If you’ve ever studied geometry, you’re likely familiar with the concept of triangles. Triangles are one of the fundamental shapes in mathematics, and they have a wide range of properties and characteristics that make them a fascinating subject to explore. In this article, we’ll delve into 19 important triangle math facts that will enhance your understanding of these geometric wonders.
We’ll cover a variety of topics, including the different types of triangles, their angles and sides, as well as various formulas and theorems associated with triangles. Whether you’re a student looking to deepen your understanding of geometry or simply someone interested in expanding their general knowledge, this article will provide you with key insights into the intriguing world of triangle mathematics.
So, grab your protractor and compass, and let’s embark on an educational journey into the realm of triangles!
Key Takeaways:
- Triangles have special rules, like their angles always add up to 180 degrees. They’re used in real life for building, navigation, and even finding the area of a field.
- Trigonometry uses triangles to solve problems in fields like engineering and physics. It’s like a secret code that helps us understand the world around us.
The sum of the interior angles in a triangle is always 180 degrees.
This fundamental fact in triangle geometry holds true for any type of triangle, whether it is equilateral, isosceles, or scalene. The three angles inside a triangle will always add up to 180 degrees, making it a key concept in solving triangle-related problems.
An equilateral triangle has all three sides of equal length.
In an equilateral triangle, all three sides are exactly the same length. This means that the angles in an equilateral triangle are also equal, each measuring 60 degrees. Equilateral triangles are often used as building blocks in geometric constructions.
A right triangle has one angle that measures 90 degrees.
A right triangle is a special type of triangle that has one angle equal to 90 degrees. This angle is often referred to as the right angle. The other two angles in a right triangle are acute, meaning they are less than 90 degrees. Right triangles play a crucial role in trigonometry, where the relationships between their sides and angles are extensively studied.
The Pythagorean theorem relates the sides of a right triangle.
The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. This theorem, formulated by the ancient Greek mathematician Pythagoras, has numerous practical applications in geometry and physics.
The area of a triangle is half the product of its base and height.
