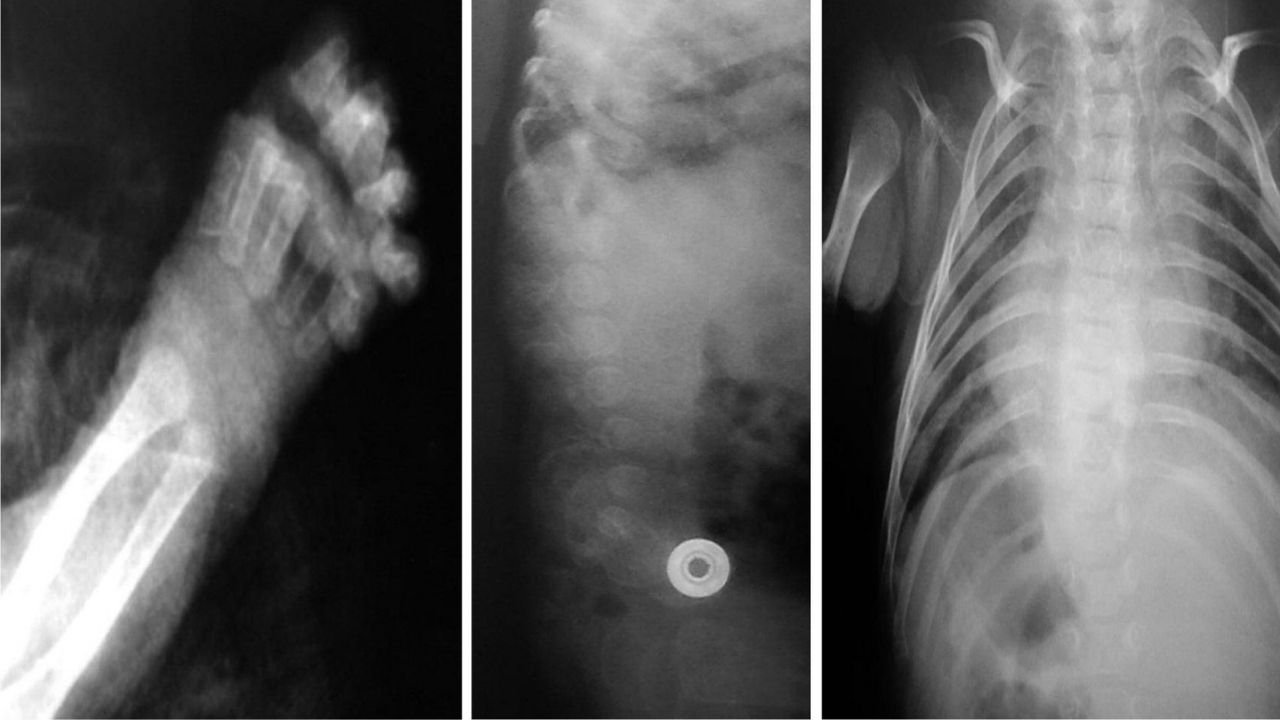
Microcephalic Osteodysplastic Primordial Dwarfism (MOPD) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by small stature, distinct facial features, and skeletal abnormalities. MOPD affects growth and development from before birth, leading to significantly shorter height compared to peers. Individuals with this condition often have a smaller head size (microcephaly) and unique bone structure. Despite these challenges, many lead fulfilling lives with proper medical care and support. Understanding MOPD can help raise awareness and foster a more inclusive society. This article delves into 40 intriguing facts about Microcephalic Osteodysplastic Primordial Dwarfism, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and the remarkable resilience of those affected.
Key Takeaways:
- MOPD is a rare genetic disorder causing small stature and health challenges. Support and early intervention are crucial for better outcomes and improved quality of life.
- Individuals with MOPD face physical, social, and emotional hurdles. Research and advocacy offer hope for better understanding and treatments in the future.
What is Microcephalic Osteodysplastic Primordial Dwarfism?
Microcephalic Osteodysplastic Primordial Dwarfism (MOPD) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by small stature, skeletal abnormalities, and a smaller head size. This condition affects various aspects of growth and development. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about MOPD.
-
MOPD is extremely rare. Only a few hundred cases have been documented worldwide, making it one of the rarest forms of dwarfism.
-
There are several types of MOPD. The most common types are MOPD Type I, Type II, and Type III, each with distinct characteristics and severity.
