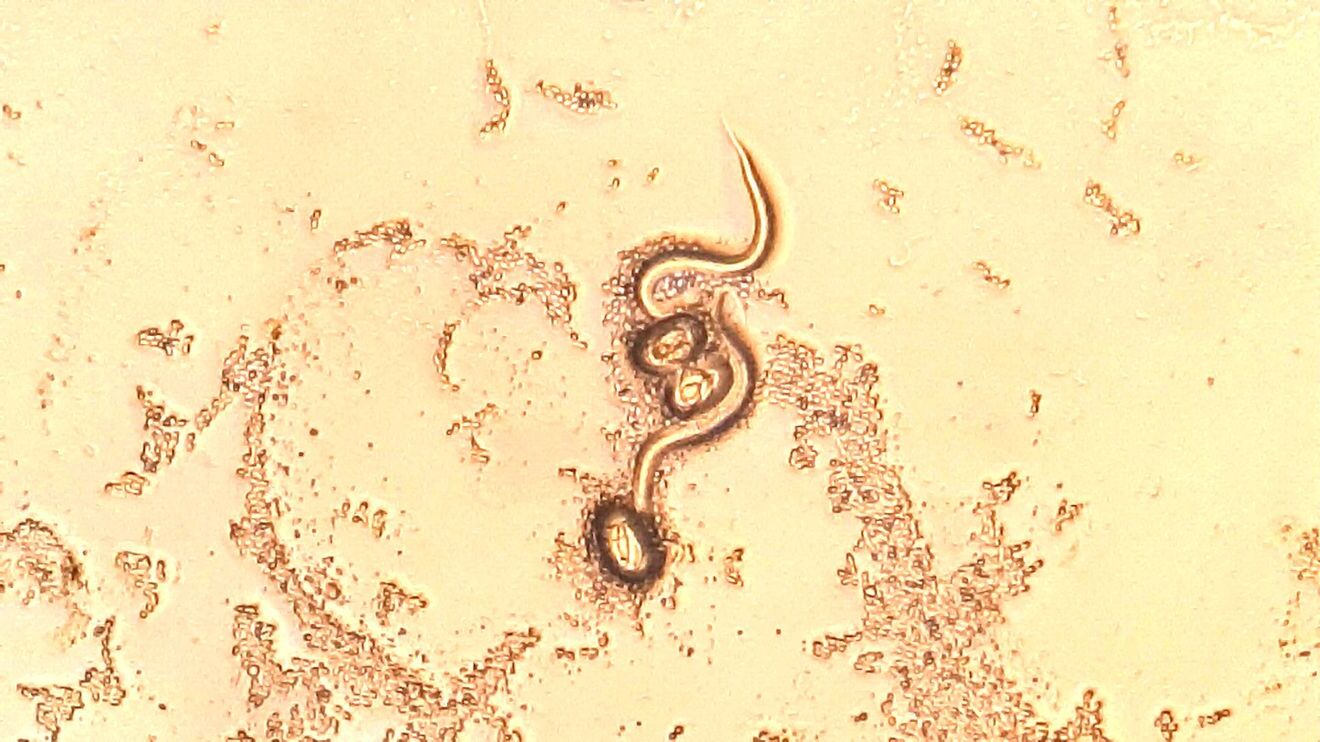
Strongyloidiasis is a parasitic infection caused by the nematode Strongyloides stercoralis. This tiny worm can wreak havoc on the human body, especially in tropical and subtropical regions. How does one contract strongyloidiasis? Through direct contact with contaminated soil, usually by walking barefoot or touching the ground with bare skin. Once inside, the larvae travel through the bloodstream to the lungs, then migrate to the small intestine, where they mature and reproduce. Symptoms can range from mild, such as itching and rash, to severe, including abdominal pain, diarrhea, and even life-threatening complications in immunocompromised individuals. Understanding this disease is crucial for prevention and treatment. Let's dive into 50 fascinating facts about strongyloidiasis that will help you grasp its impact and significance.
Key Takeaways:
- Strongyloidiasis, caused by a sneaky parasite, can lurk in the body for decades without showing symptoms. It's crucial to wear shoes and practice good hygiene to prevent infection.
- Public health efforts and global awareness are vital in controlling the spread of strongyloidiasis, a resilient and complex parasitic infection with significant implications for public health.
