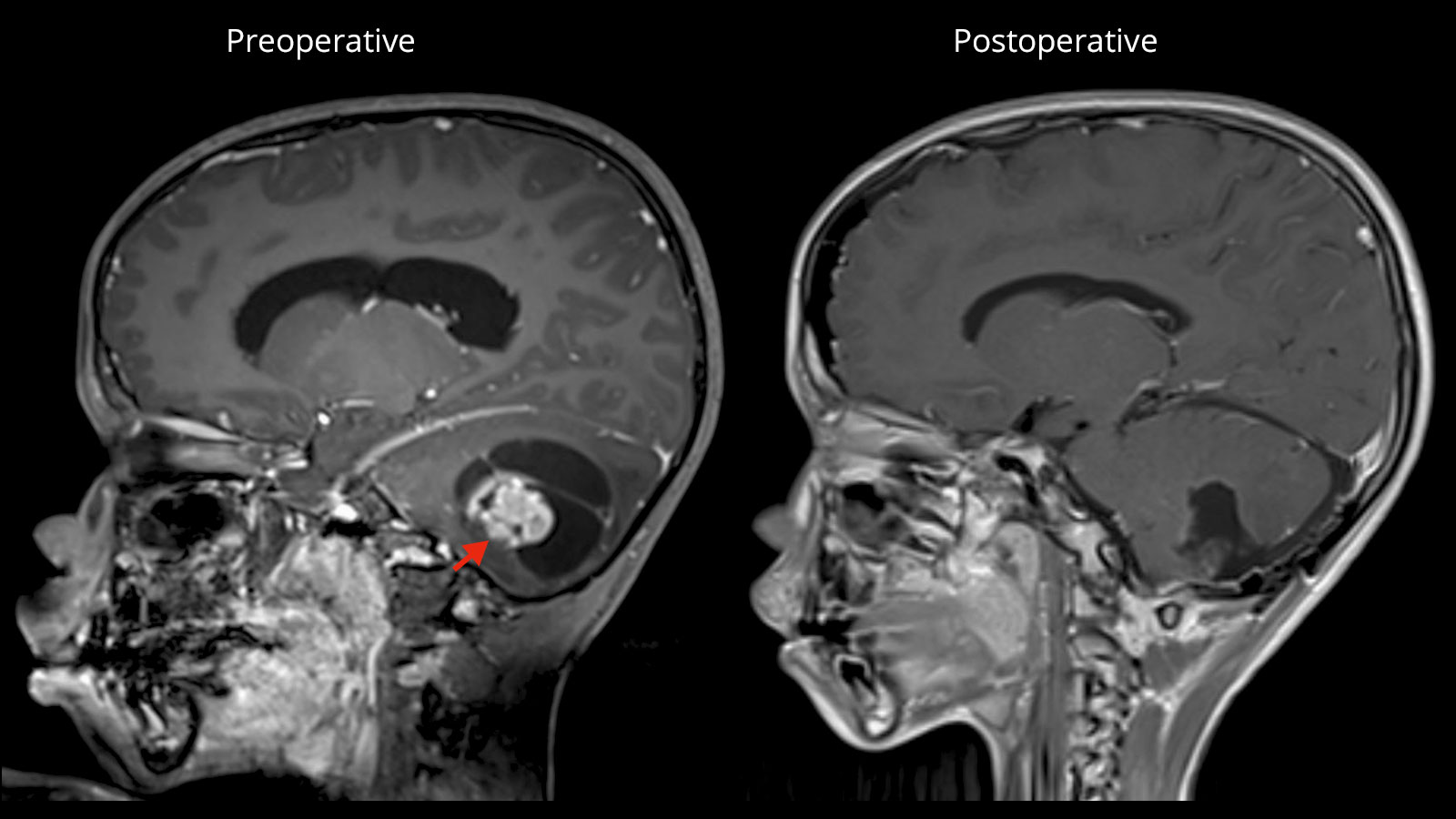
What is Pilocytic Astrocytoma? It's a type of brain tumor that mostly affects children and young adults. Unlike other tumors, this one grows slowly and is usually not cancerous. Found mostly in the cerebellum, it can also appear in the brainstem, hypothalamus, or optic nerve. Symptoms vary but often include headaches, nausea, and balance problems. Treatment usually involves surgery to remove the tumor, and sometimes radiation or chemotherapy is needed. Early detection can make a big difference in outcomes. Understanding this condition is important for those affected and their families. Let's explore 50 facts about this unique tumor to better grasp its nature and impact.
