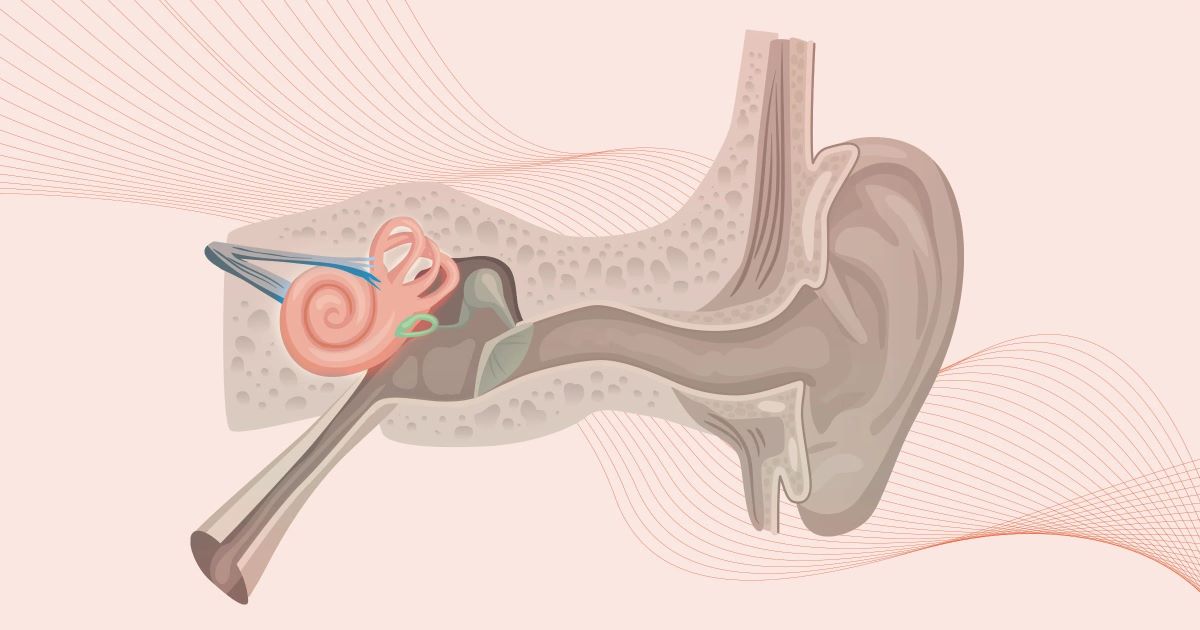
Sensorineural hearing loss is a condition affecting millions worldwide, impacting how sound is perceived and processed. What exactly is sensorineural hearing loss? It's a type of hearing impairment caused by damage to the inner ear or the nerve pathways from the inner ear to the brain. Unlike other forms of hearing loss, this one often results from aging, exposure to loud noise, or genetic factors. It's not just about turning up the volume; it's about clarity and understanding. Imagine trying to listen to your favorite song, but the lyrics are muffled and unclear. This condition can make conversations challenging, leading to feelings of isolation. Understanding the facts about sensorineural hearing loss can help in managing it effectively. From the latest treatments to everyday coping strategies, there's much to learn about living with this condition. Let's dive into the world of sensorineural hearing loss and uncover the facts that matter most.
Key Takeaways:
- Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is the most common and irreversible form of permanent hearing impairment, often caused by factors like age, loud noises, genetics, and medical conditions.
- Understanding the causes, diagnosis, and living strategies for SNHL can help individuals manage their condition and improve their quality of life. Exciting research developments offer hope for potential treatments in the future.
Understanding Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is a common type of hearing impairment. It occurs when there's damage to the inner ear or the nerve pathways from the inner ear to the brain. Let's explore some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Most Common Type: SNHL is the most prevalent form of permanent hearing loss. It affects millions worldwide, making it a significant public health concern.
-
Inner Ear Damage: This type of hearing loss results from damage to the tiny hair cells in the cochlea or the auditory nerve itself.
-
Irreversible Condition: Unlike conductive hearing loss, SNHL is usually irreversible. Once the hair cells in the cochlea are damaged, they cannot regenerate.
-
Age-Related Hearing Loss: Known as presbycusis, age-related hearing loss is a form of SNHL. It typically affects both ears equally and progresses gradually over time.
-
Noise-Induced Hearing Loss: Exposure to loud noises can lead to SNHL. This is common among individuals who work in noisy environments or frequently attend loud concerts.
-
Genetic Factors: Some forms of SNHL are hereditary. Genetic mutations can affect the development and function of the inner ear.
-
Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss (SSHL): This is a rapid loss of hearing, occurring over a few days. It's considered a medical emergency and requires immediate attention.
-
Ototoxic Medications: Certain medications, known as ototoxic drugs, can cause SNHL. These include some antibiotics, chemotherapy drugs, and high doses of aspirin.
-
Meniere’s Disease: This inner ear disorder can lead to SNHL. It's characterized by vertigo, tinnitus, and fluctuating hearing loss.
-
Tinnitus Connection: Many people with SNHL experience tinnitus, a ringing or buzzing noise in the ears.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors of SNHL can help in prevention and management. Here are some key points to consider.
