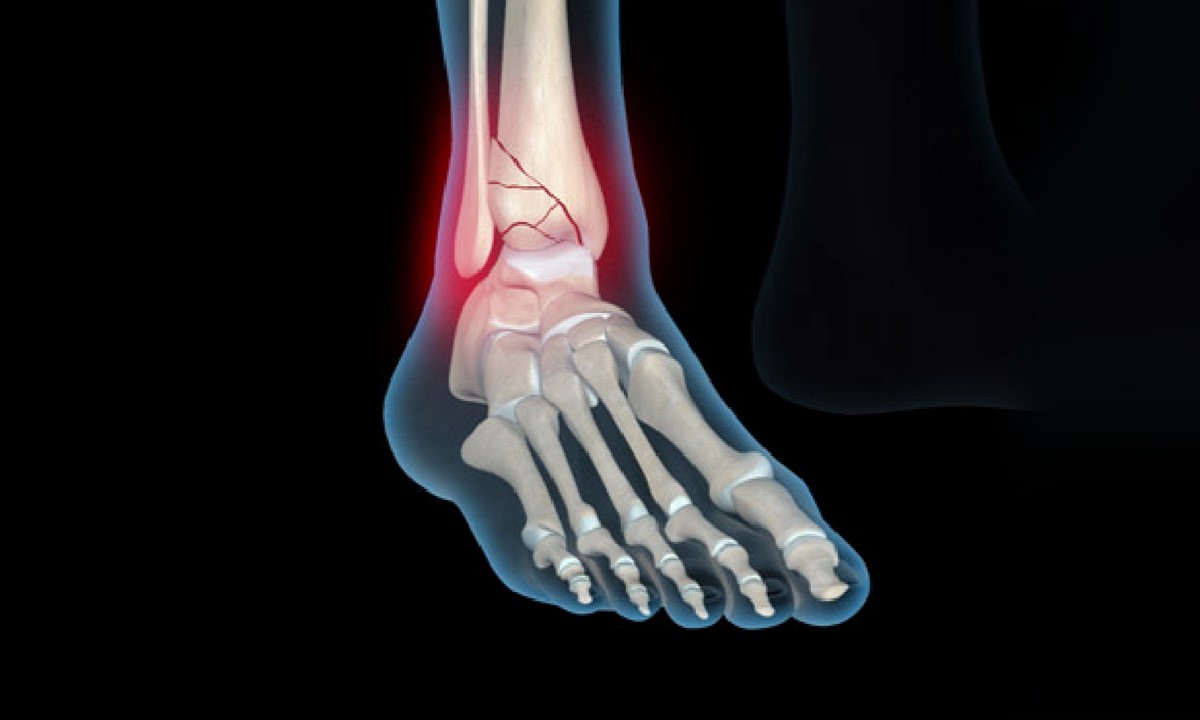
What exactly is a plafond fracture? A plafond fracture, also known as a pilon fracture, involves a break at the bottom of the tibia, where it meets the ankle joint. These fractures often result from high-energy impacts like car accidents or falls from significant heights. Why should you care? Understanding plafond fractures is crucial because they can lead to long-term complications if not treated properly. What makes them unique? Unlike other fractures, these often involve multiple breaks and can affect the cartilage, leading to arthritis. How are they treated? Treatment usually requires surgery to realign the bones, followed by extensive rehabilitation. Want to know more? Keep reading to uncover 40 essential facts about these complex injuries.
Key Takeaways:
- Plafond fractures, also known as pilon fractures, are severe ankle injuries often caused by high-impact trauma. They require accurate diagnosis, comprehensive treatment, and lengthy rehabilitation for full recovery.
- Preventing plafond fractures involves wearing protective gear, strengthening exercises, and maintaining a safe work environment. Regular bone density tests and a healthy diet can also help reduce the risk of these severe ankle injuries.
What is a Plafond Fracture?
A plafond fracture, also known as a pilon fracture, is a break in the distal part of the tibia, involving the ankle joint. These fractures are often severe and can be challenging to treat due to the complexity of the ankle's anatomy.
- Plafond fractures typically result from high-energy trauma, such as car accidents or falls from significant heights.
- The term "pilon" comes from the French word for "pestle," reflecting the crushing nature of these injuries.
- These fractures often involve both the tibia and fibula, complicating treatment and recovery.
