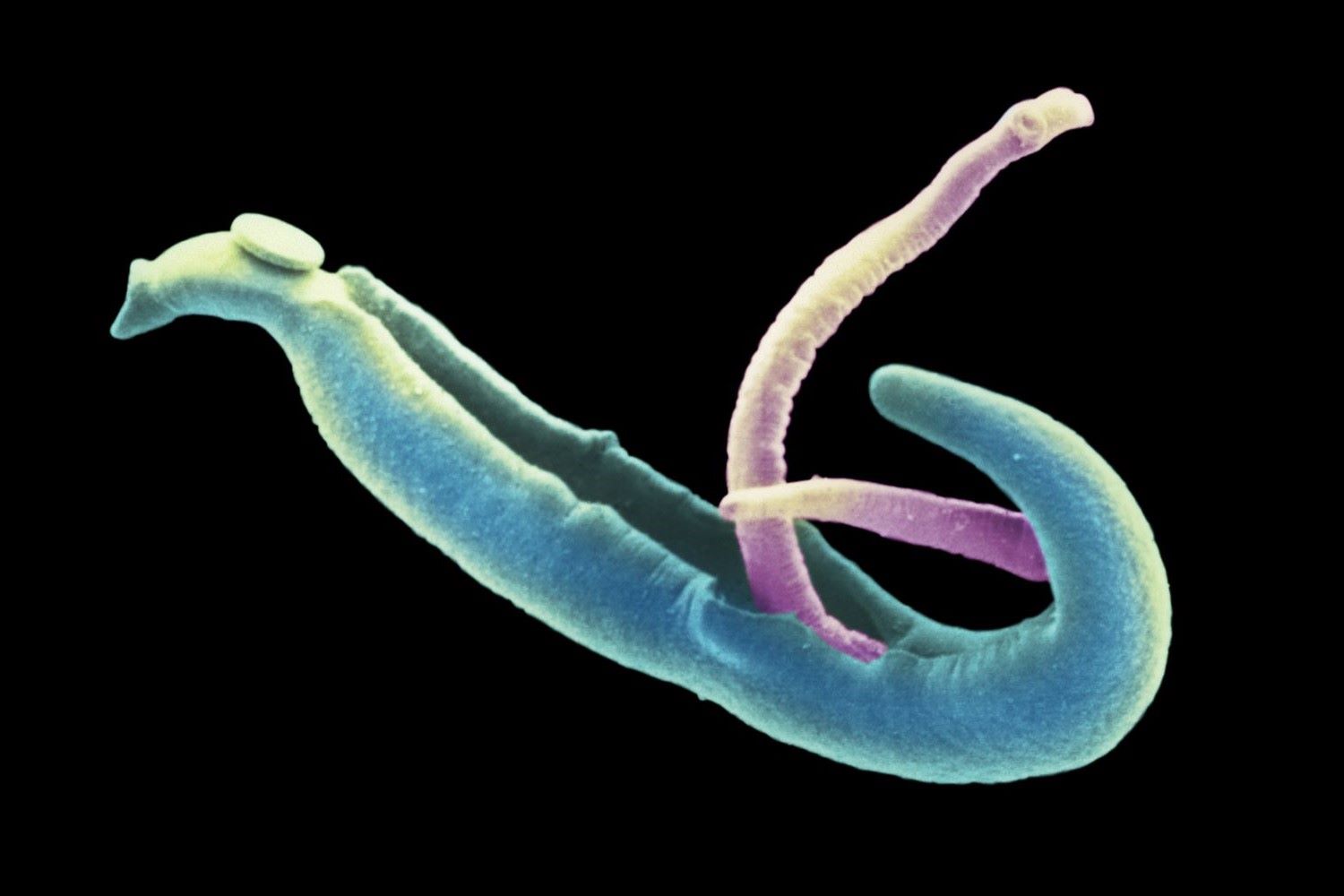
What is schistosomiasis? It's a disease caused by parasitic worms, affecting millions globally. These pesky parasites, known as schistosomes, thrive in freshwater snails before finding their way into humans. Once inside, they can cause a range of health issues, from mild symptoms like a rash or itchy skin to more severe problems such as liver damage or bladder cancer. Schistosomiasis is most common in tropical and subtropical regions, particularly in Africa, Asia, and South America. Despite its prevalence, many people remain unaware of this condition. Prevention involves avoiding contaminated water and improving sanitation. Treatment is available, with medications like praziquantel effectively combating the infection. Understanding schistosomiasis is crucial for reducing its impact on affected communities. Let's dive into 50 fascinating facts about this disease, shedding light on its history, symptoms, and the ongoing efforts to control it.
