Poxviridae diseases have intrigued scientists and historians alike for centuries. These viruses, responsible for illnesses like smallpox and cowpox, have shaped human history in profound ways. Did you know that smallpox was the first disease ever to be eradicated by a vaccine? This monumental achievement showcases the power of scientific collaboration. Poxviridae viruses are unique because they replicate in the cytoplasm of host cells, unlike most DNA viruses that replicate in the nucleus. These viruses can infect both humans and animals, making them a significant concern for public health. Understanding the history, biology, and impact of Poxviridae diseases can help us appreciate the strides made in medical science and prepare for future challenges.
Key Takeaways:
- Poxviridae, a family of large and contagious viruses, has caused significant historical impacts and shaped medical advancements, leading to the eradication of smallpox and ongoing research for future prevention and treatment.
- Understanding the types, symptoms, transmission, and prevention of poxviridae diseases is crucial for controlling outbreaks and developing effective treatments, including vaccines and antiviral drugs.
What is Poxviridae?
Poxviridae is a family of viruses known for causing diseases in humans and animals. These viruses are large, complex, and have a unique ability to replicate in the cytoplasm of host cells.
- Poxviridae viruses are among the largest viruses known, with some reaching up to 300 nanometers in size.
- They have a complex structure, including a double-stranded DNA genome.
- These viruses can infect both vertebrates and invertebrates.
- Smallpox, caused by the variola virus, is the most infamous disease from this family.
- Poxviridae viruses can survive outside a host for extended periods, making them highly contagious.
Types of Poxviridae Viruses
There are several types of Poxviridae viruses, each causing different diseases. Understanding these types helps in identifying and treating infections.
- Variola virus causes smallpox, a disease eradicated in 1980 through global vaccination efforts.
- Vaccinia virus is used in the smallpox vaccine and can cause mild infections.
- Monkeypox virus, similar to smallpox, primarily affects monkeys but can infect humans.
- Cowpox virus, found in cows, can also infect humans and other animals.
- Molluscum contagiosum virus causes skin lesions in humans, particularly in children.
Symptoms of Poxviridae Diseases
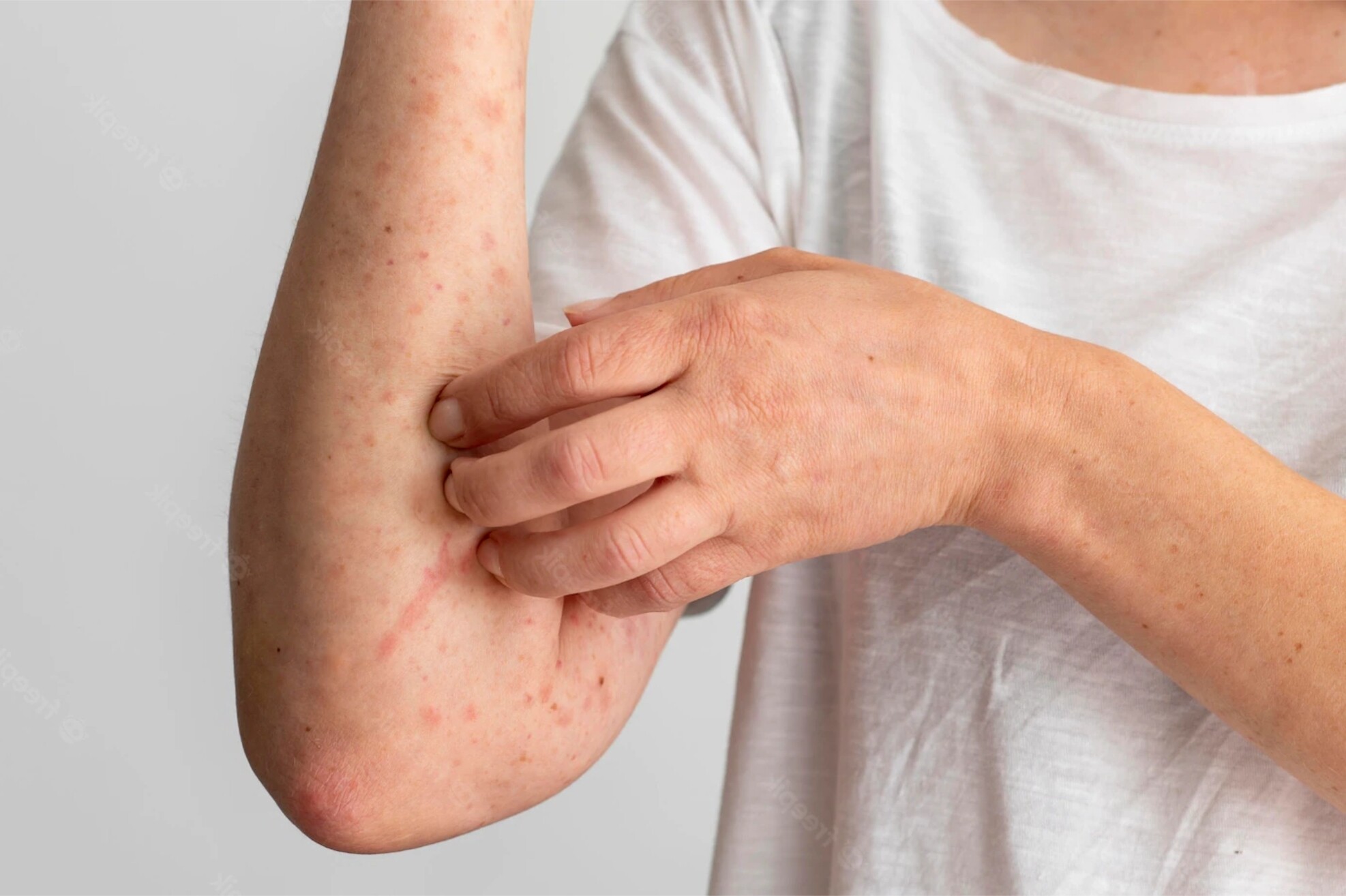
Symptoms vary depending on the specific virus but often include skin lesions and systemic effects. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment.
