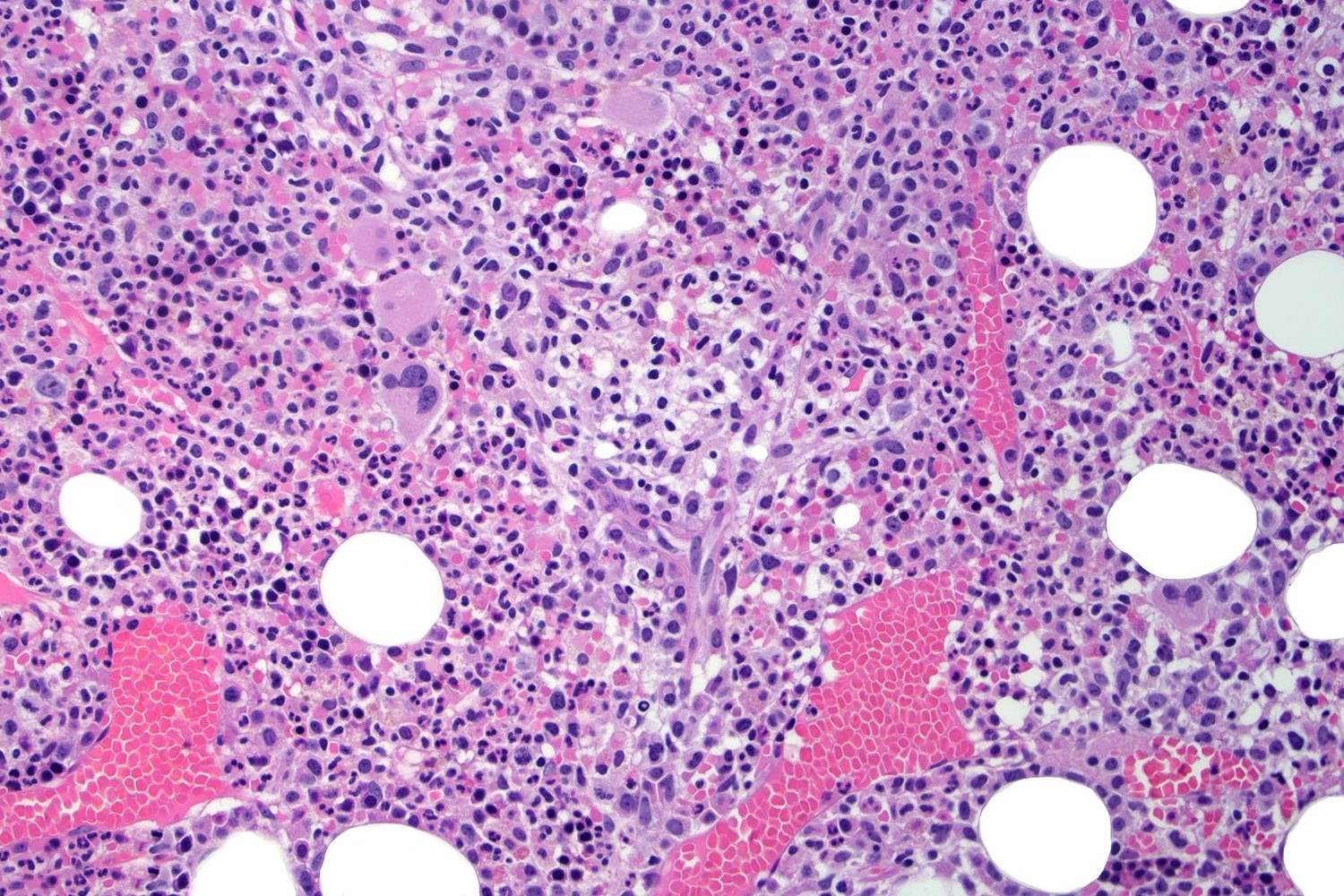
What is Angioimmunoblastic T-Cell Lymphoma (AITL)? AITL is a rare and aggressive type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that originates from T-cells, a crucial part of the immune system. It primarily affects older adults and is characterized by symptoms like fever, night sweats, skin rashes, and swollen lymph nodes. This condition can be tricky to diagnose due to its overlapping symptoms with other diseases. AITL involves the abnormal growth of T-cells, leading to immune system dysfunction. Treatment often includes chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or stem cell transplants, but the prognosis varies. Understanding AITL is vital for early detection and effective management. This post will guide you through 50 essential facts about AITL, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, treatments, and ongoing research. Whether you're a patient, caregiver, or just curious, these insights aim to provide clarity on this complex disease.
Key Takeaways:
- Angioimmunoblastic T-Cell Lymphoma is a rare cancer affecting the immune system, often diagnosed in older adults. It causes symptoms like fever, night sweats, and swollen lymph nodes, requiring specialized diagnosis and treatment.
- Treatment for Angioimmunoblastic T-Cell Lymphoma involves chemotherapy, stem cell transplants, and targeted therapies. Patients may face challenges such as treatment resistance, side effects, and infection risks, highlighting the need for comprehensive care and support.
What is Angioimmunoblastic T-Cell Lymphoma?
Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL) is a rare type of cancer that affects the immune system. It primarily involves T-cells, a type of white blood cell that plays a crucial role in the body's defense against infections. Understanding AITL can be complex, but here are some intriguing facts to help simplify it.
-
Rare Occurrence: AITL accounts for only about 1-2% of all non-Hodgkin lymphomas, making it a rare condition.
-
Age Factor: It typically affects older adults, with most cases diagnosed in individuals over 60 years old.
-
Gender Bias: Men are slightly more likely to develop AITL than women.
-
Symptoms: Common symptoms include fever, night sweats, weight loss, and skin rashes.
