Immotile cilia might sound like a complex term, but these tiny, hair-like structures play a crucial role in our bodies. Unlike their motile counterparts, which move fluids and particles, immotile cilia act as sensory antennas. Found on nearly every cell, they help detect environmental signals, aiding in processes like cell growth and development. Did you know that defects in these cilia can lead to serious health issues, including respiratory problems and kidney disease? Understanding these microscopic wonders can shed light on many biological mysteries. Ready to dive into 50 fascinating facts about immotile cilia? Let's get started!
Key Takeaways:
- Immotile cilia, also known as primary cilia, are tiny structures on cells that don't move but play a big role in helping our bodies sense and respond to the environment, and defects in them can lead to serious diseases.
- Understanding immotile cilia's structure and functions is crucial for finding treatments for diseases like kidney problems, retinal degeneration, and obesity, and ongoing research is bringing hope for new therapies in the future.
What Are Immotile Cilia?
Immotile cilia are microscopic hair-like structures found on the surface of certain cells. Unlike their motile counterparts, these cilia do not move. They play crucial roles in various biological processes.
- Immotile cilia are also known as primary cilia.
- They are found on nearly every cell in the human body.
- These cilia act as sensory organelles.
- They help cells detect environmental signals.
- Primary cilia are essential for cell signaling pathways.
- They are involved in the Hedgehog signaling pathway.
- Defects in immotile cilia can lead to various diseases.
- One such disease is polycystic kidney disease.
- Another is Bardet-Biedl syndrome.
- Immotile cilia are crucial for embryonic development.
Structure of Immotile Cilia
Understanding the structure of immotile cilia helps in grasping their function. These cilia have a unique architecture that sets them apart from motile cilia.
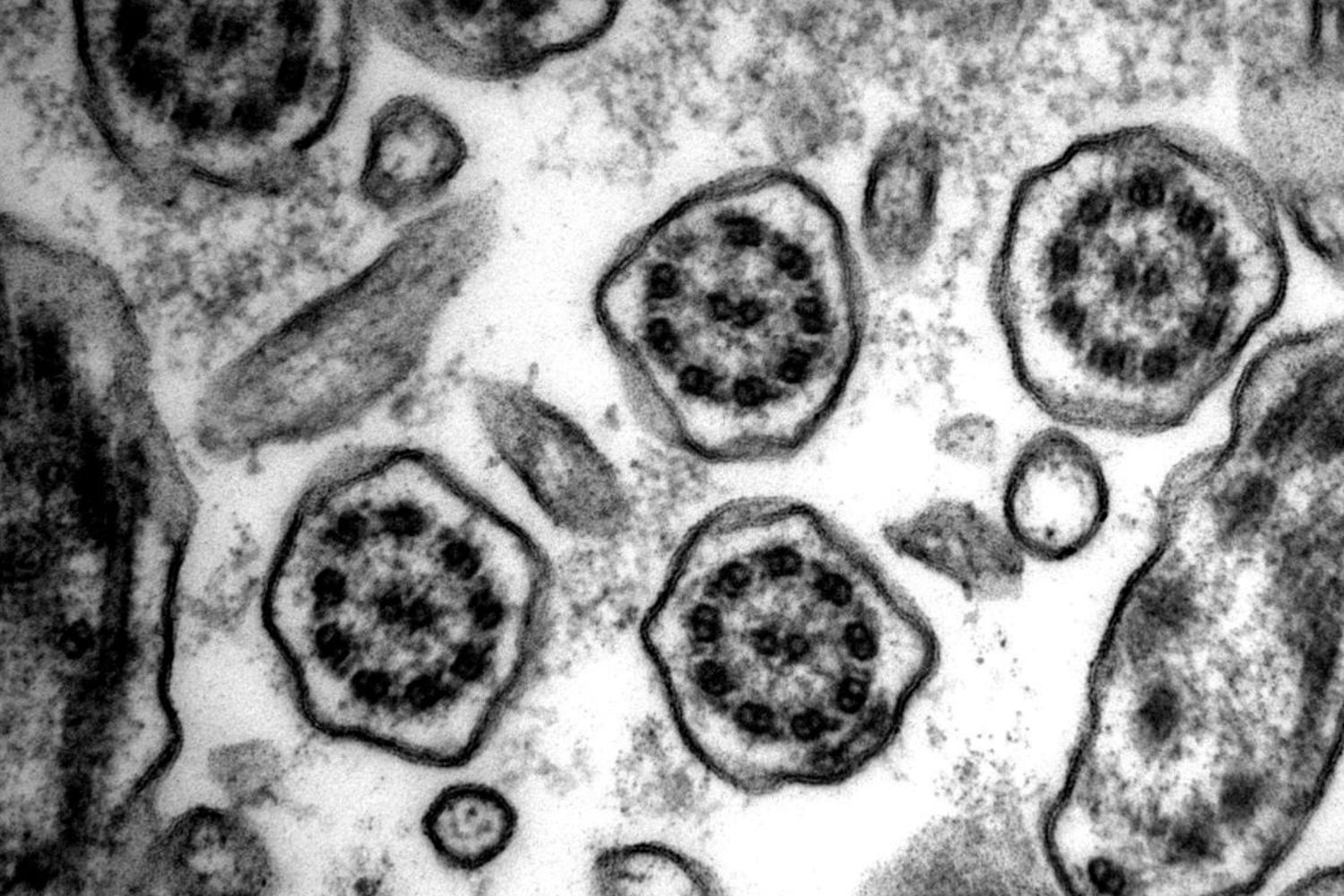
- Immotile cilia have a "9+0" microtubule arrangement.
- This means they have nine pairs of microtubules around the edge.
- Unlike motile cilia, they lack a central pair of microtubules.
- The absence of the central pair makes them immotile.
- They are anchored to the cell by a basal body.
- The basal body is derived from the mother centriole.
- The ciliary membrane covers the entire structure.
- This membrane is an extension of the cell membrane.
- The ciliary axoneme is the core structure.
- Axonemal dyneins are absent in immotile cilia.
Functions of Immotile Cilia
Immotile cilia may not move, but they are far from useless. They perform several vital functions in the body.
- They act as cellular antennas.
- These cilia detect mechanical and chemical signals.
- They play a role in cell differentiation.
