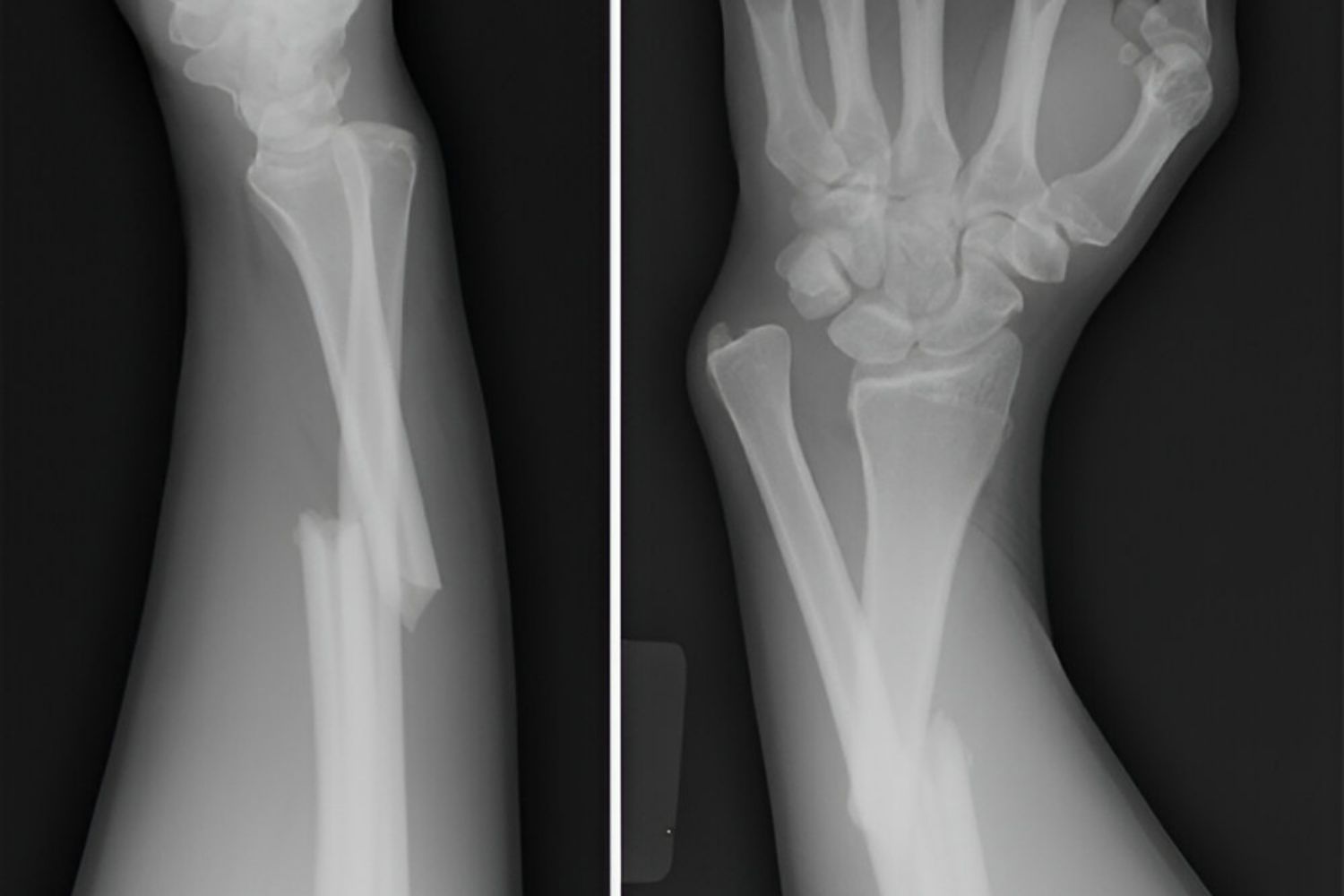
Ever heard of a Galeazzi fracture? This injury involves a break in the radius, one of the two bones in your forearm, along with a dislocation of the ulna at the wrist. Named after Italian surgeon Ricardo Galeazzi, who first described it in 1934, this fracture is often caused by a fall onto an outstretched hand. Common symptoms include pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the wrist. Treatment usually involves surgery to realign the bones and stabilize the joint. Understanding this fracture can help you recognize its symptoms and seek timely medical care. Ready to learn more? Let's dive into 50 intriguing facts about the Galeazzi fracture!