-
Viral Infections: Infections like measles, mumps, and meningitis can lead to SNHL by damaging the inner ear structures.
-
Head Trauma: Injuries to the head can result in SNHL if the inner ear or auditory nerve is affected.
-
Autoimmune Inner Ear Disease: This rare condition occurs when the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the inner ear, leading to hearing loss.
-
Diabetes Connection: People with diabetes are at a higher risk for SNHL due to potential damage to the blood vessels in the inner ear.
-
Smoking Risks: Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of SNHL, possibly due to reduced blood flow to the inner ear.
-
Cardiovascular Health: Poor cardiovascular health can affect blood flow to the cochlea, increasing the risk of SNHL.
-
Prenatal Factors: Conditions like maternal infections during pregnancy can lead to congenital SNHL in newborns.
-
Premature Birth: Babies born prematurely are at a higher risk for SNHL due to underdeveloped auditory systems.
-
Low Birth Weight: Infants with low birth weight may have a higher likelihood of developing SNHL.
-
Otosclerosis: This abnormal bone growth in the middle ear can sometimes extend to the inner ear, causing SNHL.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing and managing SNHL involves various approaches. Here are some important aspects to know.
-
Audiometry Tests: Hearing tests, such as pure-tone audiometry, are used to diagnose SNHL by measuring hearing sensitivity.
-
Speech Audiometry: This test evaluates the ability to hear and understand speech, helping to assess the extent of SNHL.
-
Otoacoustic Emissions (OAEs): These tests measure sound waves produced in the inner ear, providing information about cochlear health.
-
Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR): This test assesses the auditory nerve and brain pathways, useful for diagnosing SNHL in infants.
-
Hearing Aids: While SNHL is irreversible, hearing aids can amplify sound, helping individuals hear better.
-
Cochlear Implants: For severe SNHL, cochlear implants can bypass damaged hair cells and directly stimulate the auditory nerve.
-
Assistive Listening Devices: Devices like FM systems and amplified telephones can aid those with SNHL in specific situations.
-
Lip Reading and Sign Language: These communication methods can be beneficial for individuals with profound SNHL.
-
Tinnitus Management: Techniques such as sound therapy and cognitive behavioral therapy can help manage tinnitus associated with SNHL.
-
Regular Monitoring: Regular hearing check-ups are crucial for individuals with SNHL to monitor changes and adjust treatment as needed.
Living with Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Adapting to life with SNHL involves various strategies to improve communication and quality of life. Here are some tips.
-
Communication Strategies: Facing the person speaking, reducing background noise, and using visual cues can enhance communication.
-
Hearing Protection: Using earplugs or earmuffs in noisy environments can prevent further damage to hearing.
-
Support Groups: Joining support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice for living with SNHL.
-
Education and Awareness: Educating family and friends about SNHL can foster understanding and support.
-
Workplace Accommodations: Employers can provide accommodations like captioned telephones and quiet workspaces for employees with SNHL.
-
Technology Aids: Smartphone apps and alerting devices can assist those with SNHL in daily activities.
-
Mental Health Support: Counseling and therapy can help address the emotional impact of living with SNHL.
-
Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and a balanced diet can support overall well-being.
-
Regular Hearing Check-ups: Routine hearing assessments can help track changes and adjust interventions as needed.
-
Advocacy and Rights: Understanding legal rights and advocating for accessibility can empower individuals with SNHL.
Future Directions and Research
Research continues to advance our understanding of SNHL and potential treatments. Here are some exciting developments.
-
Gene Therapy: Scientists are exploring gene therapy as a potential treatment for hereditary SNHL.
-
Stem Cell Research: Research into stem cells offers hope for regenerating damaged hair cells in the cochlea.
-
Neuroplasticity: Studies on brain plasticity suggest that the brain can adapt to hearing loss, offering new avenues for rehabilitation.
-
Pharmacological Advances: New drugs are being developed to protect and repair inner ear structures.
-
Improved Cochlear Implants: Advances in cochlear implant technology aim to provide better sound quality and user experience.
-
Biomarkers for Early Detection: Identifying biomarkers could lead to earlier detection and intervention for SNHL.
-
Personalized Medicine: Tailoring treatments based on individual genetic profiles may improve outcomes for those with SNHL.
-
Virtual Reality Therapy: VR technology is being explored as a tool for auditory rehabilitation and tinnitus management.
-
Public Health Initiatives: Efforts to raise awareness and prevent noise-induced hearing loss are gaining momentum.
-
Global Collaboration: International research collaborations are accelerating progress in understanding and treating SNHL.
Final Thoughts on Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss, a common condition, affects millions worldwide. Understanding its causes, from genetics to noise exposure, helps in managing it better. Early detection is key, as it can lead to more effective treatments and improved quality of life. Hearing aids and cochlear implants are popular solutions, offering significant benefits to those affected. Regular hearing check-ups can catch issues early, preventing further deterioration. Protecting your ears from loud noises and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can also reduce risks. Awareness and education about this condition are crucial for both individuals and communities. By staying informed, people can make better choices for their hearing health. Remember, taking proactive steps today can lead to a better hearing tomorrow. Stay curious, stay informed, and take care of your ears. They’re your gateway to the world of sound.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