Understanding Strongyloidiasis
Strongyloidiasis is a parasitic infection caused by the nematode Strongyloides stercoralis. This infection primarily affects the intestines but can spread to other parts of the body. Here are some fascinating facts about this condition.
- Strongyloides stercoralis is the main culprit behind strongyloidiasis.
- The parasite is commonly found in tropical and subtropical regions.
- It can also be found in temperate areas, especially in rural regions.
- Strongyloidiasis is often contracted through contact with contaminated soil.
- The larvae penetrate the skin, usually through bare feet.
- Once inside, the larvae travel through the bloodstream to the lungs.
- From the lungs, they move to the throat and are swallowed.
- In the intestines, they mature into adult worms.
- Adult worms can live in the human body for decades.
- The infection can be asymptomatic, meaning no symptoms are present.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms of strongyloidiasis can vary widely, making diagnosis tricky. Here are some key points about the symptoms and how the disease is diagnosed.
- Common symptoms include abdominal pain and diarrhea.
- Some people experience a rash at the site of larval entry.
- Respiratory symptoms like coughing and wheezing can occur.
- Severe cases may lead to weight loss and malnutrition.
- Hyperinfection syndrome is a severe form of the disease.
- This syndrome can cause widespread dissemination of the larvae.
- Hyperinfection is often triggered by immunosuppression.
- Diagnosis usually involves stool sample analysis.
- Multiple stool samples may be needed for accurate diagnosis.
- Serological tests can also help in diagnosing the infection.
Treatment and Prevention
Treating and preventing strongyloidiasis requires a multi-faceted approach. Here are some important facts about managing this infection.
- Ivermectin is the drug of choice for treating strongyloidiasis.
- Albendazole is another medication used, though less effective.
- Treatment duration can vary depending on the severity of the infection.
- Preventing infection involves avoiding contact with contaminated soil.
- Wearing shoes can significantly reduce the risk of infection.
- Proper sanitation and hygiene are crucial in preventing the spread.
- In endemic areas, regular screening can help in early detection.
- Treating infected individuals can prevent the spread to others.
- Public health education is essential in endemic regions.
- Strongyloidiasis can be a lifelong infection if not properly treated.
Impact on Public Health
Strongyloidiasis has significant implications for public health, especially in endemic regions. Here are some facts about its impact.
- The infection is often underreported due to asymptomatic cases.
- It can lead to severe complications in immunocompromised individuals.
- Strongyloidiasis can exacerbate other health conditions.
- The disease can strain healthcare resources in endemic areas.
- Public health initiatives are crucial in controlling the spread.
- Strongyloidiasis is considered a neglected tropical disease.
- Efforts to control the disease are often underfunded.
- Collaboration between governments and NGOs is essential.
- Research is ongoing to develop more effective treatments.
- Global awareness can help in mobilizing resources for control efforts.
Interesting Tidbits
Here are some lesser-known but intriguing facts about strongyloidiasis that highlight the complexity and resilience of this parasitic infection.
- Strongyloides stercoralis can reproduce both sexually and asexually.
- The parasite has a unique life cycle that includes free-living and parasitic stages.
- It can survive in the environment for extended periods.
- Strongyloidiasis can be transmitted through organ transplantation.
- The infection can also be passed from mother to child during childbirth.
- Dogs and other animals can serve as reservoirs for the parasite.
- Strongyloides stercoralis has been found in ancient human remains.
- The parasite's ability to evade the immune system makes it particularly challenging to treat.
- Strongyloidiasis can mimic other gastrointestinal diseases, complicating diagnosis.
- Advances in molecular biology are helping to better understand the parasite's genetics and behavior.
Final Thoughts on Strongyloidiasis
Strongyloidiasis, caused by the Strongyloides stercoralis parasite, is a serious health issue, especially in tropical and subtropical regions. This infection can lead to severe complications if left untreated. Recognizing symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhea, and skin rashes is crucial for early diagnosis.
Preventive measures include proper sanitation, wearing shoes in endemic areas, and avoiding contact with contaminated soil. Treatment usually involves antiparasitic medications, which are effective when administered promptly.
Raising awareness about strongyloidiasis can help reduce its prevalence. Educating communities on hygiene practices and the importance of seeking medical attention for symptoms can make a significant difference.
Stay informed, take preventive steps, and consult healthcare professionals if you suspect an infection. Knowledge and proactive measures are key to combating this parasitic disease.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
