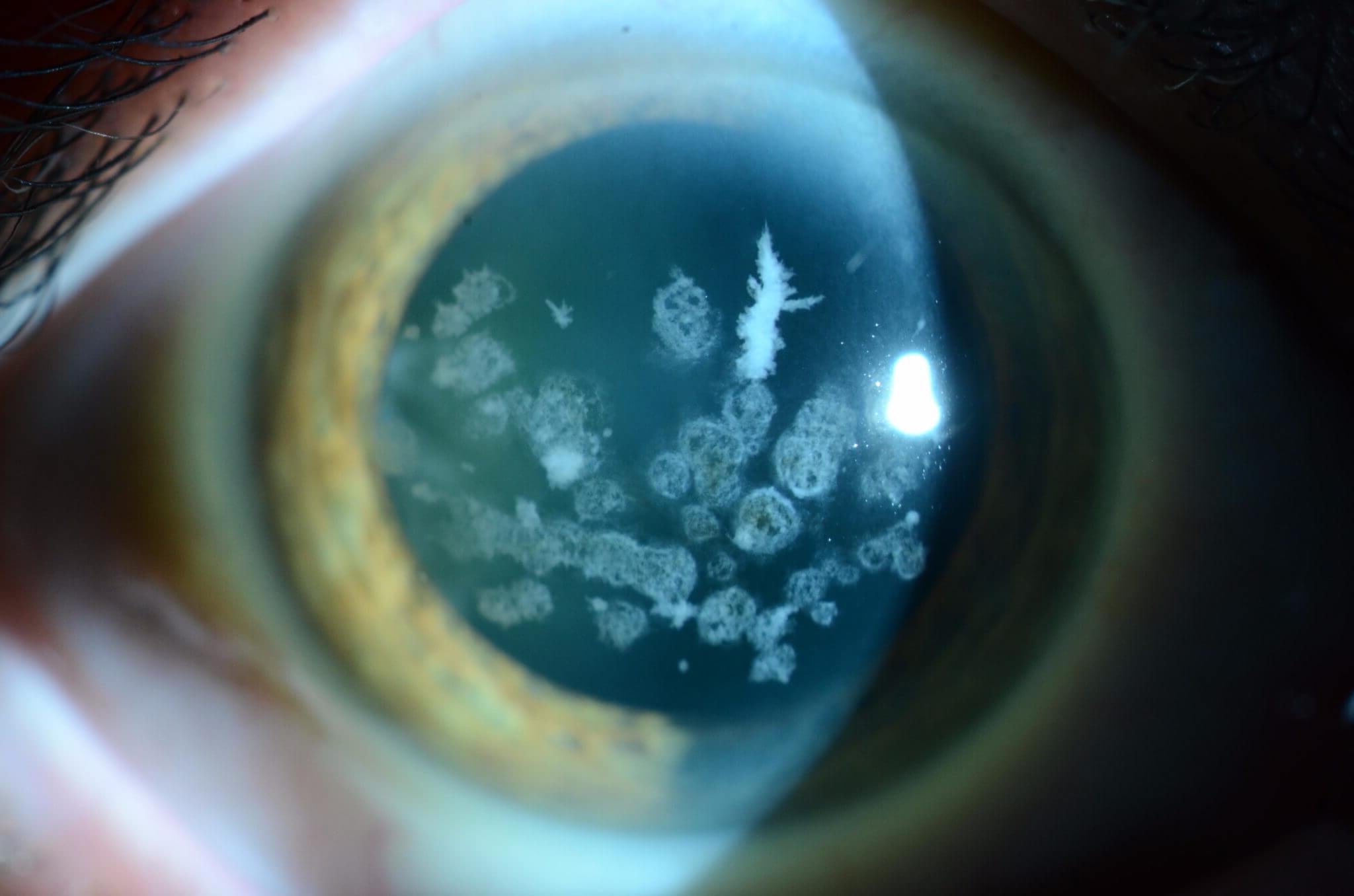
Macular Corneal Dystrophy is a rare eye disorder that affects the clarity of the cornea, leading to vision problems. This condition usually appears in childhood or adolescence and can progressively worsen over time. The cornea, which is the clear, dome-shaped surface of the eye, becomes cloudy due to the accumulation of abnormal deposits. These deposits interfere with the passage of light, causing blurred vision and other visual disturbances. Symptoms may include sensitivity to light, glare, and a gradual decrease in vision. Treatment options often involve corneal transplants to restore vision. Understanding this condition is crucial for early diagnosis and management, ensuring better outcomes for those affected.
Key Takeaways:
- Macular Corneal Dystrophy is a rare genetic eye disorder that causes vision impairment due to clouding of the cornea. It can start in childhood and worsen over time, affecting both eyes symmetrically.
