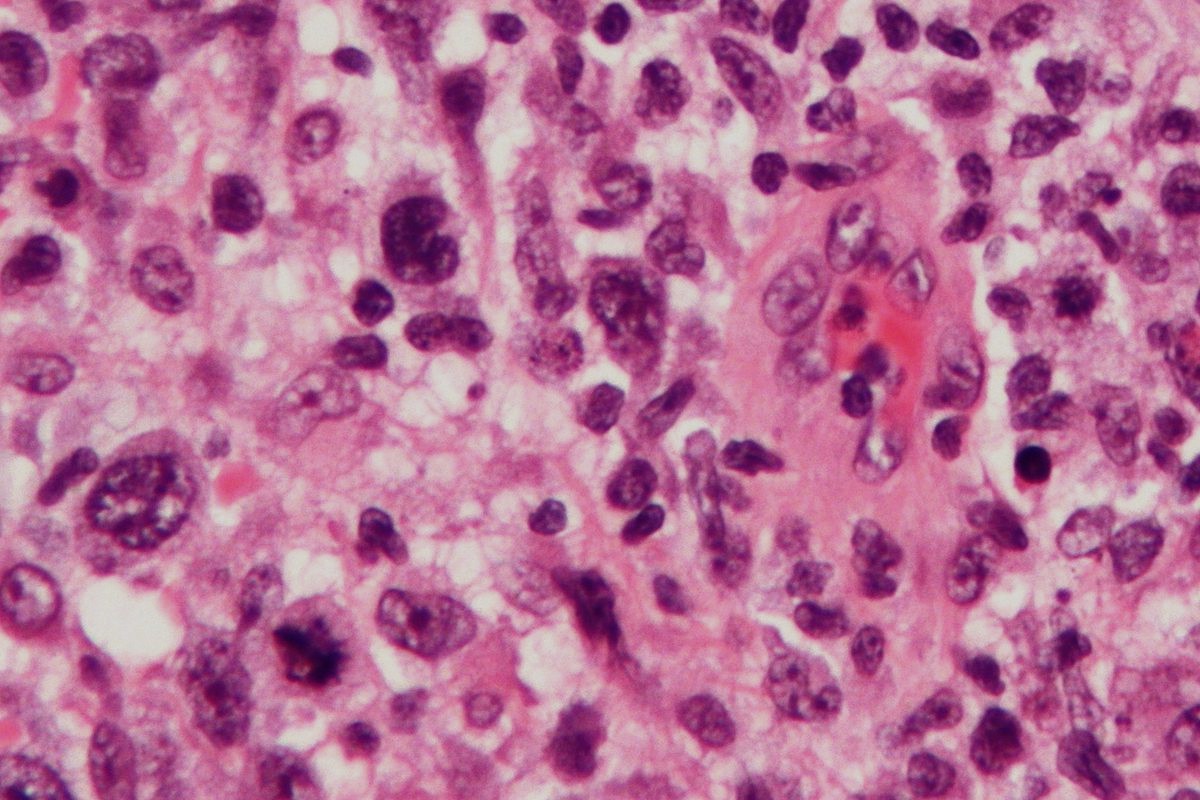
What is Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (ALCL)? Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma is a rare type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which is a cancer that affects the lymphatic system. This system is part of the body's immune system, helping to fight infections and diseases. ALCL is characterized by the presence of large, abnormal cells called anaplastic cells. These cells can grow and divide uncontrollably, leading to the formation of tumors. ALCL can occur in both children and adults, and it can affect lymph nodes as well as other parts of the body. There are different subtypes of ALCL, including systemic ALCL and primary cutaneous ALCL, each with its own unique features and treatment approaches. Understanding ALCL is crucial for early detection and effective management, offering hope for those affected by this challenging condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (ALCL) is a rare but aggressive cancer affecting the lymphatic system, with symptoms like swollen lymph nodes, skin lesions, and unexplained weight loss.
- Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for ALCL, which can be managed with chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and stem cell transplant. Supportive care and lifestyle changes can enhance quality of life for patients.
What is Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma?
Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (ALCL) is a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which is a cancer that affects the lymphatic system. This condition is rare but can be aggressive, requiring prompt medical attention. Understanding ALCL can help in recognizing symptoms and seeking timely treatment.
-
ALCL is a subtype of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which means it originates in the lymphatic system, a crucial part of the immune system.
-
It is characterized by large, abnormal lymphocytes, which are a type of white blood cell. These cells can grow uncontrollably, leading to tumors.
-
ALCL can occur in both children and adults, although it is more common in younger individuals.
-
There are two main types of ALCL: systemic ALCL, which affects the whole body, and primary cutaneous ALCL, which primarily affects the skin.
-
Systemic ALCL is further divided into ALK-positive and ALK-negative types, based on the presence of a specific protein called anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK).
Symptoms of Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma
Recognizing the symptoms of ALCL is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. Symptoms can vary depending on the type and location of the lymphoma.
-
Common symptoms include swollen lymph nodes, which may feel like lumps under the skin, often in the neck, armpit, or groin.
-
Fever, night sweats, and unexplained weight loss are systemic symptoms that can occur with ALCL.
-
Fatigue and loss of appetite are also common, as the body uses energy to fight the cancer.
-
Primary cutaneous ALCL may present as skin lesions or nodules, which can be itchy or painful.
