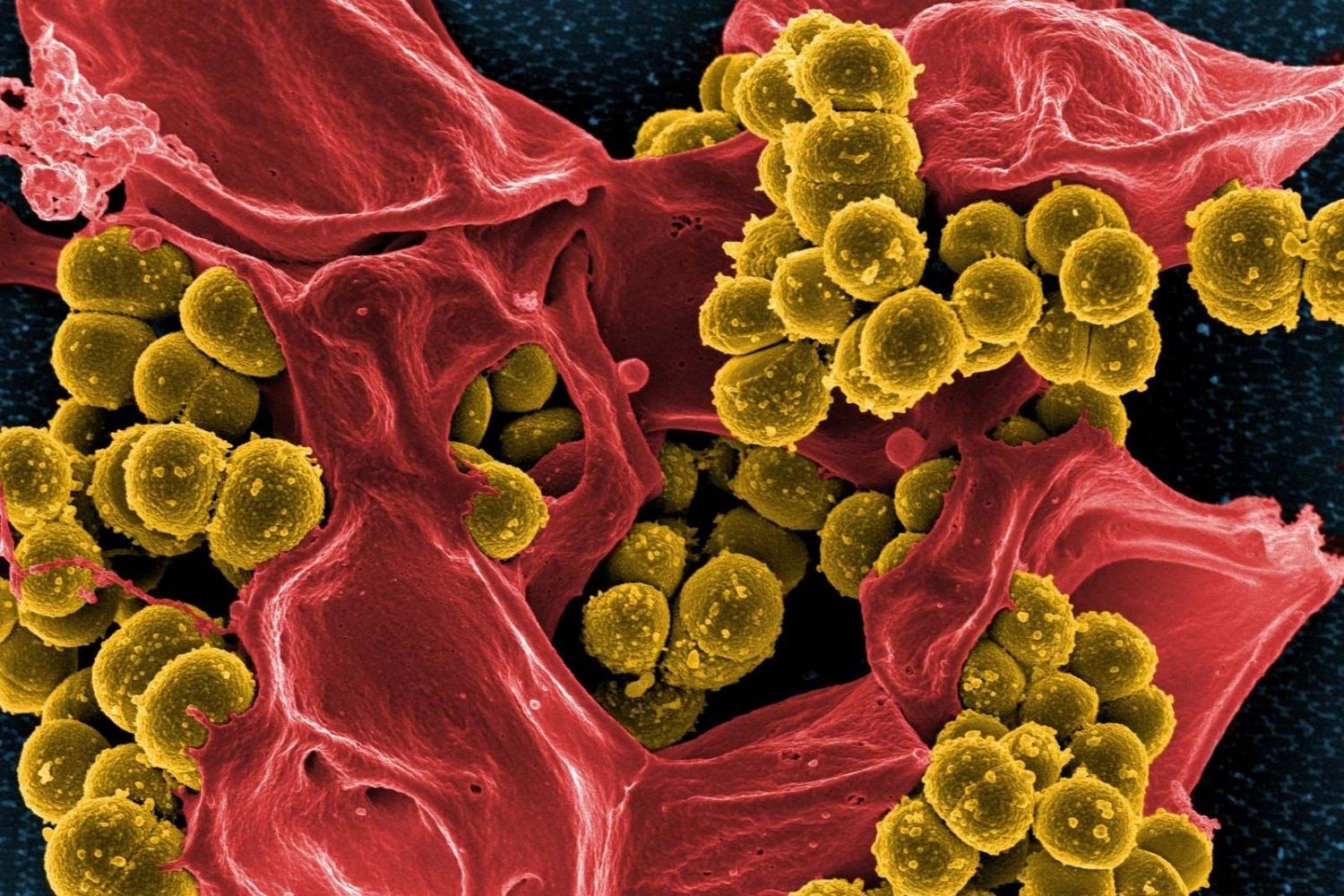
Staphylococcal infection might sound like a mouthful, but understanding it can help keep you and your loved ones safe. These infections are caused by Staphylococcus bacteria, which can lead to anything from minor skin issues to serious health problems. Did you know that about 30% of people carry these bacteria in their noses without getting sick? It's true! However, when these bacteria enter the body through cuts or wounds, they can cause infections. Symptoms can range from boils and abscesses to more severe conditions like pneumonia or bloodstream infections. Knowing the facts about staph infections can help you recognize symptoms early and seek treatment promptly. Stay informed and stay healthy!
Key Takeaways:
- Staphylococcal infections, caused by bacteria on the skin, can lead to serious illnesses. Good hygiene and early treatment are crucial for prevention and management.
- Staph bacteria are highly adaptable and can cause a range of infections, from skin issues to life-threatening conditions. Understanding their spread and treatment is essential.
What is Staphylococcal Infection?
Staphylococcal infections are caused by Staphylococcus bacteria, commonly found on the skin or in the nose. These bacteria can lead to a range of illnesses, from minor skin infections to life-threatening diseases.
- Staphylococcus bacteria are round-shaped and often form clusters resembling grapes.
- Over 30 types of Staphylococcus bacteria exist, but Staphylococcus aureus is the most common cause of infections.
- These bacteria can survive on surfaces for days, making them highly contagious.
- Staphylococcus aureus produces toxins that can damage tissues and cause severe symptoms.
- Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a type of staph bacteria resistant to many antibiotics.
Symptoms of Staphylococcal Infections
Recognizing the symptoms of a staph infection can help in seeking timely medical intervention. Symptoms vary depending on the type and severity of the infection.