Key Takeaways:
- Pilocytic astrocytoma is a slow-growing brain tumor that mostly affects children. Surgery is the main treatment, and early detection leads to high survival rates.
- Ongoing research offers hope for improved treatments and outcomes for those affected by pilocytic astrocytoma. Early detection and a strong support network are crucial.
What is Pilocytic Astrocytoma?
Pilocytic astrocytoma is a type of brain tumor that primarily affects children and young adults. It is generally considered a low-grade tumor, meaning it grows slowly and is less likely to spread. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition:
-
Common in Children: Pilocytic astrocytomas are most frequently diagnosed in children and adolescents, typically between the ages of 5 and 20.
-
Low-Grade Tumor: Classified as a Grade I tumor by the World Health Organization, indicating it is the least aggressive form of brain tumor.
-
Originates in the Brain: These tumors often develop in the cerebellum, the part of the brain responsible for balance and coordination.
-
Symptoms Vary: Symptoms can include headaches, nausea, vomiting, and balance issues, depending on the tumor's location.
-
Surgical Removal: Surgery is often the primary treatment, and complete removal can lead to a cure in many cases.
How is Pilocytic Astrocytoma Diagnosed?
Diagnosing pilocytic astrocytoma involves several steps and tests. Understanding the process can help demystify the journey for patients and families.
-
MRI Scans: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is the most common method used to detect these tumors.
-
Biopsy Confirmation: A biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and determine the tumor's grade.
-
Neurological Exams: Doctors often conduct neurological exams to assess the impact on brain function.
-
Genetic Testing: In some cases, genetic testing is done to identify specific mutations associated with the tumor.
-
Regular Monitoring: For tumors that cannot be fully removed, regular monitoring with MRI scans is essential.
Treatment Options for Pilocytic Astrocytoma
Treatment varies based on the tumor's size, location, and the patient's overall health. Here are some common approaches:
-
Surgical Resection: Complete surgical removal is the goal and can be curative.
-
Radiation Therapy: Used when surgery isn't possible or to target remaining tumor cells post-surgery.
-
Chemotherapy: Sometimes used, especially in younger children, to shrink the tumor before surgery.
-
Targeted Therapy: Newer treatments focus on specific genetic mutations within the tumor.
-
Observation: In some cases, especially with small, asymptomatic tumors, doctors may opt for a watch-and-wait approach.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Understanding the prognosis can provide hope and clarity for those affected by pilocytic astrocytoma.
-
High Survival Rate: The five-year survival rate is over 90% for patients with pilocytic astrocytoma.
-
Long-Term Monitoring: Even after successful treatment, long-term follow-up is crucial to monitor for recurrence.
-
Quality of Life: Many patients lead normal lives post-treatment, especially if the tumor is completely removed.
-
Recurrence Possible: While rare, recurrence can happen, necessitating further treatment.
-
Support Systems: Support groups and counseling can be beneficial for patients and families navigating this journey.
Research and Advances
Ongoing research continues to improve understanding and treatment of pilocytic astrocytoma. Here are some recent developments:
-
Genetic Discoveries: Researchers have identified specific genetic mutations that may drive tumor growth.
-
Improved Imaging: Advances in imaging technology allow for more precise diagnosis and treatment planning.
-
Clinical Trials: New treatments are being tested in clinical trials, offering hope for more effective therapies.
-
Immunotherapy: Emerging research is exploring the use of immunotherapy to target tumor cells.
