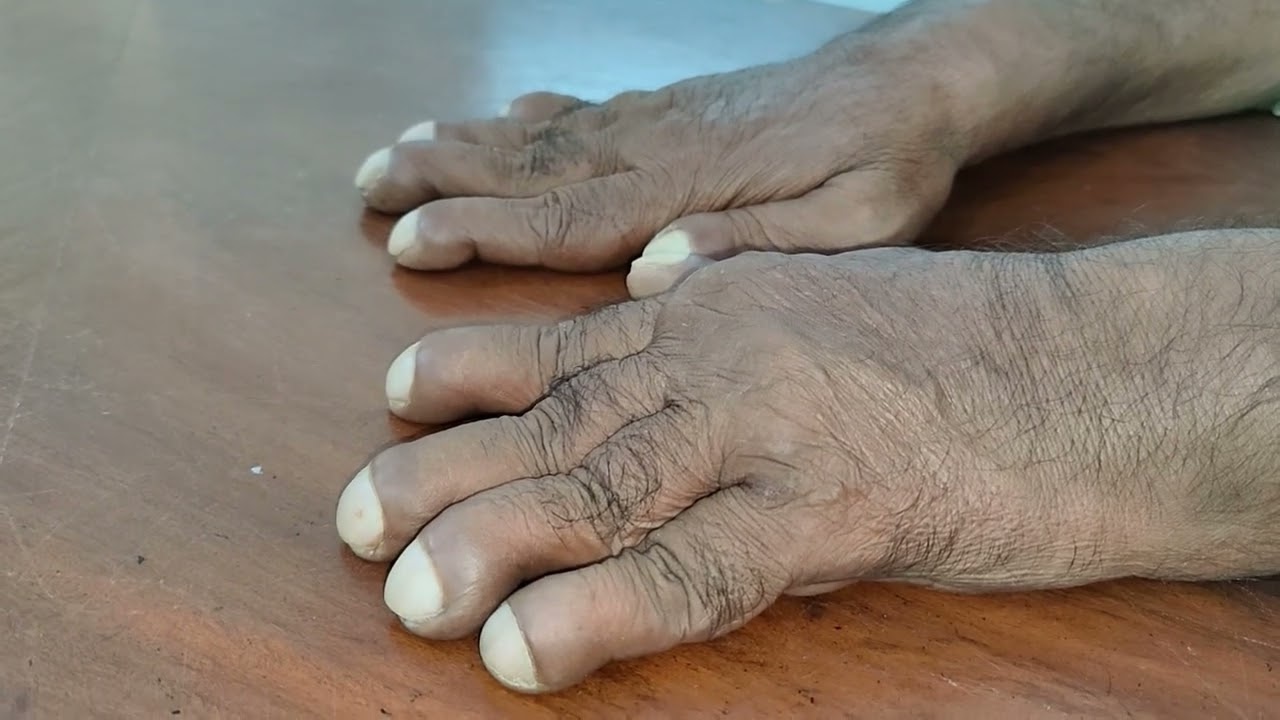
Pachydermoperiostosis might sound like a mouthful, but it's a rare genetic disorder that affects the skin and bones. Ever wondered what makes this condition unique? Pachydermoperiostosis causes thickening of the skin, especially on the face and scalp, and can lead to clubbing of the fingers and toes. This condition often begins during puberty and can be mistaken for other diseases. Despite its rarity, understanding Pachydermoperiostosis is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. In this blog post, we'll explore 50 intriguing facts about this condition, shedding light on its symptoms, causes, and the impact it has on those affected. Get ready to dive into the world of Pachydermoperiostosis and discover what makes it so fascinating.
Key Takeaways:
- Pachydermoperiostosis, or PDP, is a rare genetic disorder that thickens the skin and affects the bones. It can cause joint pain, excessive sweating, and bone deformities, but treatments like NSAIDs and retinoids can help manage symptoms.
- Ongoing research on PDP aims to better understand the condition and develop more effective treatments. Joining support groups, staying active, and staying informed about new research can help individuals living with PDP lead fulfilling lives.
