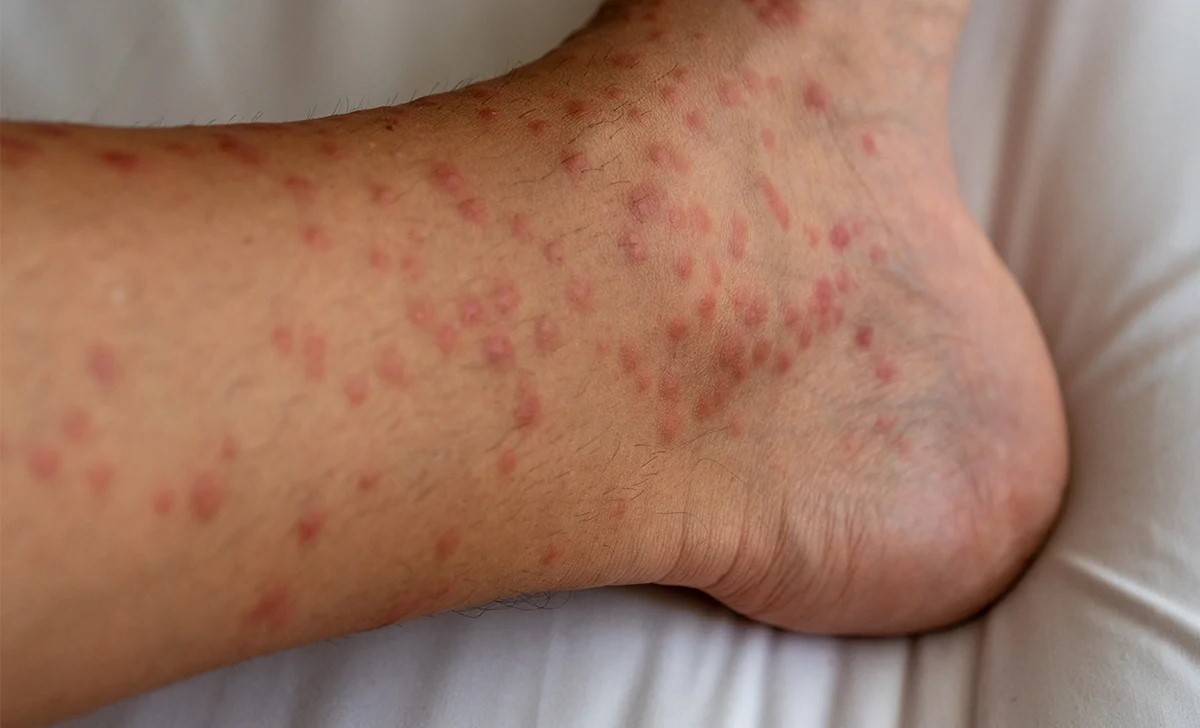
Papular urticaria is a common skin condition that affects many people, especially children. But what exactly is it? Papular urticaria is an allergic reaction to insect bites, leading to itchy, red bumps on the skin. These bumps can be quite uncomfortable and sometimes even painful. The condition often flares up during warmer months when insects are more active. Understanding the triggers and symptoms can help manage and prevent outbreaks. In this post, we'll explore 50 interesting facts about papular urticaria, from its causes and symptoms to treatment options and prevention tips. Whether you're dealing with it yourself or caring for someone who is, this guide will provide valuable insights.
Key Takeaways:
- Papular urticaria is a common skin condition caused by insect bites, especially in kids. Itchy red bumps can last for weeks, but can be managed with antihistamines and preventive measures like insect repellents.
- Preventing papular urticaria involves using insect repellents, keeping living spaces clean, and wearing protective clothing. Educating children about not scratching bites is also important to prevent complications.
What is Papular Urticaria?
Papular urticaria is a common skin condition, especially in children. It results from hypersensitivity to insect bites. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this condition.
