Malignant melanoma is a serious type of skin cancer that begins in cells known as melanocytes. These cells produce melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Melanoma can develop anywhere on the skin, but it often appears on areas exposed to the sun, such as the back, legs, arms, and face. Unlike other skin cancers, melanoma can spread to other parts of the body if not caught early. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment. Knowing the signs, such as changes in moles or new growths, can make a significant difference. Here are 50 facts to help you understand malignant melanoma better.
Key Takeaways:
- Malignant melanoma is a dangerous form of skin cancer that can develop anywhere on the skin, not just in sun-exposed areas. Early detection and prevention are crucial for saving lives.
- Understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options for malignant melanoma can help in early detection and improve survival rates. Prevention strategies like sunscreen and regular skin checks are essential for staying healthy.
What is Malignant Melanoma?
Malignant melanoma is a type of skin cancer that begins in melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. Understanding this disease is crucial for early detection and treatment.
- Malignant melanoma is the most dangerous form of skin cancer.
- It accounts for only about 1% of skin cancers but causes the majority of skin cancer deaths.
- Melanoma can develop anywhere on the skin, including areas not exposed to the sun.
- The most common sites for melanoma in men are the chest and back.
- In women, melanoma often appears on the legs.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing malignant melanoma. Knowing these can help in taking preventive measures.
- Excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds is a major risk factor.
- Having a fair complexion increases the risk of melanoma.
- A history of sunburns, especially blistering sunburns, can elevate the risk.
- Family history of melanoma also plays a significant role.
- Having many moles or unusual moles can be a warning sign.
Symptoms and Signs
Recognizing the symptoms of malignant melanoma early can lead to more effective treatment. Here are some common signs to watch for.
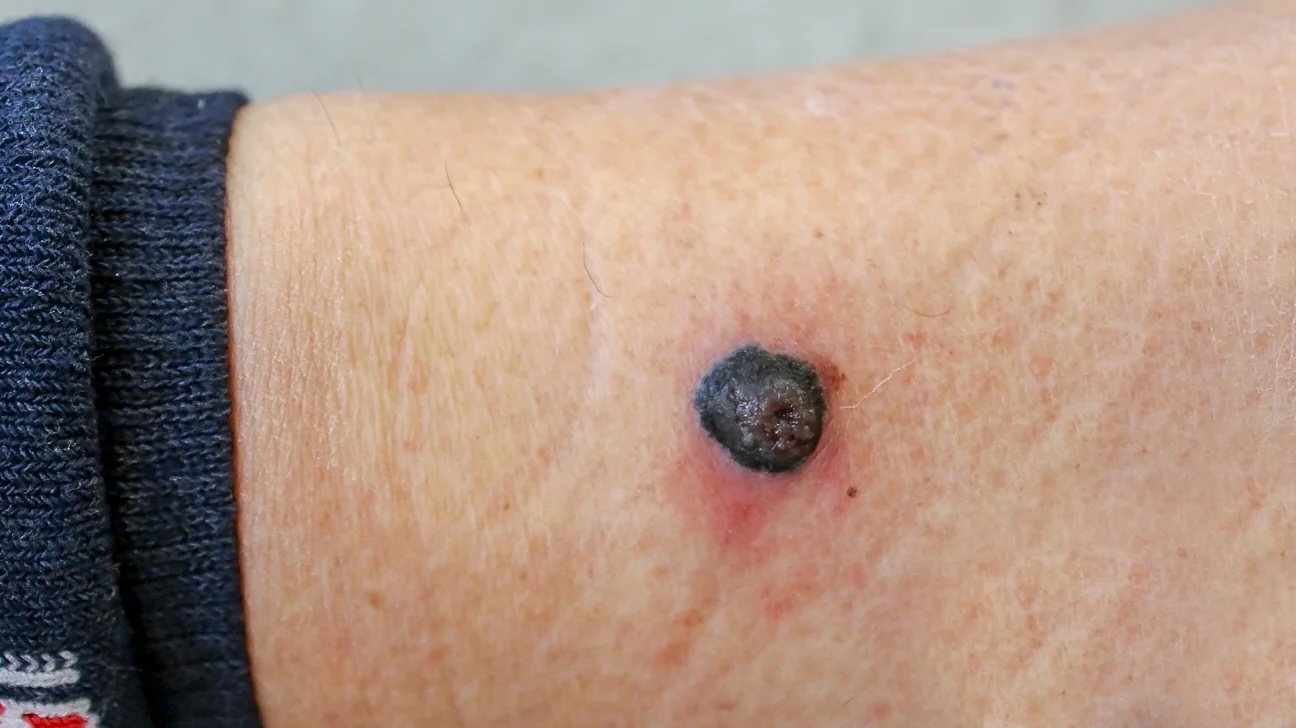
- A change in an existing mole is a common symptom.