What is Pachydermoperiostosis?
Pachydermoperiostosis (PDP) is a rare genetic disorder that affects the skin and bones. It is characterized by thickening of the skin (pachydermia) and changes in the bones, particularly in the hands and feet. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this condition.
- PDP is also known as primary hypertrophic osteoarthropathy.
- The condition was first described in 1868 by Friedrich Schinz.
- PDP is more common in males than females.
- Symptoms usually appear during adolescence.
- The disorder is often inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern.
- PDP can also occur sporadically, with no family history.
- The exact cause of PDP remains unknown.
- Mutations in the HPGD gene have been linked to some cases.
- The disorder affects the skin, bones, and sometimes internal organs.
- Thickening of the skin is most noticeable on the face and scalp.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and how PDP is diagnosed can help in managing the condition effectively. Here are some key points to consider.
- Clubbing of the fingers and toes is a common symptom.
- Joint pain and swelling often accompany the condition.
- Excessive sweating, particularly on the palms and soles, is frequently reported.
- Seborrhea, a skin condition causing scaly patches, is another symptom.
- The skin on the face may become oily and thickened.
- Bone pain, especially in the long bones, is common.
- X-rays can reveal periostosis, or new bone formation, along the shafts of long bones.
- A skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
- Blood tests can help rule out secondary causes of hypertrophic osteoarthropathy.
- Genetic testing can identify mutations in the HPGD gene.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for PDP, various treatments can help manage the symptoms. Here are some approaches used in treating the condition.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help relieve joint pain.
- Retinoids may be prescribed to reduce skin thickening.
- Physical therapy can improve joint function and mobility.
- Surgery may be necessary to correct severe bone deformities.
- Regular monitoring by a dermatologist and rheumatologist is recommended.
- Moisturizers can help manage dry, thickened skin.
- Botox injections have been used to reduce excessive sweating.
- Lifestyle changes, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, can improve overall health.
- Psychological support is important for coping with the chronic nature of the disorder.
- Early diagnosis and intervention can improve the quality of life for those with PDP.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand PDP and develop more effective treatments. Here are some exciting developments in the field.
- Studies are exploring the role of the HPGD gene in PDP.
- Researchers are investigating other potential genetic causes of the disorder.
- New imaging techniques are being developed to better visualize bone changes.
- Advances in genetic testing may lead to earlier diagnosis.
- Clinical trials are testing new medications for managing symptoms.
- Researchers are studying the long-term effects of existing treatments.
- Patient registries are being established to collect data on PDP.
- Collaboration between researchers and clinicians is improving patient care.
- Advocacy groups are raising awareness about the condition.
- Increased funding for research is leading to new discoveries.
Living with Pachydermoperiostosis
Living with PDP can be challenging, but many people find ways to manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives. Here are some tips for living with the condition.
- Joining a support group can provide emotional support and practical advice.
- Educating family and friends about PDP can help them understand your needs.
- Keeping a symptom diary can help track changes and identify triggers.
- Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are essential.
- Staying active can help maintain joint function and overall health.
- Practicing good skin care can reduce discomfort from thickened skin.
- Stress management techniques, such as meditation, can improve well-being.
- Seeking professional counseling can help with emotional challenges.
- Advocating for yourself in medical settings ensures you get the care you need.
- Staying informed about new research and treatments can empower you to make informed decisions about your health.
Final Thoughts on Pachydermoperiostosis
Pachydermoperiostosis, a rare genetic disorder, affects the skin and bones, leading to thickened skin and clubbing of fingers and toes. Understanding this condition helps in recognizing its symptoms early and seeking appropriate medical care. Treatments focus on managing symptoms, improving quality of life, and may include medications, physical therapy, and sometimes surgery.
Raising awareness about pachydermoperiostosis is crucial for better diagnosis and support for those affected. Sharing knowledge can lead to more research and improved treatments. If you or someone you know shows signs of this condition, consulting a healthcare professional is essential.
Remember, while pachydermoperiostosis is rare, support and resources are available. Stay informed, spread awareness, and contribute to a better understanding of this unique condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