-
Some patients may experience bone pain or a feeling of fullness in the abdomen, due to an enlarged spleen or liver.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of ALCL is not fully understood, certain factors may increase the risk of developing this lymphoma.
-
Genetic mutations, such as changes in the ALK gene, are known to play a role in the development of ALK-positive ALCL.
-
Exposure to certain chemicals or radiation may increase the risk, although this is not well-established.
-
Having a weakened immune system, such as from HIV/AIDS or immunosuppressive drugs, can increase susceptibility to ALCL.
-
Family history of lymphoma may also be a risk factor, suggesting a potential genetic predisposition.
-
Previous cancer treatments, like chemotherapy or radiation, might increase the risk of developing secondary cancers, including ALCL.
Diagnosis of Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Various tests and procedures are used to diagnose ALCL.
-
A biopsy is the primary method for diagnosing ALCL, where a sample of tissue is examined under a microscope.
-
Immunohistochemistry tests help identify specific proteins, such as ALK, on the surface of lymphoma cells.
-
Imaging tests like CT scans, PET scans, or MRIs are used to determine the extent of the disease and identify affected areas.
-
Blood tests can provide information about overall health, organ function, and the presence of cancer cells.
-
Bone marrow biopsy may be performed to check if the lymphoma has spread to the bone marrow.
Treatment Options for Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma
Treatment for ALCL depends on the type, stage, and overall health of the patient. Several options are available to manage this condition.
-
Chemotherapy is the most common treatment, using drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing.
-
Radiation therapy may be used to target specific areas, especially if the lymphoma is localized.
-
Targeted therapy involves drugs that specifically attack cancer cells, sparing normal cells, and is often used for ALK-positive ALCL.
-
Stem cell transplant may be considered, especially if the lymphoma returns after initial treatment.
-
Clinical trials offer access to new treatments, providing options for patients who may not respond to standard therapies.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Understanding the prognosis and survival rates can help patients and families prepare for the journey ahead.
-
The prognosis for ALCL varies, depending on factors like age, overall health, and response to treatment.
-
ALK-positive ALCL generally has a better prognosis compared to ALK-negative, due to more effective targeted therapies.
-
Early-stage ALCL has a higher survival rate, as it is more likely to respond well to treatment.
-
Ongoing research and new treatments are improving outcomes, offering hope for better survival rates in the future.
-
Supportive care and lifestyle changes can enhance quality of life, helping patients manage symptoms and side effects.
Living with Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma
Living with ALCL involves managing symptoms, treatment side effects, and emotional well-being. Support from healthcare providers, family, and friends is crucial.
-
Regular follow-up appointments are important to monitor health and detect any recurrence early.
-
Healthy lifestyle choices, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, can support overall well-being and recovery.
-
Emotional support from counseling or support groups can help patients and families cope with the challenges of living with cancer.
-
Managing stress through relaxation techniques, like meditation or yoga, can improve mental health and resilience.
-
Open communication with healthcare providers ensures that patients receive the best possible care and support.
Research and Advances in Treatment
Ongoing research is crucial for developing new treatments and improving outcomes for patients with ALCL.
-
Researchers are exploring new targeted therapies, aiming to improve effectiveness and reduce side effects.
-
Immunotherapy is a promising area of research, harnessing the body's immune system to fight cancer.
-
Genetic studies are helping to identify specific mutations, leading to more personalized treatment approaches.
-
Clinical trials are testing novel drugs and combinations, offering hope for more effective treatments.
-
Collaboration between researchers and healthcare providers is essential for translating discoveries into clinical practice.
Support and Resources for Patients and Families
Access to support and resources can make a significant difference for those affected by ALCL.
-
Patient advocacy groups provide information and support, connecting patients with others who have similar experiences.
-
Online communities offer a platform for sharing stories, advice, and encouragement.
-
Educational resources help patients understand their condition, treatment options, and what to expect during their journey.
-
Financial assistance programs can help with the cost of treatment, reducing the burden on families.
-
Healthcare teams can provide referrals to specialists, ensuring comprehensive care and support.
Raising Awareness and Funding for Research
Raising awareness and funding for ALCL research is vital for advancing treatment and improving outcomes.
-
Awareness campaigns educate the public about ALCL, promoting early detection and treatment.
-
Fundraising events support research efforts, providing resources for developing new treatments.
-
Partnerships with organizations and foundations can amplify efforts to raise awareness and funds.
-
Advocacy for increased research funding can lead to more breakthroughs and better treatments.
-
Community involvement and support are crucial, as they drive efforts to improve the lives of those affected by ALCL.
Final Thoughts on Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma
Understanding Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (ALCL) is crucial for anyone dealing with this condition. It's a rare type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that can affect both children and adults. Symptoms like swollen lymph nodes, fever, and weight loss can be alarming, but early diagnosis and treatment can make a significant difference. Treatments often include chemotherapy, radiation, or targeted therapies, depending on the specific type and stage of ALCL.
Staying informed about the latest research and treatment options is vital. Support from healthcare professionals, family, and friends can provide much-needed strength during this challenging time. Remember, each person's journey with ALCL is unique, and what works for one might not work for another. Keep asking questions, seeking support, and advocating for the best care possible. Knowledge and support are powerful allies in the fight against ALCL.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
