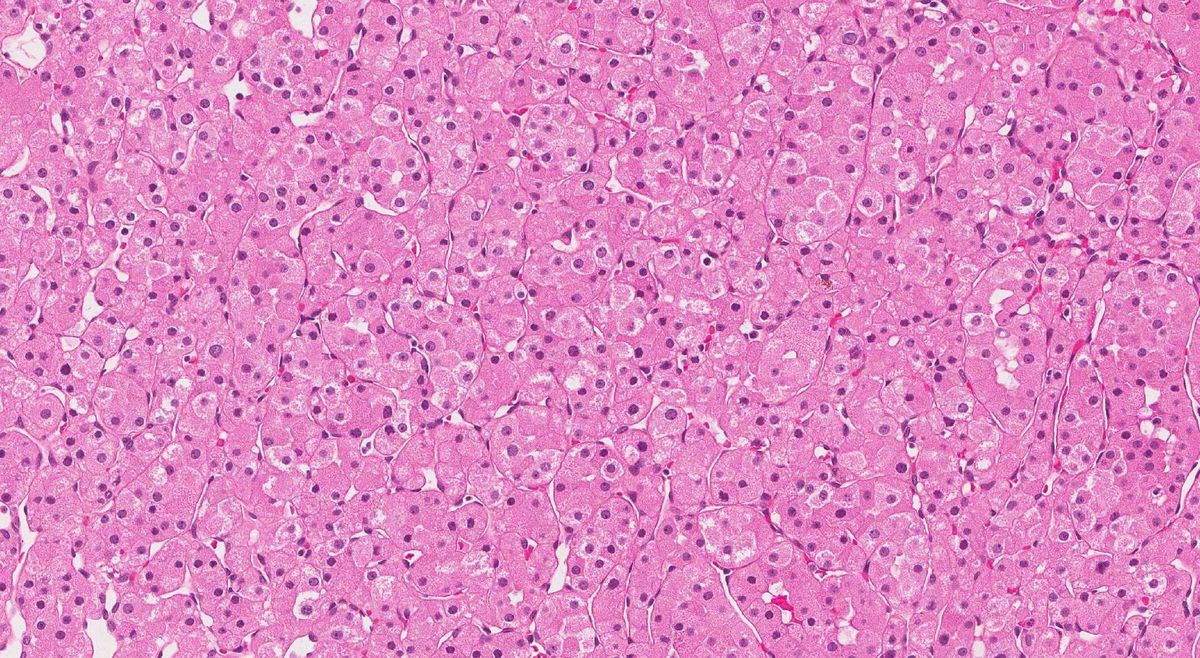
What is an oncocytoma? An oncocytoma is a type of tumor that can form in various organs, but it's most commonly found in the kidneys and salivary glands. These tumors are generally benign, meaning they are not cancerous. However, their presence can still cause health issues depending on their size and location. Oncocytomas are made up of cells called oncocytes, which are characterized by an abundance of mitochondria. This gives the cells a distinctive appearance under a microscope. While they are usually not life-threatening, it's crucial to monitor them closely to ensure they don't grow or cause complications. Understanding oncocytomas can help in managing them effectively and ensuring better health outcomes.
Key Takeaways:
- Oncocytoma, a benign tumor with abundant mitochondria, can develop in kidneys and salivary glands. Early detection and surgical removal lead to excellent prognosis and low recurrence rates.
- Ongoing research on genetic mutations and targeted therapies aims to improve treatment options for oncocytoma. Regular monitoring, healthy lifestyle, and emotional support are essential for managing the condition effectively.
What is Oncocytoma?
Oncocytoma is a type of tumor that can develop in various organs, most commonly in the kidneys and salivary glands. These tumors are generally benign, meaning they are not cancerous. However, understanding them is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Oncocytomas are composed of oncocytes, which are cells characterized by an abundance of mitochondria.
- These tumors are most frequently found in the kidneys, accounting for about 3-7% of all renal tumors.
- Oncocytomas can also occur in the salivary glands, particularly the parotid gland.
- They are generally slow-growing and often asymptomatic, meaning they may not cause noticeable symptoms.
