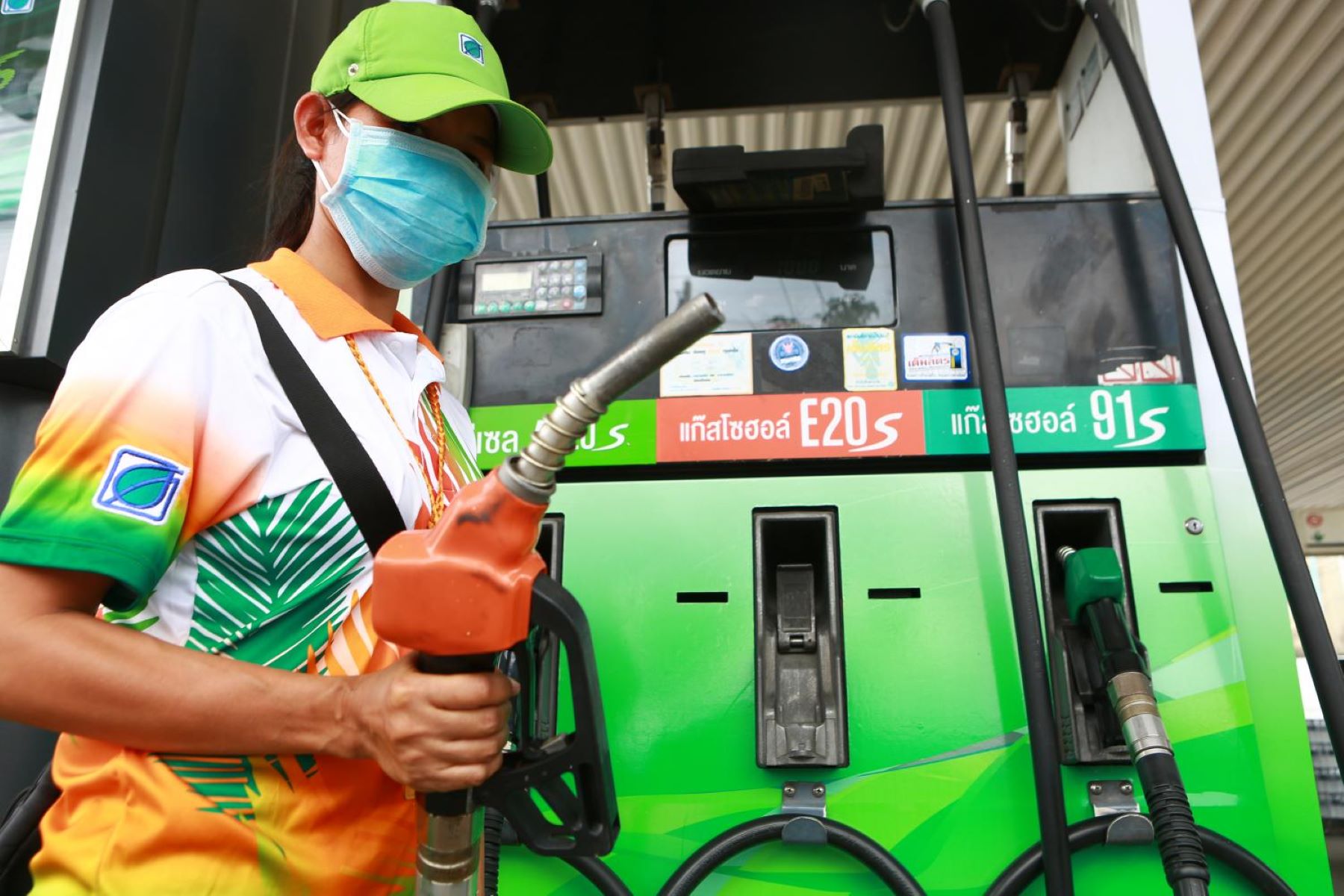
Gasohol is a widely used fuel that combines gasoline with ethanol, a renewable energy source derived from plants such as corn or sugarcane. It has gained popularity in recent years due to its potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. In this article, we will explore 19 fascinating facts about gasohol and its impact on the environment, economy, and transportation sector. From its history and production methods to its benefits and drawbacks, we will delve into the various aspects of gasohol to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of this alternative fuel. So, let’s dive into the world of gasohol and unravel its secrets!
Key Takeaways:
- Gasohol, a blend of gasoline and ethanol, reduces greenhouse gas emissions and supports agriculture, but may require engine modifications for older vehicles.
- Gasohol offers improved engine performance and reduced carbon emissions, but may be more expensive and require specific storage considerations.
Gasohol blends vary in ethanol content.
Gasohol typically contains a mixture of gasoline and ethanol, with ethanol ranging from 10% to 85% by volume. The most common blends are E10 (10% ethanol) and E85 (85% ethanol).
Ethanol in gasohol is primarily derived from corn.
The ethanol used in gasohol production is predominantly sourced from corn, making it a renewable and domestically produced fuel.
Gasohol helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Due to its ethanol content, gasohol burns cleaner than pure gasoline, resulting in lower emissions of carbon dioxide and other harmful pollutants.
Gasohol improves octane rating.
The addition of ethanol in gasohol enhances its octane rating, improving engine performance and reducing knocking or pinging during combustion.
Gasohol can improve fuel efficiency.