- Smallpox symptoms include high fever, fatigue, and a characteristic rash that turns into pus-filled sores.
- Monkeypox symptoms are similar to smallpox but also include swollen lymph nodes.
- Cowpox causes localized skin lesions, often on the hands or face.
- Molluscum contagiosum results in small, painless bumps on the skin.
- General symptoms of poxviridae infections can include fever, malaise, and swollen lymph nodes.
Transmission of Poxviridae Viruses
Understanding how these viruses spread can help in preventing outbreaks. Transmission methods vary among different viruses in the Poxviridae family.
- Smallpox spreads through respiratory droplets and direct contact with infected individuals.
- Monkeypox can be transmitted through contact with infected animals or humans.
- Cowpox is often contracted through direct contact with infected cows or contaminated objects.
- Molluscum contagiosum spreads through direct skin-to-skin contact or contaminated objects.
- Some poxviridae viruses can also be transmitted through insect bites.
Treatment and Prevention
While some poxviridae diseases have no specific treatment, others can be managed with antiviral medications and vaccines. Prevention is key to controlling these infections.
- Smallpox was eradicated through a global vaccination campaign using the vaccinia virus.
- Monkeypox can be treated with antiviral drugs like tecovirimat.
- Cowpox infections usually resolve on their own but can be treated with supportive care.
- Molluscum contagiosum can be treated with topical therapies or minor surgical procedures.
- Vaccination and good hygiene practices are essential in preventing the spread of poxviridae viruses.
Historical Impact of Poxviridae Diseases
Poxviridae diseases have had significant impacts on human history, shaping public health policies and medical advancements.
- Smallpox was responsible for countless deaths before its eradication, with mortality rates as high as 30%.
- The development of the smallpox vaccine by Edward Jenner in 1796 was a milestone in medical history.
- Smallpox vaccination campaigns in the 20th century led to the disease's eradication in 1980.
- Monkeypox outbreaks have increased in recent years, raising concerns about potential pandemics.
- The study of poxviridae viruses has contributed to advancements in virology and immunology.
Interesting Facts about Poxviridae
Here are some intriguing facts about poxviridae viruses that highlight their unique characteristics and historical significance.
- The word "pox" comes from the Old English word "pocc," meaning "pustule."
- Poxviridae viruses have a unique ability to replicate in the cytoplasm, unlike most DNA viruses.
- The smallpox vaccine was the first successful vaccine ever developed.
- Variola virus, the cause of smallpox, has no known animal reservoir, which helped in its eradication.
- Poxviridae viruses have been used in research to develop vaccines for other diseases.
Modern Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research on poxviridae viruses aims to improve treatments, develop new vaccines, and understand their biology better.
- Scientists are studying poxviridae viruses to develop vaccines for emerging infectious diseases.
- Research on antiviral drugs continues to improve treatments for poxviridae infections.
- Genetic studies of poxviridae viruses help in understanding their evolution and adaptation.
- Advances in biotechnology are enabling the development of more effective and safer vaccines.
- Ongoing surveillance and research are crucial in preventing future outbreaks of poxviridae diseases.
Final Thoughts on Poxviridae Diseases
Poxviridae diseases have shaped human history in profound ways. From smallpox, which claimed millions of lives before its eradication, to emerging threats like monkeypox, these viruses demand our attention. Understanding their transmission, symptoms, and prevention methods is crucial for public health. Vaccination remains the most effective tool against many of these diseases, highlighting the importance of continued research and global cooperation.
While smallpox is no longer a threat, vigilance is key to preventing outbreaks of other poxviruses. Public awareness and education can help mitigate risks and ensure swift responses to new cases. By staying informed and proactive, we can protect ourselves and future generations from the impact of Poxviridae diseases. Remember, knowledge is power in the fight against infectious diseases. Stay curious, stay safe, and keep learning.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