- The exact cause of oncocytoma is still unknown, but genetic factors may play a role.
Symptoms of Oncocytoma
While oncocytomas are often asymptomatic, they can sometimes cause symptoms depending on their size and location. Knowing the signs can help in early detection.
- In the kidneys, oncocytomas may cause flank pain or blood in the urine.
- Large tumors can sometimes be felt as a mass in the abdomen.
- Oncocytomas in the salivary glands may present as a painless, slow-growing lump.
- Rarely, these tumors can cause facial nerve weakness if they press on nearby nerves.
- Some patients may experience general symptoms like fatigue or weight loss, although this is uncommon.
Diagnosis of Oncocytoma
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Various methods are used to identify oncocytomas.
- Imaging techniques like CT scans and MRIs are commonly used to detect these tumors.
- Ultrasound can also be helpful, especially for kidney oncocytomas.
- A biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis by examining the tissue under a microscope.
- Fine-needle aspiration is often used for salivary gland tumors.
- Genetic testing can sometimes provide additional information, particularly if there is a family history of similar tumors.
Treatment Options for Oncocytoma
Treatment varies depending on the tumor's size, location, and whether it is causing symptoms. Here are some common approaches.
- Small, asymptomatic tumors may simply be monitored with regular imaging studies.
- Surgical removal is often recommended for larger or symptomatic tumors.
- Partial nephrectomy, where only part of the kidney is removed, is a common procedure for renal oncocytomas.
- Total nephrectomy, or removal of the entire kidney, may be necessary in some cases.
- For salivary gland oncocytomas, surgical excision of the affected gland is usually performed.
Prognosis and Outcomes
The prognosis for patients with oncocytoma is generally favorable, especially when the tumor is detected early and treated appropriately.
- Most patients with renal oncocytomas have an excellent prognosis after surgical removal.
- Recurrence is rare but can occur, so regular follow-up is important.
- Salivary gland oncocytomas also have a good prognosis, with low rates of recurrence.
- Malignant transformation, where the tumor becomes cancerous, is extremely rare.
- Long-term survival rates are high, particularly for those who undergo complete surgical excision.
Interesting Facts About Oncocytoma
Beyond the medical aspects, there are some intriguing facts about these tumors that highlight their uniqueness.
- Oncocytomas were first described in the 1940s.
- They are more common in older adults, typically appearing in people over 50.
- Men are slightly more likely to develop renal oncocytomas than women.
- The term "oncocytoma" comes from the Greek word "onkos," meaning mass or bulk.
- Oncocytomas can sometimes be mistaken for other types of tumors, making accurate diagnosis crucial.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand oncocytomas and improve treatment options. Here are some areas of focus.
- Scientists are studying the genetic mutations associated with oncocytomas to develop targeted therapies.
- Research is also exploring the role of mitochondria in the development of these tumors.
- Advances in imaging technology are helping to improve the accuracy of non-invasive diagnosis.
- Clinical trials are investigating new surgical techniques and less invasive treatment options.
- There is growing interest in the potential use of immunotherapy for treating oncocytomas.
Living with Oncocytoma
Living with an oncocytoma diagnosis can be challenging, but there are ways to manage the condition and maintain a good quality of life.
- Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor for recurrence or new symptoms.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can support overall well-being.
- Support groups and counseling can provide emotional support and practical advice.
- Patients should stay informed about new research and treatment options.
- Open communication with healthcare providers is key to managing the condition effectively.
Final Thoughts on Oncocytoma
Oncocytoma, a type of benign tumor, often affects the kidneys and salivary glands. While generally non-cancerous, these tumors can sometimes be mistaken for malignant growths due to their appearance on imaging tests. It's crucial to get an accurate diagnosis through a biopsy or other medical evaluations. Treatment usually involves surgical removal, especially if the tumor causes symptoms or grows in size. Regular monitoring is essential to ensure no complications arise. Understanding the nature of oncocytomas helps in managing them effectively and reduces unnecessary anxiety. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment options. Knowledge about oncocytomas empowers patients and their families to make informed decisions, ensuring better health outcomes. Stay proactive about your health, and don't hesitate to seek medical attention if you notice unusual symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