- Papular urticaria often appears as itchy, red bumps on the skin.
- It is most prevalent in children aged 2 to 7 years.
- The condition is triggered by bites from insects like mosquitoes, fleas, and bedbugs.
- Symptoms can last from a few days to several weeks.
- Papular urticaria is not contagious.
- The bumps can sometimes form blisters.
- It is more common in warmer climates where insects thrive.
- Scratching the bumps can lead to secondary infections.
- Antihistamines can help reduce itching.
- Topical steroids are often prescribed to reduce inflammation.
Causes and Triggers
Understanding what causes papular urticaria can help in managing and preventing it. Here are some key points about its causes and triggers.
- Insect bites are the primary cause of papular urticaria.
- Fleas from pets are a common source of bites.
- Bedbugs can also trigger the condition.
- Mosquito bites are another frequent cause.
- Not everyone bitten by insects will develop papular urticaria.
- Some individuals have a genetic predisposition to the condition.
- The immune system's overreaction to insect saliva causes the symptoms.
- Environmental factors like humidity can increase insect activity.
- Wearing protective clothing can help prevent bites.
- Using insect repellents is an effective preventive measure.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms and getting a proper diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Here are some important facts about the symptoms and diagnosis of papular urticaria.
- Itchy bumps are the most common symptom.
- The bumps are usually red and raised.
- They can appear in clusters or individually.
- The bumps often have a central punctum, indicating the bite site.
- Symptoms can worsen at night due to increased itching.
- A dermatologist can diagnose papular urticaria through a physical examination.
- A detailed history of recent insect exposure helps in diagnosis.
- Sometimes, a skin biopsy is performed to rule out other conditions.
- Blood tests are rarely needed for diagnosis.
- The condition can be mistaken for other skin issues like eczema or scabies.
Treatment and Management
Managing papular urticaria involves both treating the symptoms and preventing future outbreaks. Here are some effective treatment and management strategies.
- Antihistamines are commonly used to relieve itching.
- Topical steroids can reduce inflammation and redness.
- Keeping the skin moisturized helps prevent dryness and itching.
- Avoiding scratching is crucial to prevent secondary infections.
- Cold compresses can provide temporary relief from itching.
- Oral steroids are rarely needed but can be prescribed for severe cases.
- Antibiotics may be necessary if a secondary infection occurs.
- Regular cleaning of living spaces can reduce insect populations.
- Treating pets for fleas can prevent future outbreaks.
- Wearing long sleeves and pants can minimize skin exposure to insect bites.
Prevention Tips
Preventing papular urticaria involves reducing exposure to insect bites. Here are some practical tips to help prevent this condition.
- Using insect repellents is one of the most effective preventive measures.
- Installing screens on windows and doors can keep insects out.
- Regularly washing bedding and clothing can reduce the risk of bedbugs.
- Keeping pets clean and treated for fleas is essential.
- Avoiding areas with high insect activity, especially during peak times, can help.
- Using mosquito nets while sleeping can provide protection.
- Wearing light-colored clothing can make it easier to spot insects.
- Avoiding perfumes and scented lotions can reduce insect attraction.
- Keeping the home environment clean and clutter-free can minimize insect hiding spots.
- Educating children about the importance of not scratching bites can help prevent complications.
Final Thoughts on Papular Urticaria
Papular urticaria, often misunderstood, affects many, especially children. Knowing the symptoms and triggers helps in managing this condition better. Prevention involves avoiding insect bites and using protective measures like insect repellents and proper clothing. Treatment usually includes antihistamines and topical steroids to reduce itching and inflammation.
Understanding this condition can ease worries and improve quality of life for those affected. If symptoms persist or worsen, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial. They can provide personalized advice and treatment plans.
Stay informed, take preventive steps, and seek medical advice when needed. This approach ensures that papular urticaria doesn't interfere with daily life. Remember, knowledge and proactive care are key to managing this condition effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
