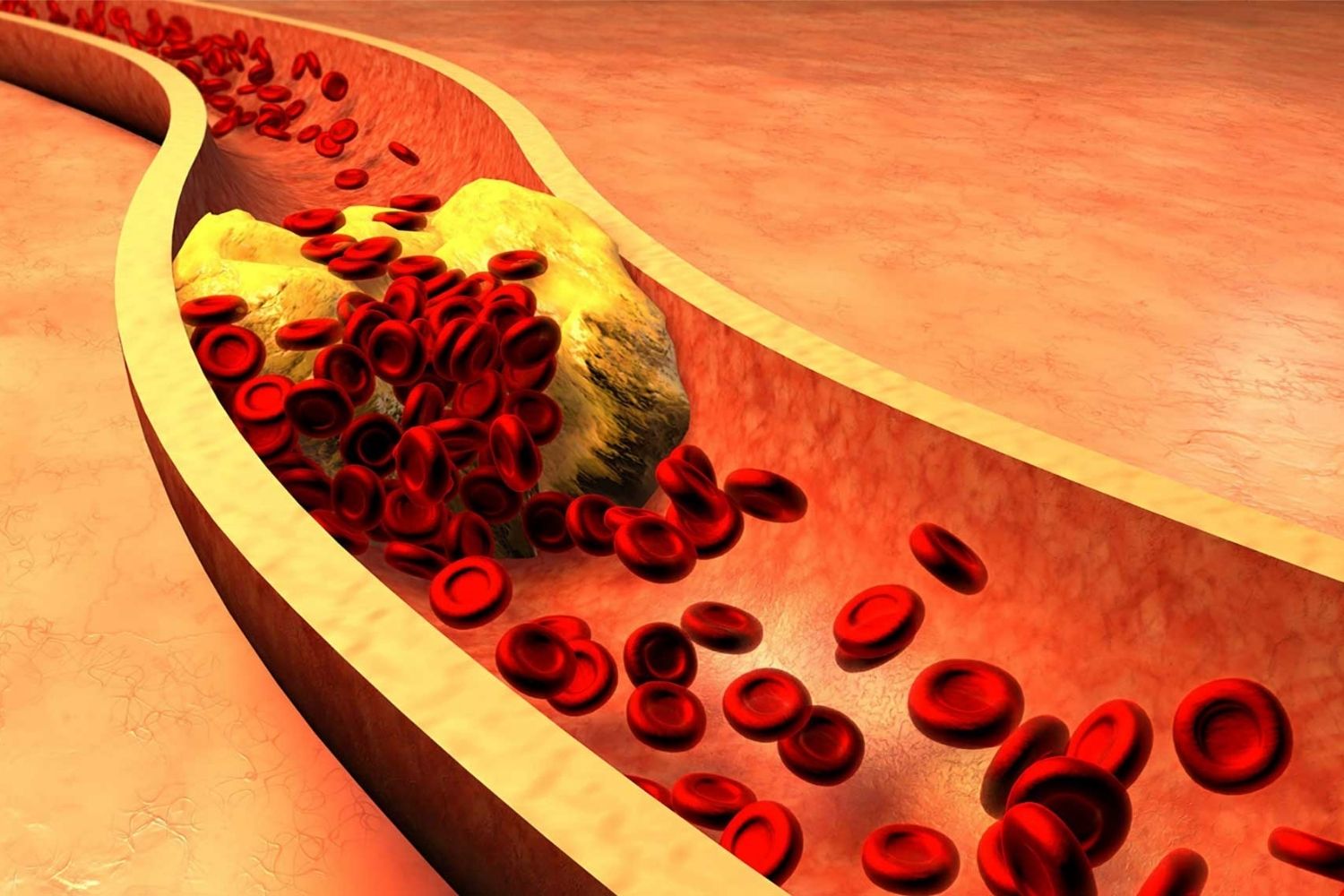
What is an embolism? An embolism happens when a foreign object, like a blood clot, air bubble, or fat globule, travels through the bloodstream and gets stuck in a blood vessel, blocking blood flow. This blockage can cause serious health issues, including heart attacks, strokes, or damage to organs. Understanding embolisms is crucial because they can strike suddenly and have life-threatening consequences. Knowing the signs, causes, and prevention methods can help save lives. In this article, we'll explore 32 essential facts about embolisms, shedding light on this critical medical condition. Stay informed and protect your health!