- Skin infections often appear as red, swollen, and painful areas, sometimes with pus or drainage.
- Boils, impetigo, and cellulitis are common skin infections caused by staph bacteria.
- Food poisoning from staph bacteria can cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach cramps.
- Toxic shock syndrome, a rare but serious condition, can result from staph infections and includes symptoms like high fever, rash, and low blood pressure.
- Staph infections can lead to sepsis, a life-threatening response to infection that can cause organ failure.
How Staphylococcal Infections Spread
Understanding how these infections spread can help in preventing them. Staph bacteria are highly adaptable and can be transmitted in various ways.
- Direct contact with an infected wound or sharing personal items like towels can spread staph bacteria.
- Poor hygiene practices, such as not washing hands regularly, increase the risk of infection.
- Crowded places like gyms, schools, and dormitories are common sites for staph outbreaks.
- Staph bacteria can enter the body through cuts, scrapes, or surgical wounds.
- Healthcare-associated infections occur when patients acquire staph bacteria in hospitals or clinics.
Treatment and Prevention
Effective treatment and preventive measures are crucial in managing staph infections. Early diagnosis and appropriate care can prevent complications.
- Antibiotics are the primary treatment for staph infections, but resistance to these drugs is a growing concern.
- MRSA infections require specific antibiotics, as they are resistant to common treatments.
- Drainage of abscesses or boils may be necessary to remove pus and promote healing.
- Good hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing and keeping wounds clean, can prevent staph infections.
- Avoiding sharing personal items like razors, towels, and clothing reduces the risk of spreading staph bacteria.
Complications of Staphylococcal Infections
Staph infections can lead to serious complications if not treated promptly. Awareness of these potential issues is essential for proper management.
- Osteomyelitis, an infection of the bone, can result from staph bacteria spreading through the bloodstream.
- Endocarditis, an infection of the heart valves, is a severe complication that can occur with staph infections.
- Pneumonia caused by staph bacteria can lead to respiratory failure if not treated effectively.
- Septic arthritis, an infection in the joints, can cause severe pain and joint damage.
- Staph infections can lead to abscesses in organs like the liver, kidneys, or brain, requiring surgical intervention.
Staphylococcal Infections in Different Populations
Certain groups are more susceptible to staph infections due to various factors. Understanding these risks can help in targeted prevention and treatment.
- Newborns and infants are at higher risk due to their underdeveloped immune systems.
- People with chronic conditions like diabetes or cancer have a higher susceptibility to staph infections.
- Athletes, especially those in contact sports, are more likely to develop skin infections from staph bacteria.
- Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as HIV patients, are at increased risk.
- Elderly people are more vulnerable to staph infections due to age-related immune decline.
Interesting Facts About Staphylococcus Bacteria
Staphylococcus bacteria have unique characteristics and behaviors that make them fascinating subjects of study.
- Staphylococcus aureus can produce a golden pigment, which helps it evade the immune system.
- These bacteria can form biofilms, protective layers that make them resistant to antibiotics.
- Staph bacteria can survive extreme conditions, including high salt concentrations and low moisture.
- Some strains of Staphylococcus aureus can produce enterotoxins, leading to food poisoning.
- The name "Staphylococcus" comes from the Greek words "staphyle," meaning bunch of grapes, and "kokkos," meaning berry.
Historical Context of Staphylococcal Infections
Staph infections have been recognized and studied for centuries. Their impact on human health has led to significant medical advancements.
- Sir Alexander Ogston first identified Staphylococcus bacteria in 1880 while studying wound infections.
- The discovery of penicillin by Alexander Fleming in 1928 revolutionized the treatment of staph infections.
- The emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains like MRSA in the 1960s highlighted the need for new treatments.
- Staph infections were a major cause of death before the advent of antibiotics.
- Research on staph bacteria has led to the development of vaccines and new therapeutic approaches.
Future Directions in Staphylococcal Infection Research
Ongoing research aims to better understand staph bacteria and develop more effective treatments. Innovations in this field hold promise for combating these infections.
- Scientists are exploring new antibiotics and alternative therapies to address antibiotic resistance.
- Research on the human microbiome may provide insights into preventing staph infections.
- Advances in genetic engineering could lead to targeted treatments for staph bacteria.
- Vaccine development is a key focus, with several candidates showing promise in clinical trials.
- Understanding the mechanisms of biofilm formation may help in developing strategies to disrupt these protective layers.
Staphylococcal Infections in Animals
Staph infections are not limited to humans; animals can also be affected. These infections can impact pets, livestock, and wildlife.
- Staphylococcus pseudintermedius is a common cause of skin infections in dogs.
- Livestock, such as cows and pigs, can develop staph infections, affecting their health and productivity.
- Staph infections in animals can sometimes be transmitted to humans, a phenomenon known as zoonosis.
- Veterinary medicine has developed specific treatments for staph infections in animals.
- Research on staph infections in animals contributes to a better understanding of these bacteria and their impact on health.
Final Thoughts on Staphylococcal Infections
Staphylococcal infections, caused by Staphylococcus bacteria, can range from minor skin issues to severe, life-threatening conditions. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for managing these infections effectively. Regular hand washing, proper wound care, and avoiding sharing personal items can help prevent the spread of these bacteria. If you suspect a staph infection, seek medical advice promptly to avoid complications. Antibiotics are often effective, but some strains, like MRSA, require more advanced treatments. Staying informed and vigilant can make a significant difference in your health and well-being. Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to combating infections. Stay safe, stay healthy, and always consult healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