-
Patient Registries: Registries help track outcomes and improve understanding of this condition.
Living with Pilocytic Astrocytoma
Living with a diagnosis of pilocytic astrocytoma can be challenging, but many resources are available to help patients and families cope.
-
Educational Support: Children may require special educational support to address learning challenges.
-
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help improve balance and coordination affected by the tumor.
-
Emotional Well-being: Counseling and support groups can aid in emotional adjustment and coping.
-
Nutritional Guidance: Proper nutrition can support overall health and recovery.
-
Family Involvement: Family support is crucial in managing the emotional and practical aspects of living with this condition.
Myths and Misconceptions
There are several myths surrounding pilocytic astrocytoma that can lead to confusion. Let's clear up some common misconceptions:
-
Not Always Cancerous: While a tumor, pilocytic astrocytoma is not considered cancerous due to its slow growth and low likelihood of spreading.
-
Not Always Fatal: Many patients live long, healthy lives post-treatment, especially with early detection and intervention.
-
Surgery is Not Always Risky: Advances in surgical techniques have significantly reduced risks associated with tumor removal.
-
Not All Tumors Require Immediate Treatment: Some small, asymptomatic tumors can be monitored without immediate intervention.
-
Not Just a Childhood Disease: Although more common in children, adults can also develop pilocytic astrocytoma.
Support and Resources
Support and resources are vital for those affected by pilocytic astrocytoma. Here are some ways to find help:
-
Support Groups: Joining a support group can provide emotional support and practical advice.
-
Online Communities: Online forums and communities offer a platform to connect with others facing similar challenges.
-
Educational Materials: Many organizations provide educational materials to help patients and families understand the condition.
-
Financial Assistance: Some charities and organizations offer financial assistance for treatment-related expenses.
-
Advocacy Organizations: Advocacy groups work to raise awareness and support research into pilocytic astrocytoma.
Future Directions in Pilocytic Astrocytoma Research
The future holds promise for those affected by pilocytic astrocytoma, with ongoing research paving the way for better treatments and outcomes.
-
Personalized Medicine: Tailoring treatment to individual genetic profiles is a growing area of research.
-
New Drug Development: Researchers are working on developing new drugs that specifically target tumor cells.
-
Improved Surgical Techniques: Advances in technology are leading to less invasive and more effective surgical options.
-
Longitudinal Studies: Long-term studies are helping to better understand the natural history of pilocytic astrocytoma.
-
Collaboration: International collaboration among researchers is accelerating progress in understanding and treating this condition.
Final Thoughts on Pilocytic Astrocytoma
While pilocytic astrocytoma presents challenges, advancements in research and treatment offer hope for those affected. Here are a few more facts to consider:
-
Early Detection is Key: Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes.
-
Multidisciplinary Approach: Successful management often involves a team of specialists, including neurologists, oncologists, and surgeons.
-
Patient Advocacy: Patients and families can play an active role in their care by staying informed and advocating for their needs.
-
Community Support: Building a strong support network can make a significant difference in coping with the condition.
-
Hope for the Future: With ongoing research and innovation, the future looks brighter for those affected by pilocytic astrocytoma.
Final Thoughts on Pilocytic Astrocytoma
Pilocytic astrocytoma, a type of brain tumor, often affects children and young adults. Despite being a tumor, it's usually benign and grows slowly. This means it often has a good prognosis with proper treatment. Symptoms can vary depending on the tumor's location, but common ones include headaches, nausea, and balance issues. Diagnosis typically involves imaging tests like MRI scans. Treatment often involves surgery to remove the tumor, and in some cases, additional therapies like radiation or chemotherapy may be needed. Research continues to improve understanding and treatment options, offering hope for even better outcomes. Families dealing with this condition should seek support from medical professionals and support groups. Staying informed and connected can make a significant difference in managing the journey. Remember, knowledge is power, and understanding the facts about pilocytic astrocytoma can help navigate this challenging path.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
