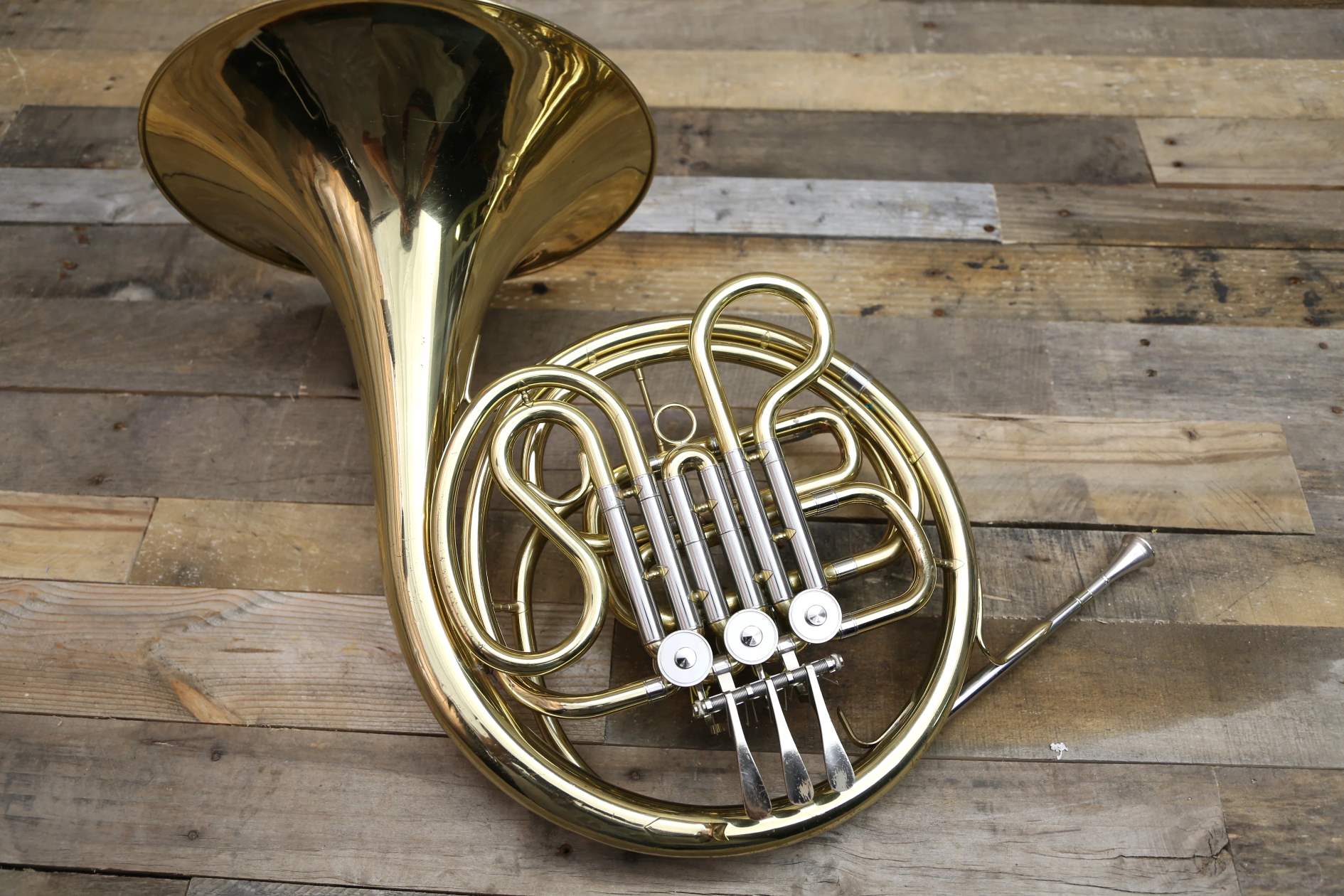
The French horn is a fascinating instrument with a rich history and a unique sound. Whether you are a music lover, a musician, or simply curious about the world of music, learning some interesting facts about the French horn can be a delightful experience. From its origins in hunting horns to its prominent role in orchestras and brass ensembles, the French horn has left a lasting impact on the world of music. In this article, we will explore 20 intriguing facts about the French horn, shedding light on its design, players, repertoire, and much more. So, whether you’re a fan of classical music or simply appreciate the beauty of this remarkable instrument, let’s dive into the world of the French horn and discover what makes it truly special.
Key Takeaways:
- The French Horn is a versatile brass instrument with a rich history and a unique sound that adds depth and complexity to various music genres.
- Playing the French Horn requires skill and technique, and its distinctive shape and wide range make it a standout instrument in orchestras and symphonies.
The French Horn is not French
Despite its name, the French Horn did not actually originate in France. It was first developed in Germany in the 19th century.
