Progressive Systemic Sclerosis, also known as scleroderma, is a rare autoimmune disease that affects the skin, blood vessels, muscles, and internal organs. This condition causes the body to produce too much collagen, leading to thickening and hardening of tissues. Symptoms can range from mild skin changes to severe organ damage. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing the disease and improving quality of life. Did you know that scleroderma affects women more often than men, typically between the ages of 30 and 50? Understanding this complex disease can help those affected and their loved ones navigate its challenges.
Key Takeaways:
- Progressive Systemic Sclerosis causes skin hardening and internal organ issues. Early diagnosis and multidisciplinary treatment are crucial for managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
- Living with Progressive Systemic Sclerosis requires regular medical check-ups, balanced diet, stress management, and strong support network for emotional and practical assistance.
What is Progressive Systemic Sclerosis?
Progressive Systemic Sclerosis (PSS), also known as systemic scleroderma, is a chronic autoimmune disease. It primarily affects the skin but can also impact internal organs. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition.
- PSS is characterized by the hardening and tightening of the skin.
- The disease can also affect blood vessels, muscles, and internal organs.
- It is more common in women than men.
- The onset typically occurs between the ages of 30 and 50.
- The exact cause of PSS remains unknown.
- Genetic factors may play a role in the development of the disease.
- Environmental triggers, such as exposure to certain chemicals, might contribute.
- PSS is classified as an autoimmune disorder.
- The immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues.
- Collagen overproduction is a hallmark of PSS.
Symptoms of Progressive Systemic Sclerosis
The symptoms of PSS can vary widely among individuals. They often depend on which parts of the body are affected.
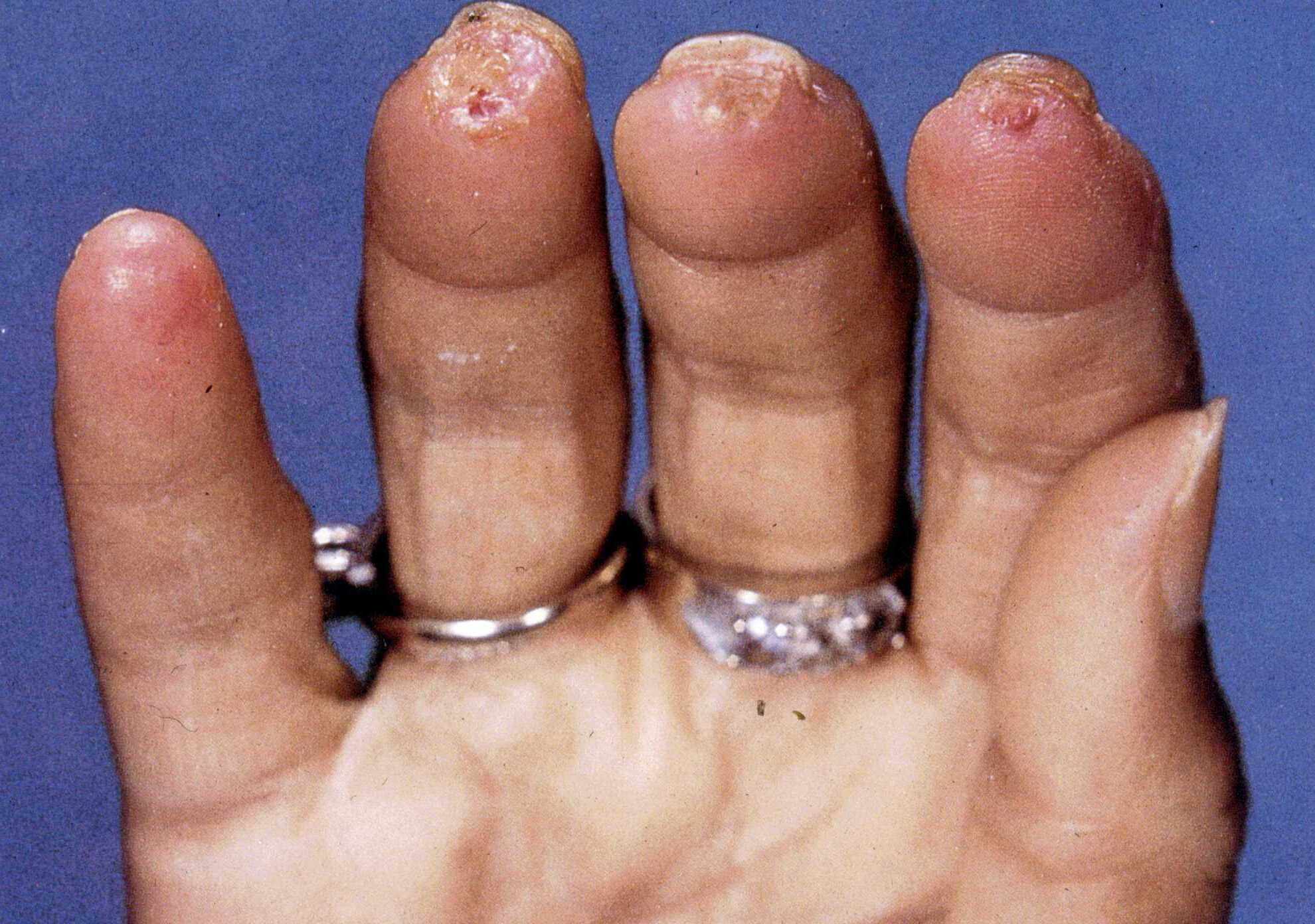
- Raynaud's phenomenon is a common early symptom.