- Immotile cilia are involved in tissue homeostasis.
- They help in the regulation of cell growth.
- These cilia are crucial for the functioning of the kidneys.
- They help in the formation of the left-right body axis.
- Immotile cilia are involved in brain development.
- They play a role in the function of the retina.
- These cilia are essential for the sense of smell.
Diseases Related to Immotile Cilia
When immotile cilia don't function properly, it can lead to a range of health issues. These cilia are vital for normal bodily functions, and their malfunction can be serious.
- Polycystic kidney disease is linked to defective immotile cilia.
- Bardet-Biedl syndrome involves mutations affecting these cilia.
- Joubert syndrome is another related condition.
- Meckel-Gruber syndrome is also associated with ciliary defects.
- Nephronophthisis affects kidney function due to ciliary issues.
- Retinal degeneration can result from defective cilia.
- Some forms of obesity are linked to ciliary dysfunction.
- Certain types of diabetes are associated with these cilia.
- Ciliopathies are a group of disorders caused by ciliary defects.
- Research is ongoing to find treatments for these conditions.
Research and Future Directions
Scientists are continually studying immotile cilia to understand their roles better. Advances in this field could lead to new treatments for related diseases.
- Researchers use advanced imaging techniques to study cilia.
- Genetic studies help identify mutations affecting cilia.
- Animal models are used to study ciliary functions.
- Stem cell research is providing new insights.
- Scientists are exploring gene therapy for ciliary disorders.
- Drug development is focused on targeting ciliary pathways.
- Understanding cilia can help in regenerative medicine.
- Research on cilia is shedding light on cancer mechanisms.
- Collaboration between disciplines is advancing ciliary research.
- Future studies may unlock new therapeutic strategies.
Final Thoughts on Immotile Cilia
Immotile cilia play a crucial role in our bodies, even though they don't move. These tiny structures are essential for sensing environmental signals and maintaining cellular health. When they malfunction, it can lead to serious health issues like Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia (PCD) and other genetic disorders. Understanding these facts helps us appreciate the complexity and importance of cilia in our overall well-being.
Research continues to uncover more about these fascinating structures, offering hope for better treatments and therapies in the future. Staying informed about immotile cilia can empower you to make better health decisions and understand the underlying causes of certain medical conditions. So, next time you hear about cilia, you'll know just how vital they are to keeping our bodies running smoothly.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