The French Horn belongs to the brass family
The French Horn is classified as a brass instrument. It is made of brass and produces sound through the vibration of the player’s lips on the mouthpiece.
The French Horn has a unique shape
The French Horn has a distinctive coiled shape, with a wide bell and a long tube that is wrapped around several times. This unique design helps to create its unique sound.
The French Horn is known for its beautiful sound
The French Horn produces a rich and warm tone that is often described as majestic and noble. It is often used in orchestras and symphonies to add depth and complexity to the music.
The French Horn has a wide range
The French Horn is capable of playing a wide range of notes, from the deep and resonant low notes to the high and bright notes. It is known for its versatility in different musical genres.
The French Horn is played with the right hand
Unlike most other brass instruments, the French Horn is played with the right hand inside the bell. This hand is used to control the pitch and produce different notes.
The French Horn requires a high level of skill
Playing the French Horn requires a high level of skill and technique. It takes years of practice to master the instrument and produce a clear and controlled sound.
The French Horn has different variations
There are different variations of the French Horn, including the single horn, double horn, and triple horn. Each variation has a slightly different range and sound.
The French Horn has valves
The French Horn has valves that are used to change the length of the tubing and therefore the pitch of the instrument. By pressing different combinations of valves, the player can produce a wide range of notes.
The French Horn is used in various music genres
The French Horn is not limited to classical music. It is also used in jazz, pop, and even in movie soundtracks to add a distinctive and memorable sound.
The French Horn is difficult to transport
Due to its size and shape, the French Horn can be challenging to transport. Many horn players use a special case or gig bag to protect their instrument when traveling.
The French Horn is versatile
The French Horn can play both solo and ensemble music. It is often featured in concertos and chamber music, as well as in symphonies and orchestral works.
The French Horn is an ancient instrument
The precursor to the French Horn can be traced back to ancient times, with early versions of horn-like instruments dating back thousands of years.
The French Horn is used in military ceremonies
The French Horn has a long-standing tradition of being used in military ceremonies, such as bugle calls and fanfares. Its powerful and commanding sound makes it well-suited for these occasions.
The French Horn has a unique playing technique
Playing the French Horn requires a special technique called hand-stopping. This involves placing the hand inside the bell to manipulate the sound and create different effects.
The French Horn has a double wall
The French Horn is constructed with a double wall, which helps to improve the intonation and resonance of the instrument.
The French Horn has a wide mouthpiece
The mouthpiece of the French Horn is larger than most brass instruments, allowing for a greater level of control and flexibility in playing.
The French Horn is used in famous classical compositions
The French Horn has been featured prominently in many famous classical compositions, such as Richard Strauss‘ “Also sprach Zarathustra” and Mozart’s “Horn Concerto No. 4.”
The French Horn is handcrafted
Each French Horn is handcrafted by skilled artisans. The process involves shaping the brass, soldering the different parts together, and fine-tuning the instrument to ensure optimal sound quality.
The French Horn is a versatile solo instrument
The French Horn is often chosen as a solo instrument in orchestral works due to its expressive capabilities and ability to evoke emotion.
Conclusion
The French horn is a fascinating instrument with a rich history and unique sound. Its versatility allows it to be played in various musical genres, from classical orchestras to jazz ensembles. Whether you’re a fan of its melodic solos or its powerful brass section contributions, the French horn is sure to leave a lasting impression. So, next time you hear the elegant tones of a French horn, take a moment to appreciate the skill and artistry required to master this remarkable instrument.
FAQs
Q: How is the French horn different from other brass instruments?
A: The French horn is distinguished by its coiled tubing, which gives it a unique shape and allows for a wide range of notes and tones. Unlike other brass instruments, such as the trumpet or trombone, the French horn is played by placing the hand inside the bell to control the pitch and timbre.
Q: What is the history of the French horn?
A: The French horn has a long and storied history, dating back to ancient times. It evolved from hunting horns used in medieval hunts to signal the presence of game. As it gained popularity in orchestras during the 18th century, innovative changes were made to improve its sound and range, leading to the instrument we know today.
Q: How difficult is it to learn to play the French horn?
A: Learning to play the French horn can be challenging, as it requires physical dexterity, breath control, and an understanding of music theory. Mastering the instrument takes time and practice, but with dedication and proper instruction, anyone can learn to play the French horn.
Q: Is the French horn only used in classical music?
A: While the French horn is commonly associated with classical music, it is also used in a variety of other genres, including jazz, rock, and even pop music. Its beautiful tone and unique sound make it a versatile instrument that can be found in a wide range of musical styles.
Q: How is the French horn played in an orchestra?
A: In an orchestra, the French horn is typically played by a dedicated horn section. The musicians sit together and coordinate their playing to create a unified sound. The French horn often plays melodic solos as well as supporting the overall harmonies and rhythms of the orchestra.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.