- This condition causes fingers and toes to turn white or blue in response to cold or stress.
- Skin changes, such as thickening and hardening, are typical.
- Patients may experience joint pain and stiffness.
- Digestive issues, including acid reflux and difficulty swallowing, are common.
- Lung involvement can lead to shortness of breath and a persistent cough.
- Kidney problems may arise, potentially causing high blood pressure.
- Heart complications, such as arrhythmias and heart failure, can occur.
- Fatigue and general malaise are often reported.
- Muscle weakness is another possible symptom.
Diagnosis of Progressive Systemic Sclerosis
Diagnosing PSS can be challenging due to its varied symptoms. Several tests and evaluations are typically required.
- A thorough medical history and physical examination are essential.
- Blood tests can help detect specific antibodies associated with PSS.
- Skin biopsies may be performed to examine tissue changes.
- Imaging studies, such as X-rays and CT scans, can assess internal organ involvement.
- Pulmonary function tests evaluate lung function.
- Echocardiograms can detect heart abnormalities.
- Gastrointestinal tests may be needed to assess digestive issues.
- Capillaroscopy examines small blood vessels in the nail folds.
- Early diagnosis is crucial for better management of the disease.
- A multidisciplinary approach often involves rheumatologists, dermatologists, and other specialists.
Treatment Options for Progressive Systemic Sclerosis
While there is no cure for PSS, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Medications can help control symptoms and slow disease progression.
- Immunosuppressive drugs may be prescribed to reduce immune system activity.
- Vasodilators can help manage Raynaud's phenomenon.
- Proton pump inhibitors and other medications treat digestive issues.
- Physical therapy can improve joint and muscle function.
- Occupational therapy helps patients adapt to daily activities.
- Regular exercise is beneficial for overall health.
- Skin care routines can help manage skin symptoms.
- Psychological support is important for coping with the emotional impact of the disease.
- Clinical trials may offer access to new and experimental treatments.
Living with Progressive Systemic Sclerosis
Living with PSS requires ongoing management and support. Patients can take several steps to improve their quality of life.
- Regular medical check-ups are essential for monitoring the disease.
- A balanced diet can help maintain overall health.
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption is important.
- Stress management techniques, such as meditation and yoga, can be beneficial.
- Support groups provide emotional support and practical advice.
- Patients should protect their skin from extreme temperatures and injuries.
- Wearing warm clothing can help manage Raynaud's phenomenon.
- Hand exercises can improve circulation and flexibility.
- Patients should stay informed about their condition and treatment options.
- Building a strong support network of family, friends, and healthcare providers is crucial.
Final Thoughts on Progressive Systemic Sclerosis
Progressive Systemic Sclerosis, also known as scleroderma, is a complex condition that affects many aspects of a person's life. Understanding its symptoms, treatments, and impacts can help those affected manage their condition better. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for improving quality of life. While there's no cure, advancements in medical research offer hope for more effective treatments. Staying informed and connected with healthcare providers is essential. Support from family, friends, and support groups can make a significant difference. Remember, knowledge is power. The more you know about scleroderma, the better equipped you'll be to handle its challenges. Keep learning, stay proactive, and never hesitate to seek help when needed.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