- While there is no cure for Macular Corneal Dystrophy, treatments like corneal transplantation and genetic counseling can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Ongoing research aims to better understand and treat this condition.
What is Macular Corneal Dystrophy?
Macular Corneal Dystrophy (MCD) is a rare genetic eye disorder affecting the cornea. It leads to vision impairment due to clouding of the cornea. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
MCD is a genetic disorder: It is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, meaning both parents must carry the defective gene.
-
Caused by mutations in the CHST6 gene: This gene is responsible for producing an enzyme crucial for maintaining corneal clarity.
-
First described in 1890: German ophthalmologist Arthur Groenouw first identified the condition.
-
Affects both eyes: MCD typically impacts both eyes symmetrically.
-
Corneal clouding starts in childhood: Symptoms often begin in the first decade of life.
-
Progressive condition: The clouding worsens over time, leading to significant vision loss.
Symptoms of Macular Corneal Dystrophy
Recognizing the symptoms early can help manage the condition better. Here are some common signs to look out for.
-
Blurred vision: One of the earliest symptoms is a gradual blurring of vision.
-
Photophobia: Increased sensitivity to light is common among those with MCD.
-
Glare and halos: Patients often see glare or halos around lights.
-
Corneal opacities: Visible cloudiness or spots on the cornea can be observed.
-
Eye discomfort: Some individuals experience mild discomfort or irritation.
-
Reduced visual acuity: Over time, the ability to see fine details diminishes.
Diagnosis of Macular Corneal Dystrophy
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for proper management. Here are some methods used to diagnose MCD.
-
Slit-lamp examination: This tool allows ophthalmologists to examine the cornea in detail.
-
Corneal topography: Maps the surface curvature of the cornea to detect irregularities.
-
Genetic testing: Identifies mutations in the CHST6 gene.
-
Histopathological examination: Analyzes corneal tissue samples under a microscope.
-
Family history: Reviewing family medical history can provide clues.
-
Visual acuity tests: Measures the sharpness of vision.
Treatment Options for Macular Corneal Dystrophy
While there is no cure, several treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
Corneal transplantation: Replacing the damaged cornea with a donor cornea can restore vision.
-
Phototherapeutic keratectomy (PTK): Uses a laser to remove superficial corneal opacities.
-
Lubricating eye drops: Help alleviate discomfort and irritation.
-
Regular monitoring: Frequent check-ups to monitor progression and adjust treatments.
-
Genetic counseling: Provides information and support to affected families.
-
Contact lenses: Special lenses can improve vision in some cases.
Living with Macular Corneal Dystrophy
Managing daily life with MCD involves several strategies to cope with vision impairment.
-
Assistive devices: Tools like magnifiers and screen readers can aid in daily tasks.
-
Adaptive techniques: Learning new ways to perform activities can help maintain independence.
-
Support groups: Connecting with others facing similar challenges can provide emotional support.
-
Low vision rehabilitation: Programs designed to maximize remaining vision.
-
Healthy lifestyle: Maintaining overall health can positively impact eye health.
-
Protective eyewear: Sunglasses can reduce photophobia and protect the eyes.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand and treat MCD. Here are some promising areas of study.
-
Gene therapy: Exploring ways to correct the defective CHST6 gene.
-
Stem cell therapy: Investigating the potential of stem cells to regenerate corneal tissue.
-
New surgical techniques: Developing less invasive methods for corneal transplantation.
-
Improved diagnostic tools: Enhancing accuracy and early detection.
-
Pharmacological treatments: Researching drugs that could slow or halt disease progression.
-
Patient registries: Collecting data to improve understanding and treatment of MCD.
Interesting Facts About Macular Corneal Dystrophy
Here are some lesser-known facts that highlight the uniqueness of MCD.
-
More common in certain populations: Higher prevalence in Iceland and parts of India.
-
Named after the macula: Despite the name, it does not affect the macula of the retina.
-
Variable severity: Symptoms can range from mild to severe, even within the same family.
-
Rare condition: MCD is one of the least common forms of corneal dystrophy.
Final Thoughts on Macular Corneal Dystrophy
Macular Corneal Dystrophy (MCD) is a rare eye condition affecting the cornea, leading to vision loss over time. Understanding MCD helps in early diagnosis and better management. Symptoms like blurred vision and corneal clouding can be alarming, but treatments like corneal transplants offer hope. Genetic factors play a significant role, so family history is crucial. Regular eye check-ups can catch early signs, making a big difference.
Awareness about MCD empowers patients and families to seek timely medical advice. Though rare, knowing the facts about this condition can lead to better outcomes and improved quality of life. Stay informed, consult eye specialists, and take proactive steps for eye health. Knowledge is power when dealing with conditions like Macular Corneal Dystrophy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