- Plafond fractures can be classified into three types: Type A (extra-articular), Type B (partial articular), and Type C (complete articular).
- Symptoms include severe pain, swelling, bruising, and inability to bear weight on the affected leg.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors can help in preventing plafond fractures. These injuries are often linked to specific activities and conditions.
- High-impact sports like skiing, snowboarding, and motocross can increase the risk of sustaining a plafond fracture.
- Osteoporosis, a condition that weakens bones, can make individuals more susceptible to fractures.
- Workplace accidents, especially in construction or manual labor, are common causes.
- Motor vehicle accidents are a leading cause of high-energy trauma resulting in plafond fractures.
- Falls from ladders or roofs are frequent culprits, particularly in older adults.
Diagnosis and Imaging
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Various imaging techniques are employed to assess the extent of the injury.
- X-rays are the first step in diagnosing a plafond fracture, providing a clear image of the bone break.
- CT scans offer detailed cross-sectional images, helping to evaluate the fracture's complexity.
- MRI scans can be used to assess soft tissue damage around the fracture site.
- Physical examination by a doctor includes checking for deformity, swelling, and range of motion.
- Sometimes, stress tests are performed to determine the stability of the fracture.
Treatment Options
Treatment varies based on the severity and type of fracture. Both surgical and non-surgical methods are considered.
- Non-surgical treatment includes immobilization with a cast or brace, primarily for less severe fractures.
- Surgical options often involve open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF), where metal plates and screws are used to stabilize the bone.
- External fixation may be used in cases with severe soft tissue damage, where pins and rods are placed outside the body.
- Bone grafting might be necessary if there is significant bone loss.
- Physical therapy is crucial post-treatment to restore mobility and strength.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery from a plafond fracture can be lengthy and requires a comprehensive rehabilitation plan.
- Initial recovery involves keeping weight off the injured leg, often using crutches or a wheelchair.
- Swelling and pain management are critical in the early stages, typically involving ice packs and medication.
- Physical therapy begins with gentle range-of-motion exercises to prevent stiffness.
- Gradual weight-bearing is introduced as healing progresses, under medical supervision.
- Full recovery can take anywhere from six months to a year, depending on the injury's severity.
Complications and Long-term Effects
Plafond fractures can lead to several complications, affecting long-term outcomes and quality of life.
- Post-traumatic arthritis is a common complication, resulting from joint surface damage.
- Non-union or delayed union, where the bone fails to heal properly, may occur.
- Infection is a risk, particularly with surgical treatment.
- Chronic pain and swelling can persist long after the fracture has healed.
- Reduced range of motion and stiffness in the ankle joint are common long-term effects.
Prevention and Risk Reduction
Taking preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of sustaining a plafond fracture.
- Wearing appropriate protective gear during high-impact sports can help prevent injuries.
- Strengthening exercises for the legs and ankles can improve stability and reduce fracture risk.
- Ensuring a safe work environment, particularly in construction, can minimize accident risks.
- Using proper techniques when lifting heavy objects can prevent falls and injuries.
- Regular bone density tests and maintaining a healthy diet rich in calcium and vitamin D can help prevent osteoporosis-related fractures.
Interesting Facts
Here are some intriguing tidbits about plafond fractures that you might not know.
- Plafond fractures are more common in men than women, likely due to higher participation in high-risk activities.
- These fractures were first described in medical literature in the early 20th century.
- Advances in surgical techniques have significantly improved outcomes for patients with plafond fractures.
- Despite their severity, many people with plafond fractures can return to their previous level of activity with proper treatment and rehabilitation.
- Research is ongoing to develop better treatment methods and improve recovery times for plafond fractures.
Final Thoughts on Plafond Fractures
Plafond fractures, also known as pilon fractures, are serious injuries that affect the lower end of the tibia. These fractures often result from high-energy trauma like car accidents or falls from significant heights. Treatment typically involves surgery, followed by a lengthy period of rehabilitation. Understanding the severity and complexity of these fractures is crucial for proper management and recovery.
Patients should follow their healthcare provider's advice closely to ensure the best possible outcome. Early intervention and adherence to a rehabilitation plan can significantly improve the chances of regaining full function. While the road to recovery can be long and challenging, advances in medical technology and surgical techniques offer hope for those affected by this debilitating injury. Stay informed, stay proactive, and prioritize your health to navigate the journey to recovery successfully.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
