Tangier Disease is a rare genetic disorder that affects the body's ability to transport cholesterol. Named after Tangier Island, where it was first identified, this condition leads to extremely low levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, often called "good cholesterol." People with Tangier Disease may experience enlarged, orange-colored tonsils, an enlarged liver or spleen, and nerve problems. Symptoms can vary widely, making diagnosis tricky. This disease is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, meaning both parents must carry the defective gene. While there's no cure, understanding Tangier Disease can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Let's dive into 40 intriguing facts about this rare condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Tangier Disease is a rare genetic disorder causing low "good cholesterol," leading to heart and nerve issues. Treatment focuses on diet, exercise, and monitoring for potential complications.
- Ongoing research for Tangier Disease includes gene therapy, stem cell research, and new medications to improve cholesterol transport and develop effective treatments.
What is Tangier Disease?
Tangier Disease is a rare genetic disorder that affects the body's ability to transport cholesterol. Named after Tangier Island in Virginia, where the first cases were identified, this condition can lead to various health issues. Here are some fascinating facts about Tangier Disease.
-
Tangier Disease is caused by mutations in the ABCA1 gene, which plays a crucial role in the transport of cholesterol and phospholipids.
-
The disease is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, meaning both parents must carry the defective gene for a child to be affected.
-
People with Tangier Disease often have extremely low levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), commonly known as "good cholesterol."
-
The first case of Tangier Disease was identified in 1961 on Tangier Island, Virginia.
-
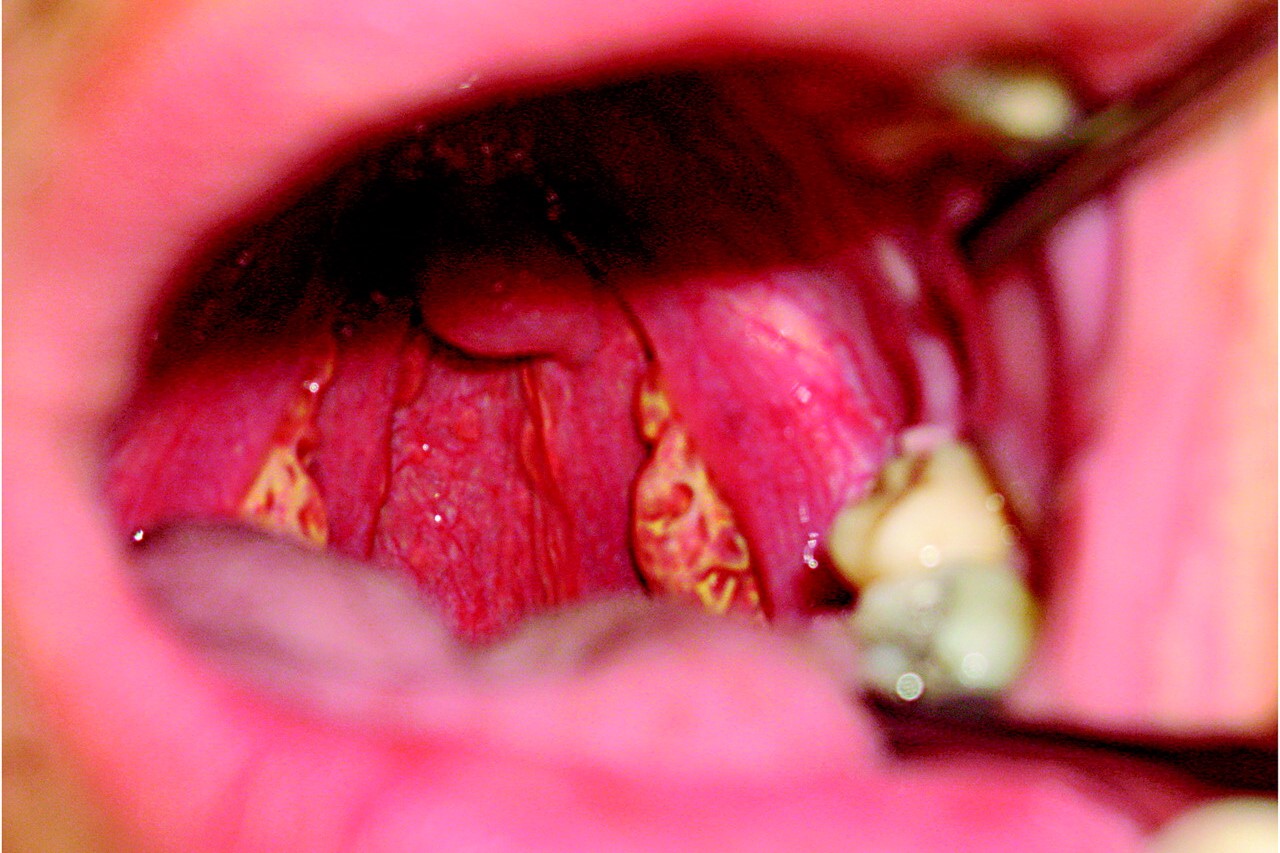
Orange-colored tonsils are a hallmark sign of Tangier Disease, caused by the accumulation of cholesterol esters.
