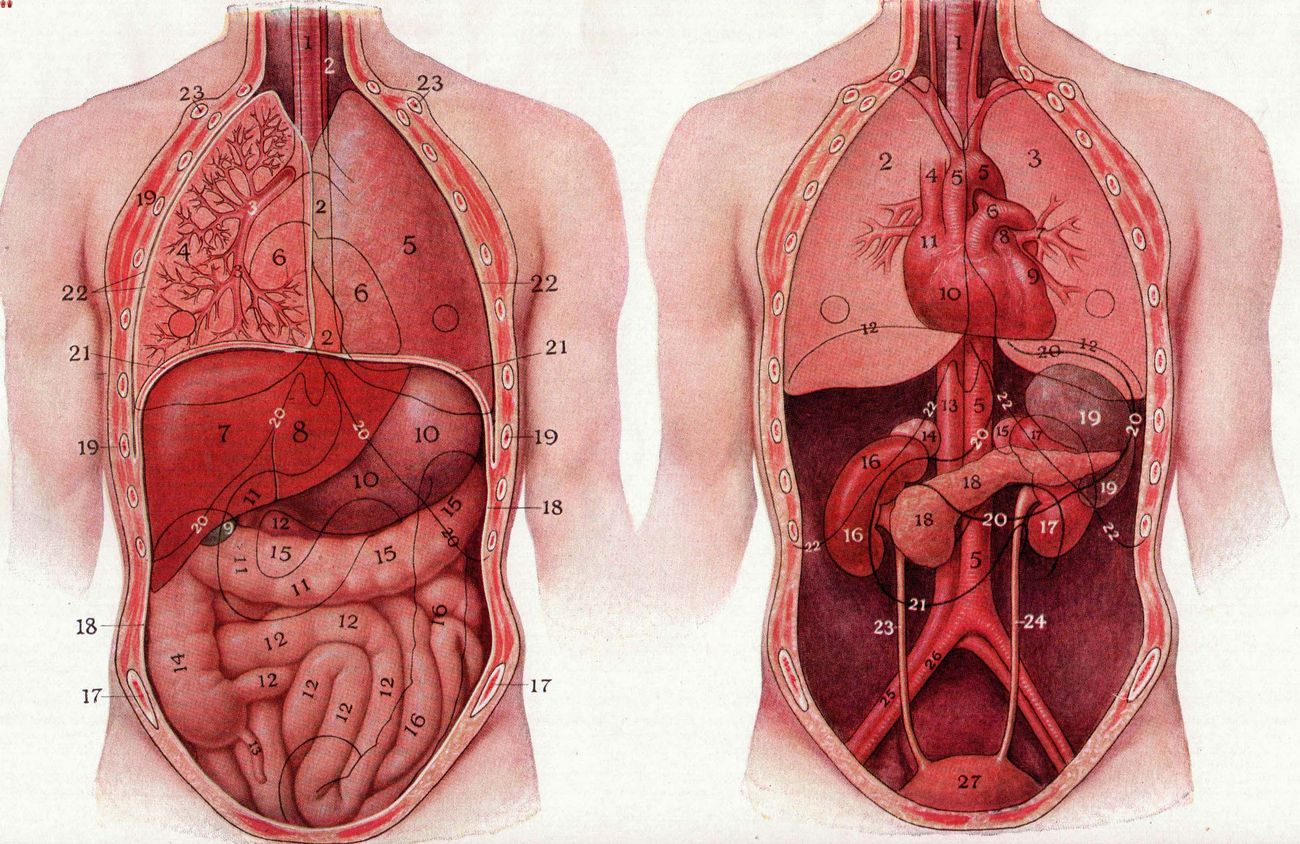
Heterotaxy is a rare condition where the internal organs are abnormally arranged across the left-right axis of the body. Did you know that this condition can affect the heart, liver, spleen, and intestines? In some cases, individuals may have organs on the opposite side of their body or even have duplicated or missing organs. Understanding heterotaxy is crucial because it often leads to complex congenital heart defects and other serious health issues. This blog post will provide 50 intriguing facts about heterotaxy, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and treatments. Whether you are a student, a parent, or just curious, these facts will help you grasp the complexities of this condition. Let's dive in and learn more about the fascinating world of heterotaxy!