Key Takeaways:
- Schistosomiasis, caused by parasitic worms in contaminated water, affects over 200 million people worldwide, with children being particularly vulnerable. Prevention and early treatment are crucial for managing this widespread disease.
- Understanding the impact of schistosomiasis on the body, its diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies is essential for global health. Ongoing research, innovations, and technology offer hope for better control and eventual eradication of this disease.
What is Schistosomiasis?
Schistosomiasis, also known as bilharzia, is a disease caused by parasitic worms. These parasites are found in freshwater sources in tropical and subtropical regions. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about this disease and its impact on global health.
-
Schistosomiasis is caused by parasitic worms. These worms belong to the genus Schistosoma, and they infect humans through contact with contaminated water.
-
The disease is prevalent in tropical and subtropical areas. Regions in Africa, the Middle East, Asia, and South America are most affected.
-
Freshwater snails play a crucial role. These snails act as intermediate hosts, releasing larvae that can penetrate human skin.
-
Over 200 million people are affected worldwide. This makes schistosomiasis one of the most widespread parasitic diseases globally.
-
Children are particularly vulnerable. Kids playing in contaminated water are at higher risk of infection.
How Does Schistosomiasis Affect the Body?
Once inside the human body, these parasites can cause a range of health issues. Understanding the impact on the body helps in grasping the seriousness of the disease.
-
The worms live in blood vessels. They primarily reside in the blood vessels around the intestines or bladder.
-
Eggs cause the most damage. The immune response to these eggs can lead to inflammation and tissue damage.
-
Symptoms vary widely. They can range from mild itching to severe organ damage, depending on the infection's severity.
-
Chronic infection can lead to serious complications. These include liver damage, kidney failure, and bladder cancer.
-
Anemia is a common consequence. The disease often leads to chronic blood loss, resulting in anemia.
How is Schistosomiasis Diagnosed and Treated?
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing schistosomiasis effectively. Let's explore how healthcare professionals tackle this disease.
-
Diagnosis often involves stool or urine samples. These samples are examined for the presence of parasite eggs.
-
Blood tests can also be used. They help detect antibodies or antigens related to the infection.
-
Praziquantel is the primary treatment. This medication is effective in killing the adult worms.
-
Treatment is most effective in early stages. Early intervention can prevent long-term complications.
-
Mass drug administration is a common strategy. In high-risk areas, entire communities may receive treatment to control the spread.
What are the Prevention Strategies?
Preventing schistosomiasis involves a combination of public health measures and individual actions. Let's look at some effective strategies.
-
Avoiding contaminated water is key. People are advised to stay away from freshwater sources in endemic areas.
-
Improving sanitation reduces risk. Proper sanitation facilities can prevent the spread of the parasite.
-
Health education is crucial. Educating communities about the risks and prevention methods can significantly reduce infection rates.
-
Controlling snail populations helps. Reducing the number of intermediate hosts can lower transmission rates.
-
Vaccines are under development. Research is ongoing to create a vaccine that could offer long-term protection.
What is the Global Impact of Schistosomiasis?
The disease has far-reaching effects on health, economies, and societies. Understanding its global impact highlights the importance of control efforts.
-
Schistosomiasis contributes to poverty. The disease can impair physical and cognitive development, affecting productivity.
-
It places a burden on healthcare systems. Treating and managing the disease requires significant resources.
-
Economic losses are substantial. Affected individuals may miss work or school, impacting economic growth.
-
International organizations are involved in control efforts. The World Health Organization and others work to reduce the disease's prevalence.