-
MOPD Type II is the most studied. Researchers have focused more on Type II due to its relatively higher prevalence among the types.
-
Genetic mutations cause MOPD. Mutations in specific genes, such as the PCNT gene, are responsible for the disorder.
-
MOPD affects both genders equally. There is no gender preference; males and females are equally likely to be affected.
-
Individuals with MOPD have a smaller head size. Microcephaly, or a smaller head circumference, is a hallmark of the condition.
-
Growth is significantly delayed. Children with MOPD grow at a much slower rate compared to their peers.
-
Skeletal abnormalities are common. These can include short limbs, curved spine, and joint problems.
-
Facial features are distinct. Individuals often have a prominent nose, large eyes, and a small jaw.
-
Intellectual development varies. While some individuals have normal intelligence, others may experience developmental delays.
Health Challenges Faced by Individuals with MOPD
Living with MOPD comes with various health challenges. Understanding these can help in providing better care and support.
-
Heart problems are prevalent. Congenital heart defects are common in individuals with MOPD.
-
Respiratory issues can occur. Due to their small size, respiratory complications are a concern.
-
Vision problems are frequent. Many individuals experience issues such as nearsightedness or farsightedness.
-
Hearing loss is possible. Some may have partial or complete hearing loss.
-
Dental issues are common. Crowded teeth and delayed tooth eruption are typical dental problems.
-
Bone fragility is a risk. Bones may be more prone to fractures and other injuries.
-
Hormonal imbalances can happen. Growth hormone deficiencies are often observed.
-
Seizures may occur. Some individuals are prone to epileptic seizures.
-
Kidney problems are possible. Renal abnormalities can be part of the condition.
-
Skin conditions are frequent. Dry skin and eczema are common among those with MOPD.
Social and Emotional Aspects of MOPD
Living with MOPD affects not just physical health but also social and emotional well-being. Here are some insights into these aspects.
-
Social interactions can be challenging. Due to their small stature, individuals may face social stigma.
-
Bullying is a concern. Children with MOPD are often targets of bullying due to their appearance.
-
Support groups are beneficial. Connecting with others who have MOPD can provide emotional support.
-
Family support is crucial. Families play a vital role in the well-being of individuals with MOPD.
-
Mental health needs attention. Anxiety and depression are common and need to be addressed.
-
Education can be tailored. Special education programs can help meet their learning needs.
-
Adaptive devices are helpful. Tools like hearing aids and glasses improve quality of life.
-
Physical therapy is beneficial. Helps in managing mobility and physical health.
-
Occupational therapy aids daily living. Supports independence in daily activities.
-
Recreational activities are important. Engaging in hobbies and sports boosts morale.
Advances in Research and Treatment
Research on MOPD is ongoing, and advancements are being made in understanding and treating the condition.
-
Genetic testing is available. Helps in diagnosing MOPD and understanding its genetic basis.
-
Early intervention is key. Starting treatment early can improve outcomes.
-
Growth hormone therapy is an option. Can help in managing growth deficiencies.
-
Surgical interventions are possible. Corrective surgeries can address skeletal abnormalities.
-
Multidisciplinary care is essential. Involves a team of specialists for comprehensive care.
-
Clinical trials are ongoing. Research studies are exploring new treatments.
-
Patient registries are helpful. Collecting data on individuals with MOPD aids research.
-
Awareness is increasing. Efforts are being made to raise awareness about MOPD.
-
Advocacy groups are active. Organizations support individuals and families affected by MOPD.
-
Future looks promising. With ongoing research, better treatments and understanding of MOPD are on the horizon.
Final Thoughts on Microcephalic Osteodysplastic Primordial Dwarfism
Microcephalic Osteodysplastic Primordial Dwarfism (MOPD) is a rare genetic condition that affects growth and development. Understanding the facts about MOPD helps raise awareness and support for those living with this condition. From its genetic roots to its impact on daily life, every detail matters.
People with MOPD face unique challenges but also show incredible resilience. Advances in medical research continue to improve the quality of life for those affected. Sharing knowledge about MOPD can lead to better support systems and more inclusive communities.
Remember, every fact learned contributes to a greater understanding of this rare condition. Stay informed, spread awareness, and support those with MOPD. Knowledge is power, and together, we can make a difference.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
