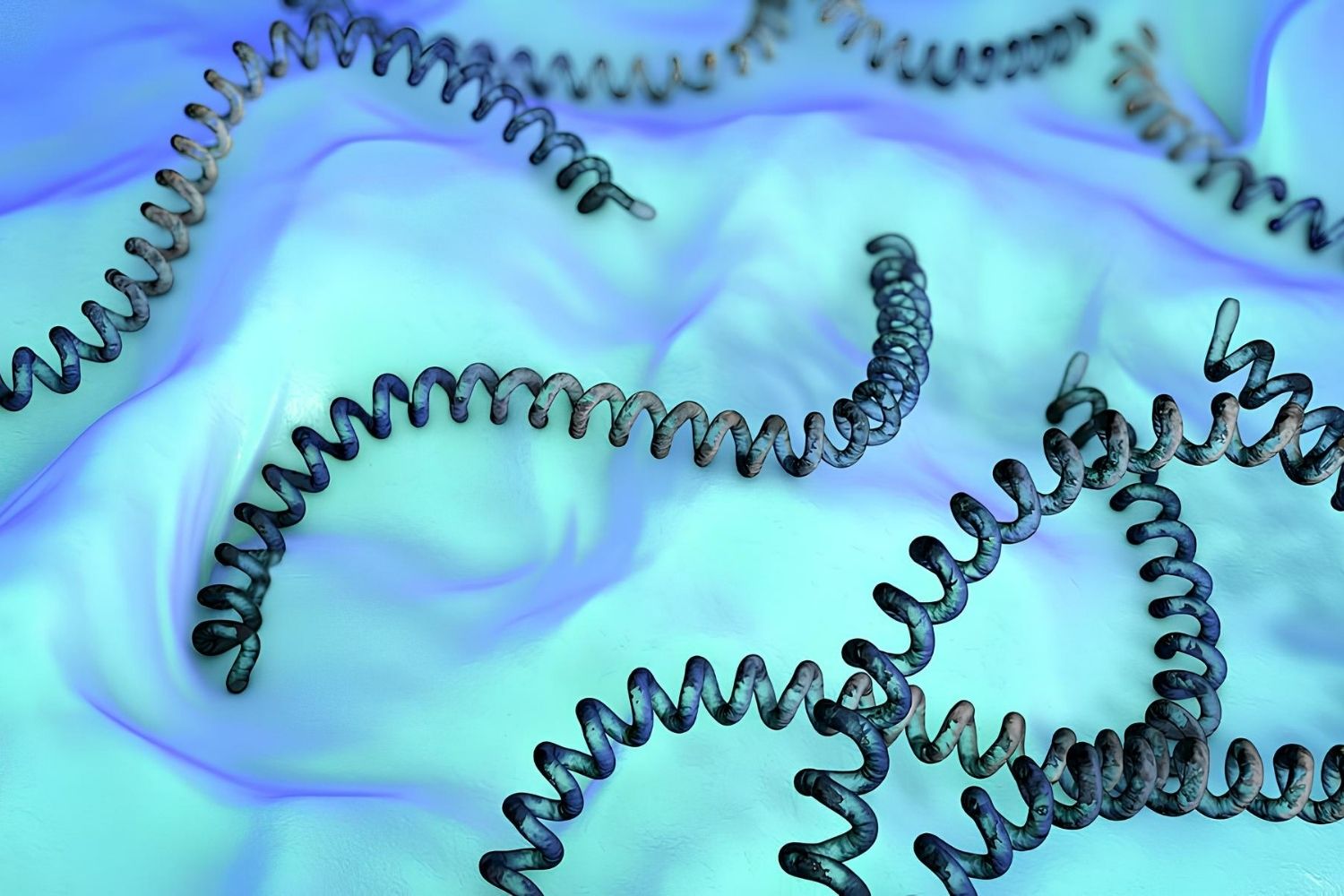
Weil's Disease, also known as Leptospirosis, is a bacterial infection that can affect both humans and animals. It's caused by bacteria from the genus Leptospira. This disease spreads through water contaminated by the urine of infected animals, often rodents. Symptoms can range from mild flu-like signs to severe illness, including liver damage, kidney failure, and bleeding. Early diagnosis and treatment with antibiotics are crucial for recovery. Preventive measures include avoiding contact with contaminated water, wearing protective clothing, and maintaining good hygiene. Understanding Weil's Disease helps in recognizing risks and taking steps to protect oneself and others.
Key Takeaways:
- Weil's Disease, also known as leptospirosis, is a serious bacterial infection that can be transmitted from animals to humans. It can cause severe symptoms and even lead to death if not treated promptly.
- Preventing Weil's Disease involves avoiding contact with contaminated water, wearing protective clothing, and vaccinating pets. Public health campaigns and rodent control also play a crucial role in reducing the risk of transmission.
What is Weil's Disease?
Weil's Disease, also known as leptospirosis, is a bacterial infection that affects both humans and animals. It is caused by bacteria of the genus Leptospira. This disease can be severe, leading to organ damage and even death if not treated promptly.
- Weil's Disease is named after Adolf Weil, who first described it in 1886.