The area of a triangle can be calculated using the formula A = 0.5 * base * height. The base is any side of the triangle, and the height is the perpendicular distance from that base to the opposite vertex. This formula is widely used in various fields, including architecture, engineering, and design.
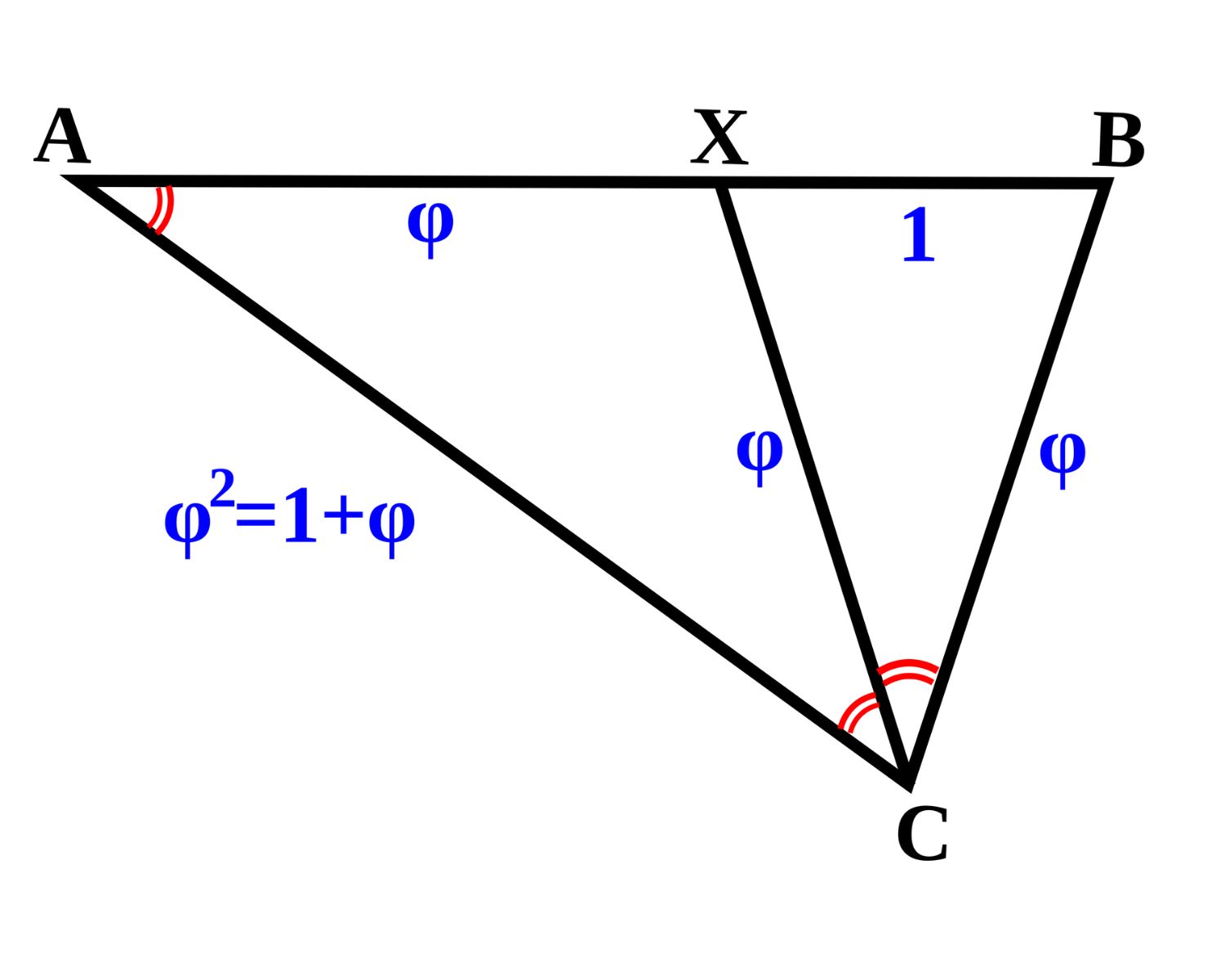
Similar triangles have the same shape but may differ in size.
Two triangles are similar if their corresponding angles are equal and their corresponding sides are in proportion. This means that their shapes are identical, but one triangle may be larger or smaller than the other. The concept of similarity is crucial in geometry and is utilized in various real-world applications, such as map scaling and 3D modeling.
An isosceles triangle has two sides of equal length.
In an isosceles triangle, two sides have the same length, while the third side is different. The angles opposite the equal sides are also equal. Isosceles triangles often arise in mathematical problems and constructions due to their symmetrical properties.
A scalene triangle has no equal sides or angles.
A scalene triangle is a triangle in which no two sides or angles are equal. Each side and angle of a scalene triangle is unique. This type of triangle poses interesting challenges and calculations in geometry due to its asymmetrical nature.
A right angle in a triangle creates a special trigonometric relationship.
The presence of a right angle in a triangle allows for the establishment of trigonometric relationships using the sine, cosine, and tangent functions. These functions define the ratios between the lengths of the sides of a right triangle with respect to its acute angles. Trigonometry is widely used in fields such as engineering, physics, and navigation.
Heron’s formula can be used to find the area of a triangle when its side lengths are known.
Heron’s formula is named after Hero of Alexandria and provides a way to calculate the area of a triangle when the lengths of its three sides are known. This formula is particularly useful for triangles where it may not be easy to measure the height or base. It involves using the lengths of the sides to find the semi-perimeter and then applying the square root function. Heron’s formula finds applications in geometry, engineering, and architecture.
The Law of Sines relates the ratios of a triangle’s side lengths to the sines of its angles.
The Law of Sines states that the ratio of the length of a side of a triangle to the sine of its opposite angle is constant for all sides and angles in the triangle. This trigonometric relationship allows for the calculation of unknown side lengths or angles in triangles. The Law of Sines is particularly useful in situations where only a limited amount of information is known about a triangle.
