
Modern Tattooing
The invention of the electric tattoo machine revolutionized the industry, making it faster and more accessible. -
Future of Tattooing
The future of tattooing holds many possibilities, from bio-hacking to advanced tattoo removal technologies.
The Ever-Evolving Art of Tattooing
Tattooing has a rich history spanning thousands of years and countless cultures. From Ötzi the Iceman's ancient ink to the intricate designs of Polynesian chiefs, tattoos have always held deep significance. The electric tattoo machine revolutionized the industry, making tattoos more accessible and less painful. Today, tattoos are a global phenomenon, reflecting personal stories, cultural heritage, and artistic expression. As technology advances, the future of tattooing promises even more innovation, from bio-hacking to advanced removal techniques. Understanding the history of tattooing helps us appreciate its cultural importance and the artistry behind it. Whether you're a tattoo enthusiast or just curious, the journey of tattooing is a testament to human creativity and resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.