What is an Embolism?
An embolism is a blockage in one of the body's blood vessels. This blockage can be caused by a blood clot, air bubble, fat globule, or other substances. Understanding embolisms is crucial because they can lead to serious health problems.
- An embolism can travel through the bloodstream and lodge in a blood vessel, blocking blood flow.
- The most common type of embolism is a pulmonary embolism, which occurs in the lungs.
- Embolisms can also occur in the brain, causing a stroke.
- Fat embolisms can result from bone fractures or surgery.
- Air embolisms can happen during medical procedures or deep-sea diving.
Causes of Embolism
Various factors can lead to the formation of an embolism. Knowing these causes can help in prevention and early detection.
- Blood clots, known as thrombi, are the most common cause of embolisms.
- Atrial fibrillation, a type of irregular heartbeat, can lead to blood clots forming in the heart.
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT), a condition where blood clots form in deep veins, often in the legs, can lead to embolisms.
- Trauma or injury can cause fat or air embolisms.
- Certain medical conditions, like cancer, increase the risk of blood clots and embolisms.
Symptoms of Embolism
Recognizing the symptoms of an embolism can be life-saving. Symptoms vary depending on the type and location of the embolism.
- Shortness of breath is a common symptom of a pulmonary embolism.
- Chest pain that worsens with deep breathing can indicate a pulmonary embolism.
- Sudden weakness or numbness, especially on one side of the body, can signal a stroke.
- Confusion or difficulty speaking can also be symptoms of a stroke.
- Swelling and pain in the legs may indicate deep vein thrombosis, which can lead to an embolism.
Diagnosis of Embolism
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Various tests and procedures help diagnose embolisms.
- Ultrasound is often used to detect deep vein thrombosis.
- CT scans can help identify pulmonary embolisms.
- MRI scans are useful for detecting embolisms in the brain.
- Blood tests can reveal clotting disorders that may lead to embolisms.
- Echocardiograms can detect heart-related embolisms.
Treatment Options
Treating an embolism promptly can prevent serious complications. Treatments vary based on the type and severity of the embolism.
- Anticoagulants, or blood thinners, are commonly used to treat blood clots.
- Thrombolytics are medications that dissolve clots quickly.
- Surgery may be necessary to remove large clots or embolisms.
- Oxygen therapy can help patients with pulmonary embolisms.
- Compression stockings can prevent deep vein thrombosis and subsequent embolisms.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing embolisms involves lifestyle changes and medical interventions. These strategies can significantly reduce the risk.
- Regular exercise helps improve blood circulation and prevent clots.
- Staying hydrated reduces the risk of blood clots.
- Avoiding long periods of immobility, such as during long flights, can prevent deep vein thrombosis.
- Medications, like anticoagulants, may be prescribed for high-risk individuals.
- Healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can improve overall vascular health.
- Smoking cessation is crucial, as smoking increases the risk of blood clots.
- Regular medical check-ups can help detect and manage conditions that increase embolism risk.
Final Thoughts on Embolism Facts
Understanding embolism is crucial for recognizing its impact on health. These 32 facts highlight the importance of early detection and treatment. Knowing the symptoms, like sudden shortness of breath or chest pain, can save lives.
Blood clots are the most common cause, but air bubbles and fat particles can also lead to embolisms. Risk factors include prolonged immobility, surgery, and certain medical conditions. Preventative measures, such as staying active and following medical advice, play a significant role in reducing risk.
Medical advancements have improved treatment options, making recovery more achievable. However, awareness and education remain key. By sharing this knowledge, we can help others stay informed and proactive about their health.
Stay vigilant, stay informed, and take steps to protect yourself and loved ones from the dangers of embolism. Knowledge truly is power when it comes to health.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