Key Takeaways:
- Galeazzi fractures involve the radius and ulna in the forearm, often caused by falls. Prompt diagnosis and surgical intervention are crucial for effective treatment and preventing long-term complications.
- Symptoms include severe pain, deformity, and limited motion. Treatment involves surgery, immobilization, and physical therapy. Complications can arise, requiring close monitoring and management.
What is a Galeazzi Fracture?
A Galeazzi fracture is a specific type of injury involving the radius and the ulna, two bones in the forearm. This fracture is often caused by a fall or direct trauma to the forearm. Understanding this injury can help in recognizing symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment.
- Named after Italian surgeon Ricardo Galeazzi, who first described it in 1934.
- Involves a fracture of the radius, typically in the distal third.
- Accompanied by a dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ).
- Commonly results from a fall on an outstretched hand.
- More frequent in children than adults.
- Often referred to as a "fracture of necessity" due to the need for surgical intervention.
- Accounts for about 7% of all forearm fractures in children.
- In adults, it represents around 3% of forearm fractures.
- Can be associated with nerve injuries, particularly the median nerve.
- Requires prompt diagnosis to prevent long-term complications.
Symptoms of a Galeazzi Fracture
Recognizing the symptoms of a Galeazzi fracture is crucial for timely treatment. The symptoms can vary but generally include pain and deformity in the forearm.
- Severe pain in the forearm.
- Visible deformity or abnormal angulation of the forearm.
- Swelling and bruising around the injury site.
- Limited range of motion in the wrist and forearm.
- Numbness or tingling in the hand or fingers.
- Difficulty in rotating the forearm.
- Tenderness over the distal radius.
- Instability in the wrist joint.
- Pain exacerbated by movement or pressure.
- Sometimes accompanied by a "clicking" sensation in the wrist.
Diagnosis of Galeazzi Fracture
Proper diagnosis involves clinical examination and imaging studies. Early and accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment.
- Physical examination to assess pain, swelling, and deformity.
- X-rays are the primary imaging tool used.
- X-rays should include both the forearm and wrist.
- CT scans may be used for complex cases.
- MRI can help assess soft tissue damage.
- Comparison with the uninjured forearm may be necessary.
- Assessment of nerve function to check for nerve damage.
- Evaluation of the distal radioulnar joint for dislocation.
- Checking for associated injuries like ligament tears.
- Sometimes requires multiple imaging angles for a complete view.
Treatment Options for Galeazzi Fracture
Treatment typically involves surgical intervention, especially in adults. The goal is to realign the bones and stabilize the joint.
- Closed reduction may be attempted in children.
- Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) is common in adults.
- ORIF involves using plates and screws to stabilize the radius.
- Immobilization with a cast or splint post-surgery.
- Physical therapy to restore function and strength.
- Pain management with medications.
- Regular follow-up visits to monitor healing.
- Possible use of external fixation in severe cases.
- Early mobilization to prevent stiffness.
- Monitoring for complications like infection or non-union.
Complications of Galeazzi Fracture
Despite treatment, complications can arise. Awareness of potential complications helps in early detection and management.
- Non-union or delayed union of the fracture.
- Malunion leading to deformity.
- Chronic pain in the forearm or wrist.
- Stiffness and limited range of motion.
- Persistent instability of the distal radioulnar joint.
- Nerve damage resulting in numbness or weakness.
- Infection at the surgical site.
- Reflex sympathetic dystrophy, a chronic pain condition.
- Post-traumatic arthritis in the wrist joint.
- Need for additional surgeries if complications occur.
Final Thoughts on Galeazzi Fractures
Galeazzi fractures, a specific type of forearm injury, involve a break in the radius and dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint. These injuries often result from falls or direct trauma. Recognizing the symptoms, such as pain, swelling, and deformity, is crucial for timely treatment. Diagnosis typically involves X-rays, and treatment usually requires surgical intervention to realign the bones and stabilize the joint. Post-surgery, physical therapy plays a vital role in regaining strength and mobility. Understanding the nature of Galeazzi fractures helps in better managing the injury and ensuring a smoother recovery process. Always consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Stay informed, stay safe, and take care of your bones!
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