The Law of Cosines relates the lengths of a triangle’s sides to the cosine of one of its angles.
The Law of Cosines is a trigonometric relationship that allows the calculation of unknown side lengths or angles in a triangle. It relates the square of a side length to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, adjusted by the cosine of the included angle. The Law of Cosines is essential in solving triangles where all three sides or two sides and an included angle are known.
A triangle inequality states that the sum of any two sides of a triangle must be greater than the length of the third side.
The triangle inequality is a fundamental concept in geometry, stating that the sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle must be greater than the length of the third side. This inequality serves as a vital criterion for determining whether three given side lengths can form a valid triangle or not.
The altitude of a triangle is a line segment from a vertex to its opposite side, forming a right angle.
The altitude of a triangle is a line segment drawn from a vertex of a triangle to the opposite side, creating a right angle. The altitude provides a way to measure the height of the triangle and is essential in calculating the area of a triangle. It is also used in various geometric constructions and proofs.
The median of a triangle is a line segment connecting a vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side.
A median of a triangle is a line segment drawn from a vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side. Each triangle has three medians, and they intersect at a single point called the centroid. The medians divide the triangle into six smaller triangles of equal area, and the centroid is the center of gravity of the triangle.
The orthocenter of a triangle is the point of intersection of its altitudes.
The orthocenter of a triangle is the point where all three altitudes intersect. An altitude is a line segment drawn from a vertex of the triangle perpendicular to the opposite side. The orthocenter holds significant geometric properties and is used in various constructions and proofs.
The circumcenter of a triangle is the center of the circle that passes through all three vertices.
The circumcenter of a triangle is the point where the perpendicular bisectors of the sides intersect. It is the center of the circle that passes through all three vertices of the triangle. The circumcenter has various applications in geometry, such as determining the center of a polygon or constructing inscribed triangles.
The incenter of a triangle is the center of the circle inscribed within the triangle.
The incenter of a triangle is the point where the angle bisectors intersect. It is the center of the circle that touches all three sides of the triangle. The incenter holds geometric significance and is used in various constructions and calculations involving triangles.
Triangles are widely used in the field of trigonometry.
Trigonometry, a branch of mathematics that deals with the relationships between the angles and sides of triangles, heavily relies on triangle properties and concepts. Trigonometry has important applications in navigation, engineering, physics, and many other scientific and technical fields.
Conclusion
In conclusion, triangle math facts are a fundamental aspect of geometry that play a crucial role in various mathematical concepts and problem-solving. By understanding and mastering these facts, individuals can gain a solid foundation in geometry and enhance their mathematical skills. Whether it’s knowing the properties of triangles, the relationships between sides and angles, or the formulas to calculate area and perimeter, having a strong grasp of these facts is essential.Triangles are not just shapes we encounter in the real world, but they are also the building blocks of more complex geometric forms. Therefore, being well-versed in triangle math facts is beneficial for anyone pursuing careers in architecture, engineering, or any other field that involves spatial reasoning.By continually practicing and reviewing these facts, individuals can boost their problem-solving abilities and become more confident in tackling geometry-related challenges. So, embrace the world of triangles, explore their fascinating properties, and uncover the wonders of geometry!
FAQs
1. What are the three sides of a triangle called?
The three sides of a triangle are called the base, the adjacent side, and the opposite side.
2. What is the sum of the interior angles in a triangle?
The sum of the interior angles in a triangle is always 180 degrees.
3. How many types of triangles are there?
There are several types of triangles, including equilateral, isosceles, scalene, acute, right, and obtuse triangles.
4. How can I calculate the area of a triangle?
The area of a triangle can be calculated using the formula: Area = (base x height) / 2.
5. Are all triangles similar?
No, not all triangles are similar. Triangles are considered similar if they have the same shape but may vary in size.
6. Can a triangle have more than one right angle?
No, a triangle can have at most one right angle, which measures 90 degrees.
7. What is the Pythagorean theorem?
The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