-
Lymph Node Swelling: One of the hallmark signs is the swelling of lymph nodes, often in the neck, armpits, or groin.
-
Immune System Involvement: AITL affects the immune system, leading to increased susceptibility to infections.
-
Autoimmune Features: Some patients may experience autoimmune symptoms, where the immune system attacks the body's own tissues.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus Connection: The Epstein-Barr virus is often found in the cancerous cells of AITL patients, suggesting a possible link.
-
Genetic Mutations: Certain genetic mutations, such as in the TET2, DNMT3A, and RHOA genes, are frequently observed in AITL cases.
-
Diagnosis: A biopsy of the affected lymph node is essential for diagnosing AITL.
How is Angioimmunoblastic T-Cell Lymphoma Diagnosed?
Diagnosing AITL involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. Here are some key facts about the diagnostic process.
-
Biopsy Importance: A lymph node biopsy is crucial for confirming the diagnosis and distinguishing AITL from other lymphomas.
-
Immunophenotyping: This test helps identify specific markers on the surface of T-cells, aiding in the diagnosis.
-
Blood Tests: Routine blood tests can reveal abnormalities such as anemia or elevated liver enzymes.
-
Imaging Studies: CT scans or PET scans are often used to assess the extent of the disease.
-
Bone Marrow Examination: Sometimes, a bone marrow biopsy is performed to check for cancer spread.
-
Flow Cytometry: This technique analyzes the characteristics of cells in a sample, providing valuable diagnostic information.
-
Molecular Testing: Genetic testing can identify mutations associated with AITL, helping to confirm the diagnosis.
-
Histopathology: Examining the tissue under a microscope reveals specific patterns characteristic of AITL.
-
Differential Diagnosis: AITL must be distinguished from other types of lymphomas and autoimmune disorders.
-
Consultation with Specialists: A team of specialists, including hematologists and oncologists, is often involved in the diagnostic process.
What are the Treatment Options for Angioimmunoblastic T-Cell Lymphoma?
Treatment for AITL can be challenging due to its aggressive nature and the involvement of the immune system. Here are some facts about the available treatment options.
-
Chemotherapy: Combination chemotherapy is the standard treatment for AITL, often using CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone).
-
Stem Cell Transplant: In some cases, a stem cell transplant may be considered, especially for younger patients.
-
Targeted Therapy: Newer treatments target specific molecules involved in the growth of cancer cells.
-
Immunotherapy: This approach aims to boost the body's immune response against cancer cells.
-
Radiation Therapy: Sometimes used to treat localized disease or relieve symptoms.
-
Clinical Trials: Participation in clinical trials may provide access to experimental treatments.
-
Supportive Care: Managing symptoms and side effects is an essential part of treatment.
-
Multidisciplinary Approach: Treatment often involves a team of healthcare professionals working together.
-
Response Monitoring: Regular follow-up and monitoring are crucial to assess the effectiveness of treatment.
-
Relapse Management: If the disease returns, alternative treatment strategies may be needed.
What is the Prognosis for Angioimmunoblastic T-Cell Lymphoma?
The prognosis for AITL varies depending on several factors, including the stage of the disease and the patient's overall health. Here are some insights into the prognosis.
-
Aggressive Nature: AITL is considered an aggressive form of lymphoma, often requiring intensive treatment.
-
Survival Rates: The five-year survival rate for AITL is approximately 30-40%.
-
Age Impact: Older age at diagnosis is associated with a poorer prognosis.
-
Response to Treatment: Patients who respond well to initial treatment tend to have a better outlook.
-
Genetic Factors: Certain genetic mutations may influence the prognosis.
-
Comorbidities: The presence of other health conditions can affect treatment outcomes.
-
Early Detection: Early diagnosis and treatment improve the chances of a favorable outcome.
-
Relapse Risk: AITL has a high risk of relapse, necessitating close monitoring.
-
Quality of Life: Managing symptoms and maintaining quality of life are important aspects of care.
-
Research Advances: Ongoing research is focused on improving treatment options and outcomes for AITL patients.
What are the Challenges in Managing Angioimmunoblastic T-Cell Lymphoma?
Managing AITL presents several challenges due to its complexity and the involvement of the immune system. Here are some of the key challenges faced by patients and healthcare providers.
-
Treatment Resistance: Some patients may not respond to standard treatments, requiring alternative approaches.
-
Side Effects: Chemotherapy and other treatments can cause significant side effects, impacting quality of life.
-
Infection Risk: AITL patients are at increased risk of infections due to immune system involvement.
-
Autoimmune Complications: Managing autoimmune symptoms can be challenging and may require additional treatments.
-
Psychosocial Impact: The emotional and psychological impact of a cancer diagnosis can be significant.
-
Access to Care: Access to specialized care and treatment options may be limited for some patients.
-
Financial Burden: The cost of treatment and supportive care can be a significant burden for patients and families.
-
Research Gaps: More research is needed to better understand AITL and develop effective treatments.
-
Patient Education: Educating patients and families about the disease and treatment options is crucial.
-
Support Networks: Building a strong support network can help patients cope with the challenges of AITL.
Final Thoughts on Angioimmunoblastic T-Cell Lymphoma
Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL) is a rare and complex type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for those affected. Symptoms like fever, weight loss, and skin rashes can often be mistaken for other illnesses, making early diagnosis challenging. Causes of AITL are not entirely clear, but factors like age, gender, and certain infections might play a role. Treatment usually involves chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or a combination of both. Research is ongoing to find more effective therapies and improve patient outcomes. Support from healthcare professionals and loved ones is vital for those battling this disease. Staying informed and proactive in managing health can make a significant difference. While AITL presents challenges, advancements in medical research offer hope for better treatments and improved quality of life for patients.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