Key Takeaways:
- Heterotaxy is a rare condition where organs are arranged differently, affecting 1 in 10,000 births. It can cause heart defects, breathing problems, and digestive issues, requiring lifelong medical care and support.
- Genetic mutations and environmental factors can cause heterotaxy. Early diagnosis through imaging and genetic testing is crucial for managing symptoms and complications. Treatment often involves surgery and ongoing specialist care for better outcomes.
What is Heterotaxy?
Heterotaxy is a rare condition where internal organs are abnormally arranged across the left-right axis of the body. This can affect the heart, lungs, liver, spleen, and intestines, leading to various health complications. Here are some fascinating facts about heterotaxy.
- Heterotaxy comes from Greek words meaning "different arrangement."
- It affects approximately 1 in 10,000 live births.
- The condition can be diagnosed through imaging techniques like ultrasound and MRI.
- Heterotaxy can lead to complex congenital heart defects.
- It often involves the heart being on the right side of the chest instead of the left.
- The spleen may be absent, multiple, or abnormally shaped.
- Some individuals with heterotaxy have polysplenia, meaning multiple small spleens.
- Asplenia, or absence of the spleen, increases infection risk.
- The liver may be centrally located instead of on the right side.
- The intestines can be malrotated, causing digestive issues.
Causes and Genetics of Heterotaxy
Understanding the causes and genetic factors behind heterotaxy can help in early diagnosis and management. Here are some key points about its origins.
- Heterotaxy is often linked to genetic mutations.
- Mutations in the ZIC3 gene are a common cause.
- It can be inherited in an X-linked or autosomal recessive manner.
- Environmental factors during pregnancy may also contribute.
- Some cases are sporadic with no known family history.
- Genetic counseling is recommended for affected families.
- Prenatal genetic testing can identify heterotaxy in some cases.
- Researchers are still uncovering new genes associated with the condition.
- Animal models, like mice, are used to study heterotaxy.
- Genetic research aims to develop targeted therapies.
Symptoms and Complications
Heterotaxy can present a wide range of symptoms and complications, varying from mild to severe. Here are some common issues faced by individuals with this condition.
- Cyanosis, or bluish skin, due to poor oxygenation.
- Difficulty breathing, especially in newborns.
- Feeding problems and poor weight gain.
- Frequent respiratory infections.
- Heart murmurs detected during physical exams.
- Abnormal heart rhythms or arrhythmias.
- Jaundice due to liver dysfunction.
- Bowel obstruction from intestinal malrotation.
- Increased risk of sepsis due to spleen abnormalities.
- Developmental delays in some children.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial for managing heterotaxy. Here are some important facts about how this condition is diagnosed and treated.
- Prenatal ultrasound can detect organ malpositions.
- Fetal echocardiography assesses heart defects before birth.
- Postnatal imaging includes chest X-rays and CT scans.
- Blood tests may reveal liver or spleen issues.
- Cardiac catheterization helps evaluate heart function.
- Surgery is often required to correct heart defects.
- Ladd's procedure is used to fix intestinal malrotation.
- Antibiotics are prescribed to prevent infections in asplenic patients.
- Lifelong follow-up with specialists is necessary.
- Multidisciplinary care teams improve patient outcomes.
Living with Heterotaxy
Living with heterotaxy involves ongoing medical care and lifestyle adjustments. Here are some insights into managing daily life with this condition.
- Regular check-ups with cardiologists and other specialists.
- Vaccinations are crucial for preventing infections.
- Parents should be educated on recognizing signs of infection.
- Nutritional support may be needed for growth and development.
- Physical therapy can help with motor skills.
- Emotional support is important for affected families.
- Support groups provide a sense of community.
- Advances in medical research offer hope for better treatments.
- Awareness campaigns help educate the public about heterotaxy.
- Advocacy efforts aim to improve healthcare policies for rare diseases.
Final Thoughts on Heterotaxy
Heterotaxy, a rare congenital condition, affects the arrangement of internal organs. This can lead to serious health issues, especially with the heart and digestive system. Understanding heterotaxy is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. While it presents many challenges, advancements in medical science offer hope for better management and outcomes. Families dealing with heterotaxy need support and resources to navigate this complex condition. Awareness and research are key to improving the lives of those affected. By sharing knowledge and experiences, we can foster a community that supports and uplifts each other. Remember, every bit of information helps in the fight against this rare condition. Stay informed, stay connected, and continue to advocate for those living with heterotaxy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