-
The condition can lead to neuropathy, which is damage to the peripheral nerves, causing weakness and numbness.
-
Enlarged liver and spleen are common symptoms due to the buildup of cholesterol in these organs.
-
Tangier Disease can increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases because of the low levels of HDL cholesterol.
-
Corneal opacities, or clouding of the cornea, can occur in individuals with Tangier Disease, affecting vision.
-
The disease is diagnosed through blood tests that measure cholesterol levels and genetic testing to identify ABCA1 mutations.
How Does Tangier Disease Affect the Body?
Tangier Disease impacts various systems in the body, leading to a range of symptoms and complications. Understanding these effects can help in managing the condition better.
-
Cholesterol accumulation in tissues is a primary issue, leading to the formation of yellowish-orange deposits in the skin and mucous membranes.
-
The disease can cause intestinal lipid malabsorption, leading to digestive issues and nutrient deficiencies.
-
Atherosclerosis, or the buildup of fats in the arteries, is more likely due to low HDL levels, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
-
Peripheral neuropathy can result in muscle weakness, particularly in the hands and feet, making daily activities challenging.
-
Hepatomegaly, or an enlarged liver, can cause discomfort and affect liver function.
-
Splenomegaly, or an enlarged spleen, can lead to increased vulnerability to infections and other complications.
-
Lymphadenopathy, or swollen lymph nodes, is another symptom due to cholesterol buildup in the lymphatic system.
-
Gastrointestinal issues such as diarrhea and abdominal pain can occur due to lipid malabsorption.
-
Fatigue and weakness are common complaints among those with Tangier Disease, affecting overall quality of life.
-
Skin lesions and rashes may appear due to cholesterol deposits in the skin.
Treatment and Management of Tangier Disease
While there is no cure for Tangier Disease, various treatments and lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
Dietary modifications to reduce fat intake can help manage cholesterol levels and alleviate some symptoms.
-
Regular exercise is encouraged to improve cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
-
Medications such as statins may be prescribed to manage cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
-
Pain management strategies, including medications and physical therapy, can help alleviate neuropathy symptoms.
-
Regular monitoring of liver and spleen size is essential to manage potential complications.
-
Genetic counseling can provide valuable information for affected families and help in making informed decisions about family planning.
-
Support groups and counseling can offer emotional support and practical advice for managing the disease.
-
Routine eye exams are important to monitor and manage corneal opacities.
-
Vaccinations may be recommended to reduce the risk of infections due to splenomegaly.
-
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are crucial to monitor overall health and manage any emerging symptoms.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand Tangier Disease and develop more effective treatments. Here are some exciting developments in the field.
-
Gene therapy is being explored as a potential treatment to correct the defective ABCA1 gene.
-
Stem cell research offers hope for regenerating damaged tissues and improving symptoms.
-
New medications are being developed to increase HDL levels and improve cholesterol transport.
-
Clinical trials are ongoing to test the safety and efficacy of various treatments for Tangier Disease.
-
Biomarker studies aim to identify new indicators of disease progression and treatment response.
-
Patient registries are being established to collect data and improve understanding of the disease's natural history.
-
Collaborative research efforts are bringing together scientists and clinicians from around the world to tackle Tangier Disease.
-
Public awareness campaigns are helping to educate people about Tangier Disease and the importance of early diagnosis.
-
Funding initiatives are supporting research and development of new treatments for rare diseases like Tangier Disease.
-
Advancements in genetic testing are making it easier to diagnose Tangier Disease and identify carriers of the ABCA1 mutation.
Final Thoughts on Tangier Disease
Tangier Disease, a rare genetic disorder, impacts the body's ability to process cholesterol. This leads to extremely low levels of HDL, often called "good cholesterol." People with Tangier Disease may experience enlarged tonsils, orange-colored tonsils, and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. The condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, meaning both parents must carry the gene for a child to be affected. While there's no cure, managing symptoms and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help improve quality of life. Understanding Tangier Disease is crucial for early diagnosis and better management. If you or someone you know shows symptoms, consulting a healthcare professional is essential. Awareness and education about this rare condition can lead to better outcomes for those affected. Stay informed, stay healthy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
