Ever heard of the Osborn Wave? This intriguing phenomenon, also known as the J wave, appears on an electrocardiogram (ECG) and can be a sign of hypothermia or other medical conditions. Named after Dr. John Osborn, who first described it in 1953, this wave has puzzled and fascinated cardiologists for decades. But what exactly is an Osborn Wave? It's a positive deflection at the J point, where the QRS complex meets the ST segment on an ECG. Understanding this wave can be crucial for diagnosing certain heart conditions. Ready to dive into 50 facts about the Osborn Wave? Let's get started!
Key Takeaways:
- The Osborn Wave is a unique feature on an ECG that can indicate severe hypothermia and other serious medical conditions. It looks like a camel hump and requires careful diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
- Recognizing Osborn Waves on an ECG can help doctors identify and treat conditions like hypothermia, hypercalcemia, and brain injury. It's like finding a hidden clue to solve a medical mystery!
What is the Osborn Wave?
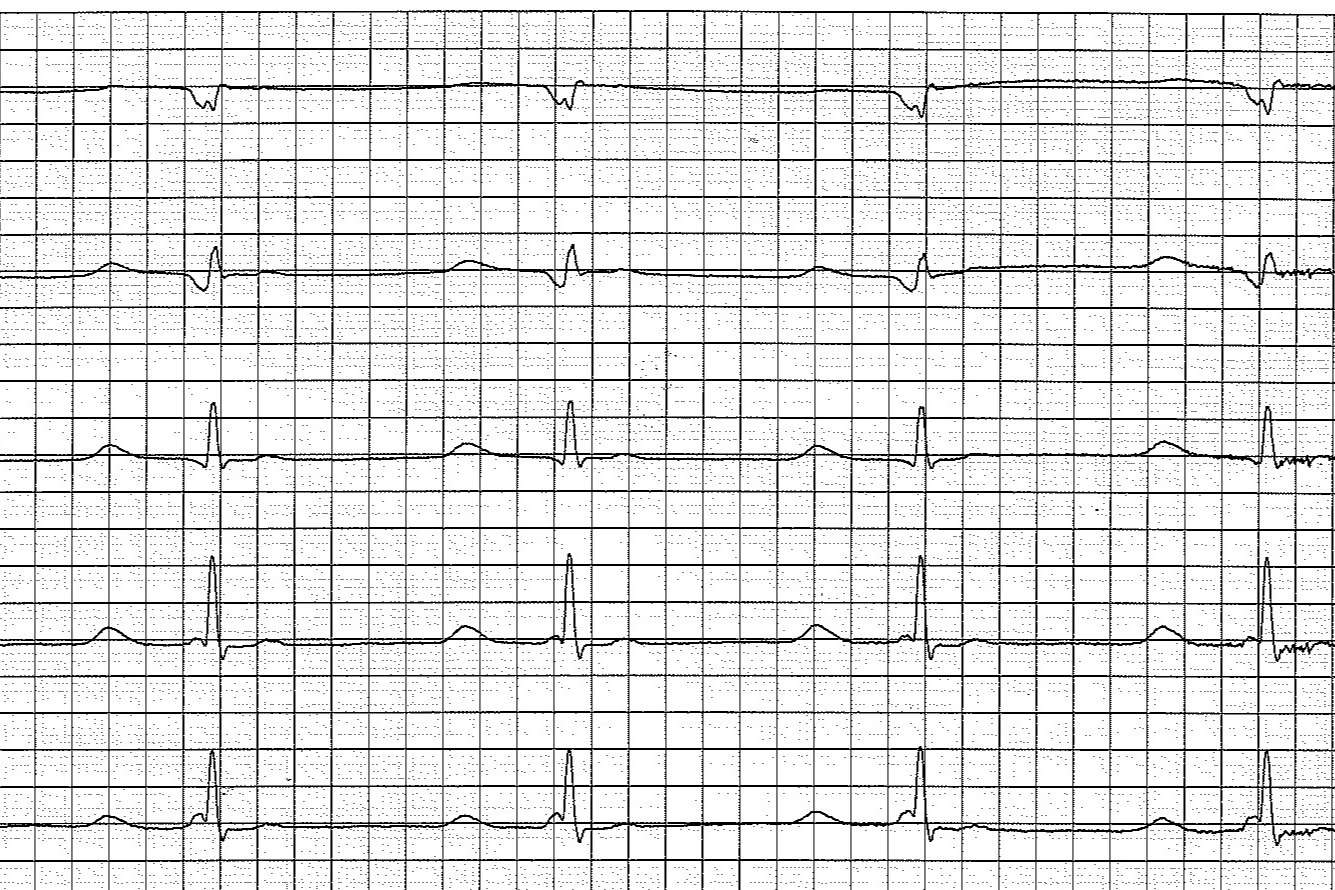
The Osborn Wave, also known as the J wave, is a distinctive feature seen on an electrocardiogram (ECG). It is often associated with hypothermia but can appear in other conditions too. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this intriguing phenomenon.