When used in vehicles optimized for ethanol blends, such as flex-fuel vehicles, gasohol can provide improved fuel efficiency compared to pure gasoline.
Gasohol can cause compatibility issues in older vehicles.
Some older vehicles and small engines may experience compatibility issues with higher ethanol blends due to their less resilient fuel system components.
Gasohol can contribute to engine corrosion.
While modern vehicles are designed to handle ethanol blends, prolonged use of gasohol in older vehicles with incompatible materials can lead to accelerated engine corrosion.
Gasohol is widely available.
Gasohol is readily available at most fuel stations throughout the world, making it easily accessible to consumers.
Gasohol can be more expensive than regular gasoline.
Due to the additional processing required for ethanol production, gasohol blends can be slightly more expensive than traditional gasoline.
Gasohol supports agricultural communities.
The production and use of gasohol contribute to the demand for corn, benefiting farmers and supporting agricultural economies.
Gasohol reduces dependence on foreign oil.
By utilizing domestically produced ethanol, gasohol reduces the reliance on imported petroleum products, enhancing energy security.
Gasohol is a renewable energy source.
As ethanol is derived from plants, the production of gasohol is considered a renewable energy source with a lower carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels.
Gasohol requires specific storage considerations.
Ethanol absorbs water, so gasohol should be stored in airtight containers to prevent contamination and maintain its performance.
Gasohol can have a shorter shelf life.
Gasohol with higher ethanol content has a shorter shelf life compared to pure gasoline since ethanol is more prone to evaporation and degradation.
Gasohol may require engine modifications.
For vehicles not designed to run on high-ethanol blends, engine modifications may be necessary to avoid adverse effects on performance and longevity.
Gasohol has lower energy content than gasoline.
Due to the lower energy content of ethanol, gasohol provides slightly less mileage per gallon compared to pure gasoline.
Gasohol production can generate by-products.
During the production of gasohol, by-products such as distillers’ grains (a livestock feed) and carbon dioxide are generated, providing additional economic and environmental benefits.
Gasohol reduces carbon monoxide emissions.
By promoting more complete combustion, gasohol helps reduce carbon monoxide emissions, contributing to cleaner air quality.
Gasohol usage has government support.
Many governments around the world incentivize the use of gasohol through tax credits, subsidies, and regulations aimed at reducing reliance on conventional gasoline.
Conclusion
Gasohol, with its blend of gasoline and ethanol, offers an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional fuels. It is a versatile fuel option that reduces greenhouse gas emissions and supports agriculture while offering performance benefits. However, it does come with certain considerations and may require specific engine modifications. With ongoing advancements in renewable energy and the growing emphasis on sustainable transportation, gasohol is likely to play an increasingly significant role in our automotive future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, gasohol is a fascinating fuel alternative that combines gasoline and ethanol to reduce emissions and dependency on fossil fuels. We have explored 19 facts about gasohol, shedding light on its benefits, drawbacks, production process, and environmental impact. Gasohol offers a lower carbon footprint, increased octane rating, and potential cost savings. However, it is important to consider its impact on engine performance and overall fuel efficiency. As the demand for cleaner energy grows, gasohol continues to play a significant role in the transition towards a more sustainable future.
FAQs
1. What is gasohol?
Gasohol is a fuel blend that consists of gasoline and ethanol. It is commonly used as an alternative to traditional gasoline and is designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
2. How is gasohol produced?
Gasohol is produced by blending gasoline with a certain percentage of ethanol, usually derived from corn, sugarcane, or other agricultural crops. The ethanol component is added to reduce the carbon footprint of the fuel.
3. What is the advantage of using gasohol?
Gasohol offers several advantages, including lower emissions, increased octane rating, and potential cost savings. It also helps decrease our reliance on fossil fuels and promotes the use of renewable energy sources.
4. Can I use gasohol in any vehicle?
Gasohol is compatible with most gasoline-powered vehicles. However, it is important to check your vehicle’s manufacturer recommendations and any potential limitations regarding gasohol usage to ensure optimal performance.
5. Is gasohol more expensive than gasoline?
The cost of gasohol can vary depending on factors such as ethanol availability and government subsidies. In some cases, gasohol can be slightly more expensive than regular gasoline, but it may offer cost savings in terms of improved fuel efficiency and reduced engine maintenance.
6. Does gasohol affect fuel efficiency?
Gasohol can have a slightly lower energy density compared to gasoline, which may result in a slight decrease in fuel efficiency. However, this can vary depending on the ethanol percentage and the specific vehicle’s engine and performance.
7. Is gasohol better for the environment?
Gasohol is considered better for the environment compared to regular gasoline, as it reduces greenhouse gas emissions. Ethanol, the main component of gasohol, is derived from renewable resources, making it a more sustainable fuel option.
8. Are there any drawbacks to using gasohol?
One drawback of gasohol is that it can cause compatibility issues with certain older vehicles or small engines. Ethanol can also have a corrosive effect on some materials, potentially leading to engine damage if not properly addressed.
9. Can I use gasohol as a substitute for gasoline?
Yes, gasohol can be used as a substitute for gasoline in most vehicles. However, it is crucial to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.
10. Is gasohol available in all regions?
Gasohol availability may vary depending on the region and local government regulations. In some countries, gasohol is widely available, while in others, it may be limited or not available at all.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.