What is a Posterior Circulation Infarct? It's a type of stroke that affects the back part of the brain, including areas like the brainstem, cerebellum, and occipital lobes. This condition can lead to symptoms such as dizziness, double vision, and difficulty with balance or coordination. Unlike more common strokes affecting the front of the brain, posterior circulation infarcts can be trickier to diagnose because their symptoms often mimic other conditions. Understanding this type of stroke is crucial because it requires different treatment approaches. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, and diabetes. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes. If you or someone you know experiences sudden dizziness or vision changes, it's vital to seek medical attention immediately. Recognizing the signs can make all the difference in recovery and quality of life.
Key Takeaways:
- Posterior Circulation Infarct (PCI) can affect anyone, not just older adults, and its symptoms can be subtle. Early diagnosis and lifestyle changes are crucial for prevention and effective management.
- PCI can impact vision, balance, and emotions, but support systems and rehabilitation play a vital role in recovery. Understanding the myths and realities of PCI is essential for better management.
Understanding Posterior Circulation Infarct
Posterior circulation infarct (PCI) involves a stroke in the back part of the brain, affecting areas supplied by the vertebrobasilar arteries. This condition can be tricky to diagnose due to its varied symptoms. Let's explore some fascinating facts about PCI.
-
Location Matters: PCI affects the brainstem, cerebellum, and occipital lobes, which are crucial for balance, vision, and coordination.
-
Silent Symptoms: Symptoms can be subtle, including dizziness, double vision, or difficulty speaking, making it harder to identify than other types of strokes.
-
Risk Factors: High blood pressure, smoking, and diabetes increase the risk of PCI, similar to other strokes.
-
Age Factor: While strokes are more common in older adults, PCI can occur at any age, even in young people.
-
Gender Differences: Men are slightly more prone to PCI than women, though the reasons are not entirely clear.
Causes and Diagnosis
Understanding what causes PCI and how it is diagnosed can help in managing this condition effectively.
-
Artery Blockage: Most PCIs occur due to a blockage in the vertebrobasilar arteries, cutting off blood supply to the brain.
-
Embolism: A blood clot traveling from another part of the body can also cause PCI.
-
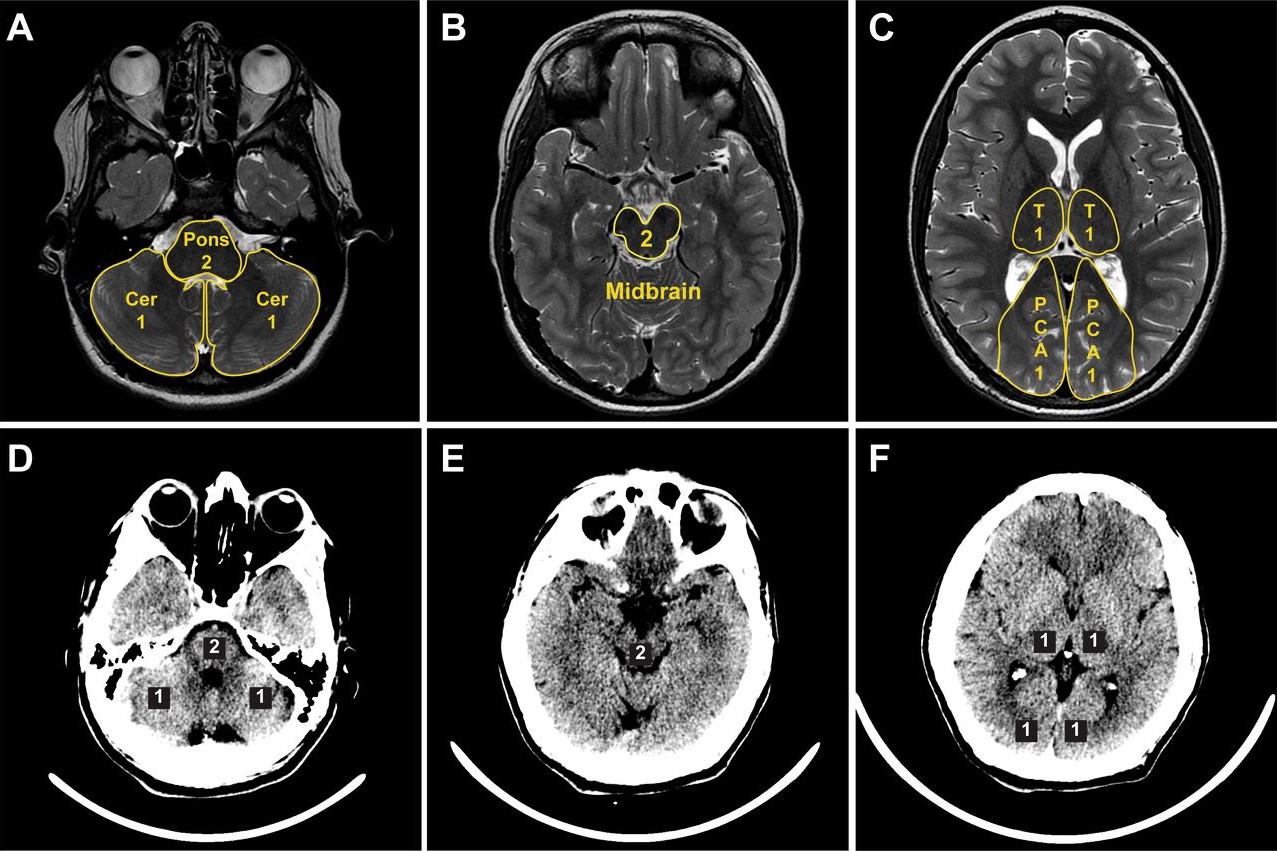
Imaging Techniques: MRI and CT scans are essential tools for diagnosing PCI, providing detailed images of the brain.
