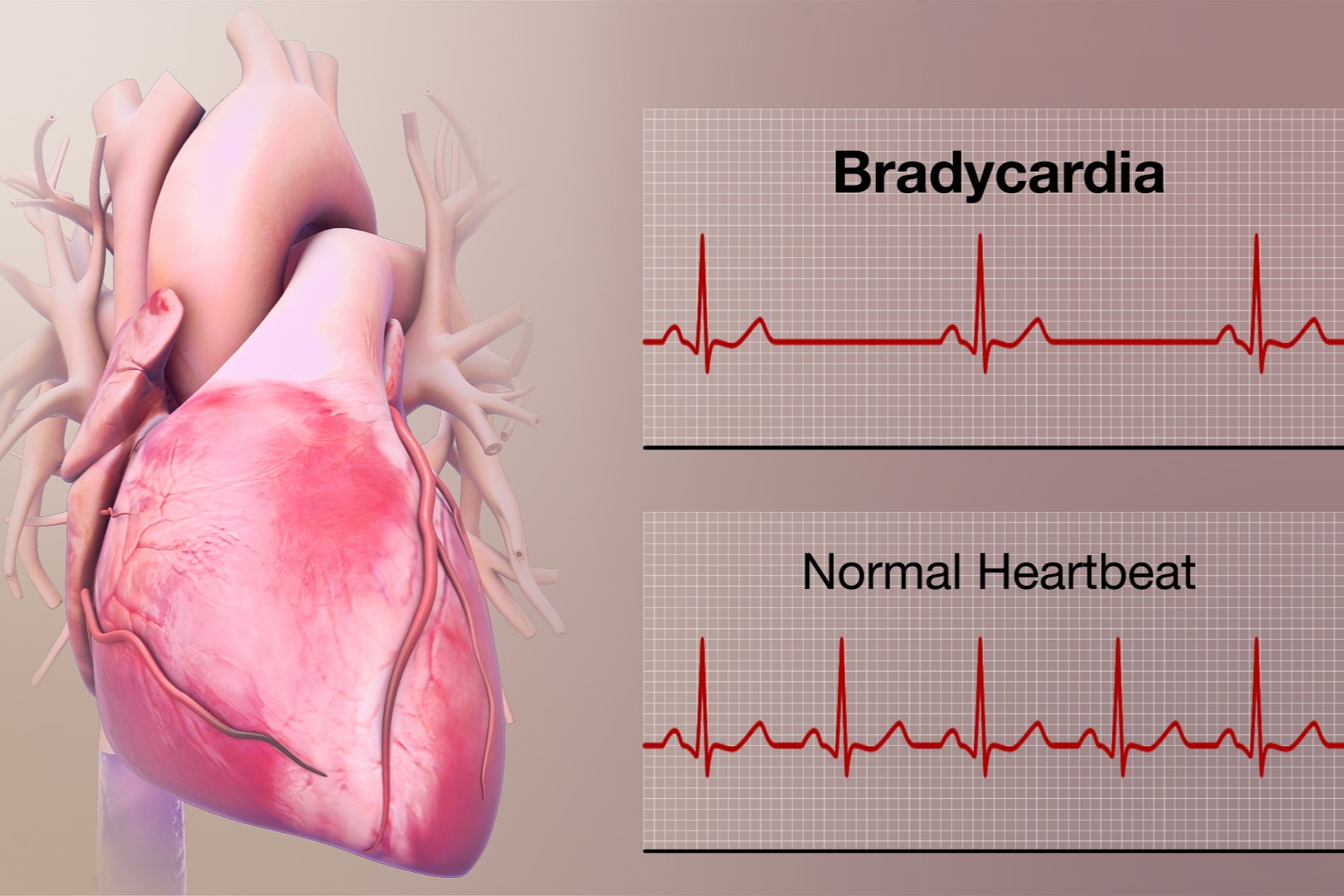
Bradycardia is a condition where the heart beats slower than normal, typically under 60 beats per minute. This can be perfectly normal for some, especially athletes, but for others, it might signal an underlying health issue. What causes bradycardia? It can stem from problems with the heart's electrical system, certain medications, or even aging. Symptoms might include dizziness, fatigue, or shortness of breath. Is bradycardia dangerous? Sometimes, yes. If the heart isn't pumping enough blood, it can lead to serious complications. Understanding bradycardia is crucial for maintaining heart health. Let's dive into 37 facts that will help you grasp this condition better.