- The Osborn Wave was first described by Dr. John J. Osborn in 1953.
- It appears as a positive deflection at the junction between the QRS complex and the ST segment on an ECG.
- Hypothermia is the most common cause of Osborn Waves.
- The wave can also be seen in cases of hypercalcemia.
- It is sometimes referred to as the "camel-hump sign" due to its shape.
- The presence of Osborn Waves can indicate a body temperature below 32°C (89.6°F).
- These waves are more prominent in the precordial leads (V1-V6) of an ECG.
- The amplitude of the Osborn Wave increases as the body temperature decreases.
- They can also be seen in patients with brain injury or subarachnoid hemorrhage.
- The wave is named after Dr. John J. Osborn, who was a cardiologist.
Clinical Significance of Osborn Waves
Understanding the clinical significance of Osborn Waves can help in diagnosing and managing various medical conditions. Here are some key points to consider.
- Osborn Waves are often a sign of severe hypothermia.
- They can help differentiate between hypothermia and other conditions causing similar ECG changes.
- The presence of Osborn Waves can guide the treatment of hypothermia.
- They can be an early warning sign of life-threatening conditions.
- Osborn Waves can also be seen in patients with sepsis.
- They are sometimes mistaken for other ECG abnormalities, such as ST elevation.
- Recognizing Osborn Waves can prevent misdiagnosis and inappropriate treatment.
- They can indicate the need for immediate medical intervention.
- Osborn Waves can be a sign of underlying metabolic disturbances.
- They are often seen in patients with a history of alcohol abuse.
Conditions Associated with Osborn Waves
Osborn Waves are not exclusive to hypothermia. They can appear in various other medical conditions. Here are some examples.
- Hypercalcemia can cause Osborn Waves.
- They can be seen in patients with brain injury or subarachnoid hemorrhage.
- Osborn Waves can appear in cases of severe hypokalemia.
- They are sometimes seen in patients with myocardial ischemia.
- Osborn Waves can be present in patients with Brugada syndrome.
- They can appear in cases of severe acidosis.
- Osborn Waves can be seen in patients with hypomagnesemia.
- They can be present in cases of severe hypophosphatemia.
- Osborn Waves can appear in patients with hypothyroidism.
- They can be seen in cases of severe dehydration.
Diagnosing Osborn Waves
Diagnosing Osborn Waves involves careful analysis of the ECG and consideration of the patient's clinical condition. Here are some important points to keep in mind.
- Osborn Waves are best seen in the precordial leads (V1-V6) of an ECG.
- They appear as a positive deflection at the junction between the QRS complex and the ST segment.
- The amplitude of the Osborn Wave increases as the body temperature decreases.
- They can be mistaken for other ECG abnormalities, such as ST elevation.
- Recognizing Osborn Waves requires a high degree of clinical suspicion.
- The presence of Osborn Waves should prompt a search for underlying causes.
- They can be confirmed by repeating the ECG after warming the patient.
- Osborn Waves can be transient and may disappear after treatment of the underlying condition.
- They can be seen in both adults and children.
- The presence of Osborn Waves should be documented in the patient's medical record.
Treatment and Management of Conditions with Osborn Waves
Managing conditions associated with Osborn Waves involves addressing the underlying cause and providing supportive care. Here are some key points to consider.
- Hypothermia should be treated with active rewarming techniques.
- Hypercalcemia can be managed with intravenous fluids and medications to lower calcium levels.
- Brain injury or subarachnoid hemorrhage requires prompt neurosurgical intervention.
- Severe hypokalemia should be treated with potassium replacement therapy.
- Myocardial ischemia requires urgent cardiac care and possibly revascularization.
- Brugada syndrome may require an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD).
- Severe acidosis should be corrected with intravenous bicarbonate.
- Hypomagnesemia can be treated with magnesium replacement therapy.
- Severe hypophosphatemia requires phosphate replacement.
- Hypothyroidism should be managed with thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
Final Thoughts on Osborn Wave
Osborn waves, also known as J waves, are fascinating ECG findings often linked to hypothermia. These waves can also appear in cases of hypercalcemia, brain injury, or cardiac arrest. Recognizing them is crucial for healthcare professionals since they can indicate serious underlying conditions.
Understanding the mechanisms behind Osborn waves helps in diagnosing and managing patients effectively. They’re not just limited to hypothermia but can be seen in various clinical scenarios. This makes them a valuable tool in emergency medicine and cardiology.
So, next time you see a peculiar wave on an ECG, think about Osborn waves. They might just provide the clue needed for a timely and accurate diagnosis. Stay curious, keep learning, and always look deeper into those ECG readings.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