- The appearance of a new, unusual-looking growth on the skin.
- Melanomas often have irregular borders.
- They can be multi-colored, including shades of brown, black, red, white, or blue.
- Melanomas are usually larger than 6 millimeters in diameter.
Diagnosis and Staging
Diagnosing malignant melanoma involves several steps and tests. Staging helps determine the extent of the cancer.
- A skin biopsy is the primary method for diagnosing melanoma.
- The Breslow thickness measures how deep the melanoma has penetrated the skin.
- Sentinel lymph node biopsy can determine if the cancer has spread.
- Imaging tests like CT scans and MRIs may be used for staging.
- Staging ranges from Stage 0 (in situ) to Stage IV (metastatic).
Treatment Options
Treatment for malignant melanoma varies depending on the stage and location of the cancer. Here are some common treatments.
- Surgical removal of the melanoma is often the first step.
- Immunotherapy uses the body's immune system to fight cancer.
- Targeted therapy focuses on specific genes or proteins that contribute to cancer growth.
- Radiation therapy may be used to treat melanoma that has spread.
- Chemotherapy is less commonly used but can be effective in some cases.
Prevention and Early Detection
Preventing malignant melanoma and detecting it early can save lives. Here are some tips and strategies.
- Regularly using sunscreen with a high SPF can reduce the risk.
- Wearing protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses helps shield skin from UV rays.
- Avoiding tanning beds is crucial for prevention.
- Performing regular self-examinations to check for new or changing moles.
- Seeing a dermatologist for annual skin checks is recommended.
Statistics and Survival Rates
Understanding the statistics and survival rates can provide a clearer picture of the impact of malignant melanoma.
- Approximately 100,000 new cases of melanoma are diagnosed in the U.S. each year.
- The five-year survival rate for early-stage melanoma is about 99%.
- For regional melanoma, the five-year survival rate drops to 65%.
- Advanced melanoma with distant metastasis has a five-year survival rate of 25%.
- Survival rates have improved significantly with new treatments.
Research and Advances
Ongoing research and advances in treatment are continually improving outcomes for those with malignant melanoma.
- Researchers are exploring new immunotherapy drugs.
- Advances in genetic testing help identify individuals at higher risk.
- Combination therapies are showing promise in clinical trials.
- Artificial intelligence is being used to improve early detection.
- Personalized medicine is becoming more common in melanoma treatment.
Myths and Misconceptions
There are many myths and misconceptions about malignant melanoma. Clearing these up can help in better understanding and prevention.
- Myth: Only fair-skinned people get melanoma. Fact: Anyone can get melanoma, regardless of skin color.
- Myth: Melanoma only occurs in older adults. Fact: It can affect people of all ages.
- Myth: A tan protects against melanoma. Fact: Tanning increases the risk of skin cancer.
- Myth: Melanoma is always caused by sun exposure. Fact: It can develop in areas not exposed to the sun.
- Myth: Melanoma is always fatal. Fact: Early detection and treatment can lead to high survival rates.
Living with Malignant Melanoma
Living with malignant melanoma involves managing the disease and maintaining a good quality of life. Here are some tips for those affected.
- Regular follow-up appointments are crucial for monitoring health.
- Support groups can provide emotional and practical support.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can improve overall well-being.
- Staying informed about new treatments and research is important.
- Advocating for skin cancer awareness can help others.
Staying Informed About Malignant Melanoma
Understanding malignant melanoma is crucial for early detection and treatment. This aggressive skin cancer can develop from existing moles or appear as new spots on the skin. Regular self-examinations and dermatologist visits can help catch it early. Risk factors include excessive sun exposure, fair skin, and a family history of skin cancer. Protecting your skin with sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding tanning beds can reduce your risk.
Symptoms to watch for include changes in size, shape, or color of moles, as well as new growths. If you notice anything unusual, consult a healthcare professional immediately. Treatments range from surgical removal to advanced therapies like immunotherapy and targeted drugs.
Staying informed and proactive can make a significant difference in outcomes. Share this knowledge with friends and family to help spread awareness and encourage preventive measures.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