Key Takeaways:
- Bradycardia, a condition where the heart beats slower than normal, can be caused by factors like age, medications, and heart tissue damage. It's not always dangerous, but proper diagnosis and treatment are important.
- Bradycardia can impact daily life, affecting activities like exercise and driving. However, myths about it needing treatment for all cases and exercise being harmful are not always true.
What is Bradycardia?
Bradycardia is a condition where the heart beats slower than normal. A typical heart rate ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute. Bradycardia occurs when the heart rate drops below 60 beats per minute. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this condition.
-
Bradycardia is not always dangerous. Some athletes have naturally lower heart rates due to their high fitness levels.
-
Symptoms can vary. Common symptoms include fatigue, dizziness, and shortness of breath.
-
It can be temporary. Factors like sleep, relaxation, or meditation can temporarily lower heart rate.
-
Age is a factor. Older adults are more prone to developing bradycardia.
-
Medications can cause it. Drugs for high blood pressure or heart conditions can slow the heart rate.
Causes of Bradycardia
Understanding what causes bradycardia can help in managing and preventing it. Here are some common causes:
-
Heart tissue damage. Damage from heart disease or a heart attack can lead to bradycardia.
-
Congenital heart defects. Some people are born with heart defects that cause a slow heart rate.
-
Inflammatory diseases. Conditions like lupus or rheumatic fever can affect heart rate.
-
Hypothyroidism. An underactive thyroid gland can slow down the heart.
-
Electrolyte imbalances. Low levels of potassium or calcium can affect heart function.
Diagnosing Bradycardia
Proper diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Here’s how doctors diagnose bradycardia:
-
Electrocardiogram (ECG). This test records the electrical signals in the heart.
-
Holter monitor. A portable device worn for 24-48 hours to track heart activity.
-
Event monitor. Similar to a Holter monitor but used for longer periods.
-
Echocardiogram. Uses sound waves to create images of the heart.
-
Stress test. Measures heart function during physical activity.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the severity and underlying cause of bradycardia. Here are some common treatments:
-
Medication adjustments. Changing or stopping medications that cause a slow heart rate.
-
Pacemaker. A device implanted to regulate heartbeats.
-
Lifestyle changes. Regular exercise and a healthy diet can improve heart health.
-
Treating underlying conditions. Managing diseases like hypothyroidism or electrolyte imbalances.
-
Surgery. In rare cases, surgery may be needed to correct heart defects.
Impact on Daily Life
Bradycardia can affect daily activities and overall quality of life. Here’s how:
-
Exercise limitations. People with bradycardia may need to avoid strenuous activities.
-
Driving restrictions. Severe cases may require restrictions on driving.
-
Work adjustments. Some may need to modify their work routines.
-
Monitoring. Regular check-ups and monitoring are essential.
-
Emergency preparedness. Knowing when to seek emergency care is crucial.
Myths and Misconceptions
There are many myths surrounding bradycardia. Let’s clear up some common misconceptions:
-
Only older adults get it. While more common in older adults, younger people can also develop bradycardia.
-
It always needs treatment. Not all cases require intervention.
-
Exercise is harmful. Moderate exercise can be beneficial.
-
It’s always a sign of heart disease. Bradycardia can occur without any heart disease.
-
Pacemakers are the only solution. Many cases can be managed without a pacemaker.
Interesting Facts
Here are some intriguing facts about bradycardia that you might not know:
-
Animals can have bradycardia. Some animals, like whales, naturally have slow heart rates.
-
Historical figures. Some famous athletes and historical figures had bradycardia.
-
Sleep impact. Heart rate naturally slows during deep sleep.
-
Cold water immersion. Diving into cold water can temporarily slow the heart.
-
Yoga and meditation. Practices like yoga can lower heart rate.
-
Altitude effects. High altitudes can affect heart rate.
-
Genetics. Family history can play a role in developing bradycardia.
Final Thoughts on Bradycardia
Bradycardia, a condition where the heart beats slower than normal, can be a serious health issue. Knowing the symptoms, causes, and treatments is crucial for managing it effectively. Symptoms like dizziness, fatigue, and shortness of breath shouldn't be ignored. Causes range from aging and heart disease to certain medications and lifestyle factors. Treatments vary from lifestyle changes and medications to pacemakers in severe cases.
Understanding bradycardia helps in early detection and better management. Regular check-ups and being aware of your heart rate can make a big difference. If you or someone you know shows signs of bradycardia, consult a healthcare professional. Staying informed and proactive can lead to better heart health and overall well-being. Remember, your heart's health is vital, so take care of it.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