-
Community involvement is essential. Local participation in control programs increases their effectiveness.
What are the Challenges in Controlling Schistosomiasis?
Despite efforts, several challenges hinder the control of schistosomiasis. Let's explore some of these obstacles.
-
Limited access to healthcare. In many endemic regions, healthcare services are scarce.
-
Resistance to treatment is a concern. Over time, parasites may develop resistance to drugs like praziquantel.
-
Environmental changes affect transmission. Climate change and water management practices can influence the spread of the disease.
-
Cultural beliefs may hinder prevention. Misconceptions about the disease can affect community participation in control programs.
-
Funding for control programs is often inadequate. Sustained financial support is necessary for long-term success.
What are the Research and Innovations in Schistosomiasis Control?
Ongoing research and innovations offer hope for better control and eventual eradication of schistosomiasis. Let's look at some promising developments.
-
New diagnostic tools are being developed. These tools aim to provide faster and more accurate detection of the disease.
-
Research on drug resistance is ongoing. Scientists are studying ways to overcome potential resistance to current treatments.
-
Genetic studies offer insights. Understanding the parasite's genetics can lead to new treatment and prevention strategies.
-
Innovative snail control methods are being tested. These include biological control and environmental management techniques.
-
Collaborative efforts are increasing. Partnerships between governments, NGOs, and researchers are enhancing control efforts.
What is the Role of Technology in Schistosomiasis Control?
Technology plays a significant role in advancing the fight against schistosomiasis. Let's explore how tech innovations are making a difference.
-
Mobile health apps aid in education. These apps provide information on prevention and treatment to at-risk populations.
-
Remote sensing helps track snail habitats. Satellite imagery can identify areas where snails thrive, aiding in control efforts.
-
Data analytics improve program efficiency. Analyzing data from control programs helps optimize resource allocation.
-
Telemedicine expands access to care. Remote consultations can reach individuals in hard-to-access areas.
-
Digital platforms facilitate collaboration. Online platforms enable researchers and organizations to share information and strategies.
What are the Future Prospects for Schistosomiasis Control?
The future of schistosomiasis control looks promising, with ongoing research and global efforts paving the way for progress. Let's consider what lies ahead.
-
Vaccine development is a priority. A successful vaccine could significantly reduce infection rates.
-
Integrated control programs are gaining traction. Combining multiple strategies increases the likelihood of success.
-
Community engagement is becoming more effective. Empowering local communities enhances the sustainability of control efforts.
-
Innovations in water management are emerging. Improved water infrastructure can reduce exposure to contaminated sources.
-
Global commitment is strengthening. Increased international cooperation is driving progress toward control and eradication.
What are the Social and Cultural Aspects of Schistosomiasis?
Understanding the social and cultural dimensions of schistosomiasis is crucial for effective control. Let's explore how these factors influence the disease.
-
Cultural practices can affect transmission. Traditional water use practices may increase exposure to contaminated sources.
-
Stigma can hinder treatment. Misunderstandings about the disease may lead to social stigma, affecting individuals' willingness to seek care.
-
Gender roles influence risk. Women and children may be more exposed due to their roles in water collection and household chores.
-
Community leaders play a vital role. Engaging local leaders can enhance the acceptance and success of control programs.
-
Education empowers communities. Providing accurate information helps dispel myths and encourages preventive behaviors.
Final Thoughts on Schistosomiasis
Schistosomiasis, often overlooked, is a serious health issue affecting millions worldwide. This parasitic disease, caused by flatworms, thrives in freshwater environments, especially in regions with limited access to clean water and sanitation. Understanding its symptoms—like fever, abdominal pain, and blood in urine—is crucial for early detection and treatment.
Efforts to combat schistosomiasis include mass drug administration, improving sanitation, and educating communities about preventive measures. Vaccines are under development, offering hope for future eradication.
Raising awareness and supporting global health initiatives can significantly reduce the disease's impact. By spreading knowledge and advocating for better resources, we can help protect vulnerable populations. Schistosomiasis may be a formidable foe, but with collective action, it can be controlled and eventually eliminated. Let's keep pushing for a healthier, schistosomiasis-free world.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