- The bacteria causing Weil's Disease are spiral-shaped, making them easily identifiable under a microscope.
- Leptospirosis is more common in tropical and subtropical regions due to the warm, humid climate.
- The bacteria can survive in water or soil for weeks to months.
- Weil's Disease is a zoonotic disease, meaning it can be transmitted from animals to humans.
How is Weil's Disease Transmitted?
Understanding how Weil's Disease spreads is crucial for prevention. The bacteria can enter the body through cuts, abrasions, or mucous membranes.
- Humans can contract the disease through direct contact with urine from infected animals.
- Contaminated water sources are a common transmission route.
- Farmers, sewer workers, and veterinarians are at higher risk due to their frequent contact with animals.
- Recreational activities like swimming in contaminated water can also lead to infection.
- Pets, especially dogs, can carry and transmit the bacteria to humans.
Symptoms of Weil's Disease
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to timely treatment and better outcomes. Symptoms can vary widely and often resemble those of other illnesses.
- Initial symptoms include fever, chills, and muscle aches.
- Severe cases can lead to jaundice, where the skin and eyes turn yellow.
- Kidney failure is a serious complication of Weil's Disease.
- Some patients may experience meningitis, an inflammation of the membranes around the brain and spinal cord.
- Red eyes and a rash are also common symptoms.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and treatment are vital for recovery. Medical professionals use various methods to diagnose and treat Weil's Disease.
- Blood tests can detect the presence of Leptospira bacteria.
- Urine tests are also used to identify the bacteria.
- Antibiotics like doxycycline and penicillin are effective treatments.
- Severe cases may require hospitalization and intravenous antibiotics.
- Early treatment significantly reduces the risk of severe complications.
Prevention and Control
Preventing Weil's Disease involves both personal and public health measures. Awareness and proper hygiene can go a long way in reducing the risk.
- Avoiding contact with potentially contaminated water is crucial.
- Wearing protective clothing and footwear can prevent bacteria from entering the body.
- Vaccinating pets against leptospirosis helps reduce the risk of transmission.
- Rodent control measures can minimize the presence of infected animals.
- Public health campaigns can educate communities about the risks and prevention methods.
Global Impact of Weil's Disease
Weil's Disease affects people worldwide, but its impact varies by region. Understanding its global reach can help in developing targeted interventions.
- Tropical regions report higher incidence rates due to favorable conditions for the bacteria.
- Outbreaks often occur after heavy rainfall or flooding.
- In some countries, Weil's Disease is a significant public health concern.
- The World Health Organization monitors and provides guidelines for managing outbreaks.
- International travel can spread the disease to new areas.
Weil's Disease in Animals
Animals play a crucial role in the transmission of Weil's Disease. Knowing how it affects them can help in controlling the spread to humans.
- Rodents are the primary carriers of Leptospira bacteria.
- Livestock like cattle and pigs can also be infected.
- Infected animals may not show symptoms but can still spread the bacteria.
- Wildlife, including raccoons and skunks, can be reservoirs of the disease.
- Vaccination programs for livestock can help control the spread.
Historical Cases and Outbreaks
Weil's Disease has a long history, with notable outbreaks providing valuable lessons for future prevention and control.
- The first documented outbreak occurred in Japan in the early 20th century.
- During World War II, soldiers in the Pacific theater were affected by leptospirosis.
- In 1995, Nicaragua experienced a significant outbreak following a hurricane.
- Recent outbreaks in urban areas highlight the importance of sanitation.
- Historical data helps researchers understand patterns and develop better prevention strategies.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to improve our understanding of Weil's Disease and develop more effective treatments and prevention methods.
- Scientists are studying the genetic makeup of Leptospira bacteria to develop better diagnostics.
- New vaccines are being tested to provide broader protection.
- Research into environmental factors can help predict and prevent outbreaks.
- Advances in antibiotic treatments are improving recovery rates.
- Collaboration between countries is essential for global control efforts.
Interesting Facts About Weil's Disease
Here are some lesser-known but fascinating facts about Weil's Disease that highlight its complexity and the ongoing efforts to combat it.
- Leptospira bacteria can survive in moist soil for up to six months.
- Weil's Disease is sometimes called "mud fever" due to its association with wet environments.
- The disease can affect almost any mammal, not just humans and common pets.
- Some strains of Leptospira are more virulent than others, leading to more severe disease.
- Public health initiatives have significantly reduced the incidence of Weil's Disease in many parts of the world.
Final Thoughts on Weil's Disease
Weil's disease, caused by the Leptospira bacteria, remains a serious health concern. Understanding its symptoms like fever, chills, and muscle aches can help in early detection. Transmission often occurs through contact with contaminated water or soil, making awareness crucial for those in high-risk areas. Preventive measures such as avoiding stagnant water and using protective gear can significantly reduce risk. Treatment usually involves antibiotics, which are most effective when administered early. Public health education and proper sanitation play vital roles in controlling outbreaks. By staying informed and taking necessary precautions, we can better protect ourselves and our communities from this potentially life-threatening disease. Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to combating Weil's disease. Stay safe, stay informed, and take action to prevent the spread of this dangerous infection.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
