Epidermal Nevus Syndrome (ENS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects the skin, eyes, and nervous system. Characterized by the presence of epidermal nevi, which are non-cancerous skin growths, this condition can lead to various complications. Symptoms often include seizures, developmental delays, and skeletal abnormalities. Caused by mutations in genes responsible for skin cell growth, ENS can be diagnosed through clinical evaluation and genetic testing. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and may involve medications, physical therapy, and surgical removal of nevi. Living with ENS requires a multidisciplinary approach to address the diverse challenges it presents. Understanding this syndrome is crucial for improving the quality of life for those affected.
What is Epidermal Nevus Syndrome?
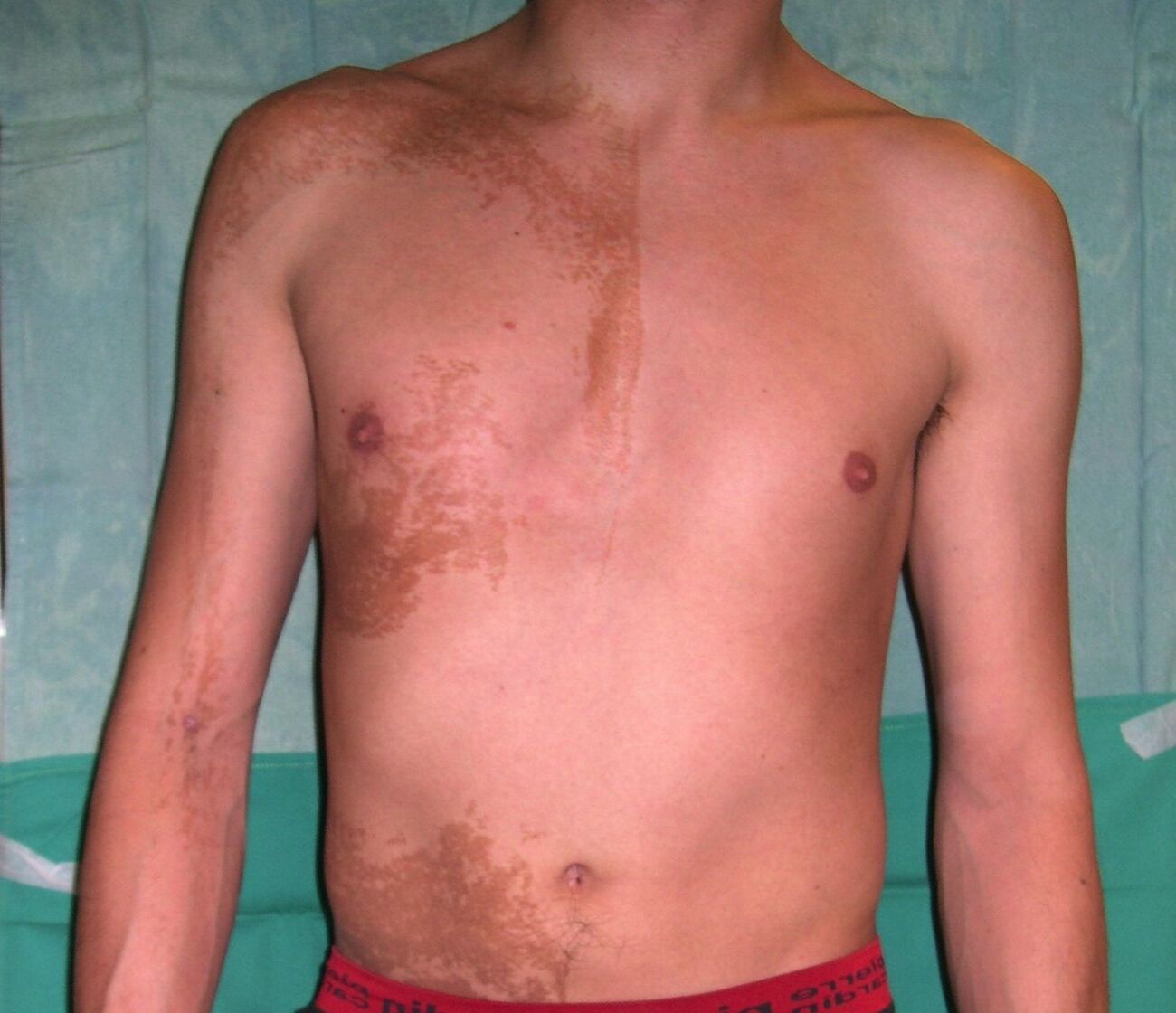
Epidermal Nevus Syndrome (ENS) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the presence of epidermal nevi, which are non-cancerous skin growths. These growths can appear at birth or develop during early childhood. ENS can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, eyes, bones, and brain.
- Epidermal Nevus Syndrome is also known as Nevus Sebaceous Syndrome or Schimmelpenning Syndrome.
- The condition is caused by mutations in genes involved in skin development.
- Epidermal nevi are often present at birth but can also develop during early childhood.
- These skin growths can vary in size, shape, and color, often appearing as warty or velvety patches.
Symptoms and Complications
ENS can present a wide range of symptoms and complications, affecting multiple organ systems. Understanding these can help in early diagnosis and management.
- Neurological symptoms may include seizures, developmental delays, and intellectual disabilities.
- Ocular complications can involve colobomas (gaps in the structure of the eye) and other vision problems.
- Skeletal abnormalities such as scoliosis, limb length discrepancies, and bone cysts are common.
- Cardiovascular issues may include congenital heart defects and vascular malformations.
Diagnosis and Genetic Testing
Early diagnosis of ENS is crucial for managing symptoms and preventing complications. Genetic testing plays a significant role in confirming the diagnosis.
- Diagnosis often involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and genetic testing.
- Genetic testing can identify mutations in genes like FGFR3, HRAS, and KRAS, which are associated with ENS.
- Skin biopsy may be performed to examine the characteristics of the epidermal nevi.
- MRI and CT scans are used to detect brain and skeletal abnormalities.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for ENS, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Topical treatments such as retinoids and corticosteroids can reduce the size and appearance of epidermal nevi.
- Surgical removal of nevi may be considered for cosmetic reasons or if they cause discomfort.
- Anticonvulsant medications are used to control seizures in patients with neurological involvement.
- Physical therapy can help manage skeletal abnormalities and improve mobility.
Living with Epidermal Nevus Syndrome
Living with ENS can be challenging, but with proper care and support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives.
- Regular follow-ups with a multidisciplinary team of specialists are essential for monitoring and managing symptoms.
- Support groups and counseling can provide emotional support and resources for patients and families.
- Educational interventions may be necessary to address developmental delays and learning disabilities.
- Awareness and advocacy efforts are crucial for improving understanding and support for those affected by ENS.
Final Thoughts on Epidermal Nevus Syndrome
Epidermal Nevus Syndrome (ENS) is a rare condition that affects the skin, eyes, and sometimes the brain. Understanding its symptoms and causes can help in managing it better. ENS often presents at birth or early childhood with skin lesions that can vary in size and shape. These lesions might be accompanied by neurological issues or eye abnormalities. While there's no cure, treatments focus on managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for better outcomes. If you or someone you know shows signs of ENS, consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and care. Awareness and education about ENS can lead to better support and resources for those affected. Stay informed, and don't hesitate to seek medical advice when needed.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.