-
Misdiagnosis Risk: Due to its varied symptoms, PCI is sometimes mistaken for other conditions like vertigo or migraines.
-
Importance of Timely Diagnosis: Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and minimizing brain damage.
Treatment and Management
Treating PCI involves a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgery.
-
Thrombolytic Therapy: Medications that dissolve blood clots can be effective if administered quickly after symptoms begin.
-
Antiplatelet Drugs: Aspirin and other antiplatelet medications help prevent further clot formation.
-
Surgical Options: In some cases, surgery may be needed to remove a blockage or repair damaged arteries.
-
Rehabilitation: Physical and occupational therapy are vital for recovery, helping patients regain lost skills and independence.
-
Lifestyle Changes: Quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, and regular exercise are key to preventing future strokes.
Impact on Daily Life
Living with PCI can be challenging, but understanding its impact can help patients and their families cope better.
-
Vision Problems: PCI can cause vision issues, affecting daily activities like reading or driving.
-
Balance and Coordination: Difficulty with balance and coordination can lead to falls and injuries.
-
Cognitive Effects: Some patients may experience memory problems or difficulty concentrating.
-
Emotional Changes: Depression and anxiety are common after a stroke, requiring psychological support.
-
Support Systems: Family and community support play a crucial role in recovery and improving quality of life.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing PCI involves managing risk factors and adopting a healthy lifestyle.
-
Regular Check-ups: Routine medical check-ups can help detect and manage risk factors like high blood pressure and diabetes.
-
Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can reduce stroke risk.
-
Exercise: Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and lowers blood pressure.
-
Avoid Smoking: Smoking cessation significantly reduces the risk of PCI and other cardiovascular diseases.
-
Limit Alcohol: Drinking in moderation can help prevent strokes and other health issues.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to improve PCI diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
-
Advanced Imaging: New imaging technologies are being developed to detect PCI more accurately and quickly.
-
Genetic Studies: Research into genetic factors may provide insights into why some people are more susceptible to PCI.
-
Innovative Therapies: Scientists are exploring new medications and therapies to improve recovery outcomes.
-
Telemedicine: Remote monitoring and consultations can help manage PCI patients, especially in rural areas.
-
Public Awareness: Increasing awareness about PCI symptoms and risk factors can lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment.
Real-Life Stories
Hearing from those who have experienced PCI can provide valuable insights and hope.
-
Survivor Stories: Many PCI survivors share their journeys, offering encouragement and advice to others.
-
Caregiver Perspectives: Caregivers play a vital role in recovery, and their experiences highlight the importance of support.
-
Community Support: Support groups and online communities provide a platform for sharing experiences and resources.
-
Inspirational Recoveries: Some patients achieve remarkable recoveries, demonstrating the power of determination and resilience.
-
Lessons Learned: Each story offers unique lessons about coping with PCI and finding strength in adversity.
Myths and Misconceptions
Clearing up common myths about PCI can lead to better understanding and management.
-
Only Older Adults: While more common in older adults, PCI can affect younger people too.
-
Always Severe: Not all PCIs result in severe disability; outcomes vary widely among individuals.
-
No Prevention: Many believe strokes can't be prevented, but lifestyle changes can significantly reduce risk.
-
Immediate Recovery: Recovery from PCI can take time and varies for each person.
-
One-Time Event: Experiencing one PCI doesn't mean another won't occur; ongoing management is crucial.
Final Thoughts on Posterior Circulation Infarct
Understanding posterior circulation infarct is crucial for recognizing its impact on health. This type of stroke affects the back part of the brain, which controls vital functions like vision and balance. Symptoms can be subtle, making early detection challenging. However, knowing the signs—such as dizziness, double vision, and difficulty speaking—can lead to quicker medical intervention.
Prevention plays a significant role. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing blood pressure, and avoiding smoking can reduce risk. If symptoms appear, seeking immediate medical help is essential. Treatments like thrombolysis or endovascular therapy can significantly improve outcomes if administered promptly.
Awareness and education about posterior circulation infarct can save lives. By spreading knowledge, we empower individuals to act swiftly, ensuring better health outcomes. Stay informed, stay healthy, and always prioritize well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
