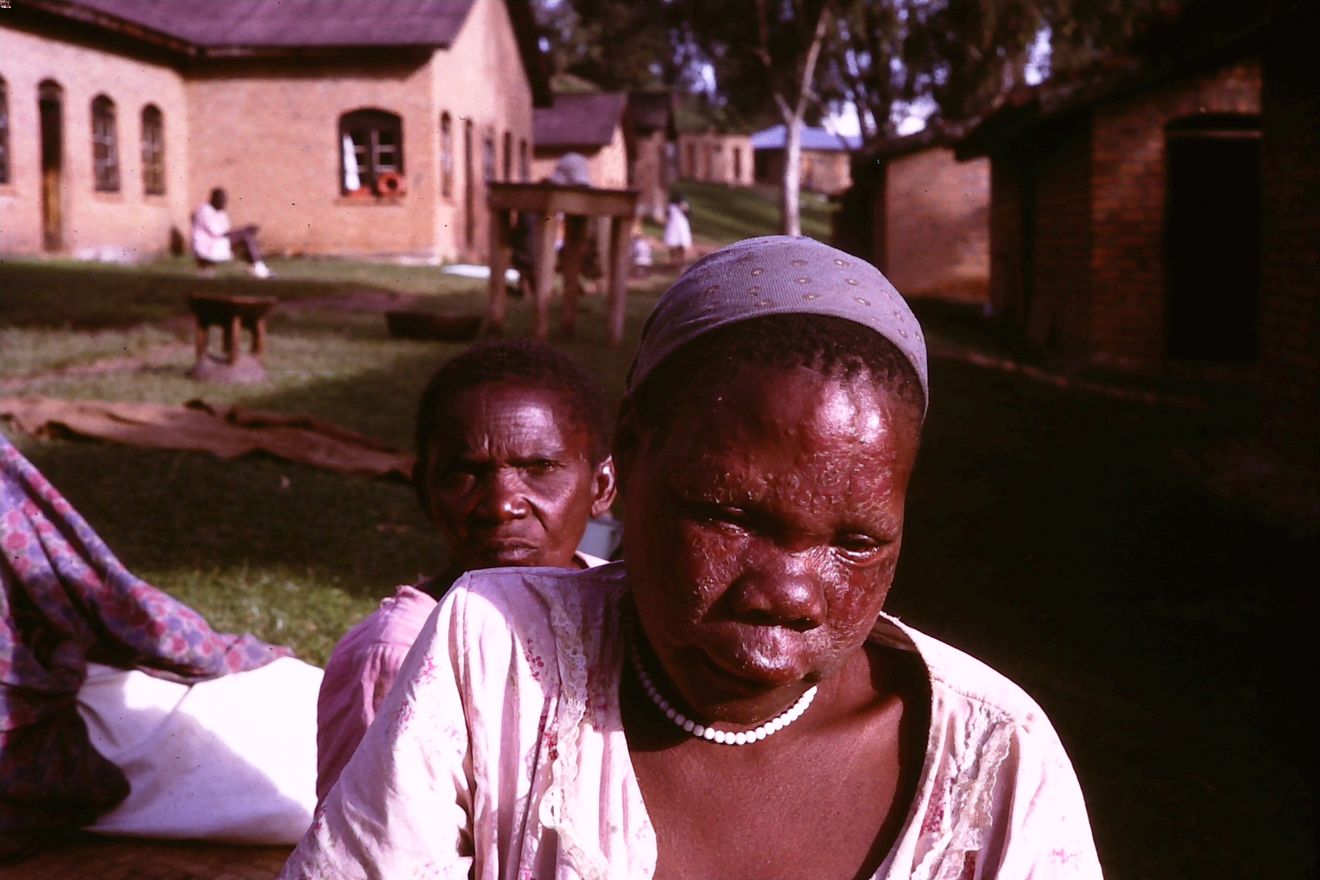
Leontiasis ossea is a rare medical condition that causes abnormal bone growth in the face and skull, leading to a lion-like appearance. This disorder, also known as leontiasis, can result from various underlying diseases, including Paget's disease, fibrous dysplasia, or hyperparathyroidism. Symptoms often include facial deformities, headaches, and vision problems due to the pressure on nerves and other structures. Treatment typically focuses on managing the underlying cause and alleviating symptoms. Understanding the complexities of leontiasis ossea is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment. Here are 40 intriguing facts about this rare condition to broaden your knowledge.
Key Takeaways:
- Leontiasis Ossea, or lion face syndrome, causes facial bone overgrowth. Symptoms include vision and hearing problems, and treatment options include surgery and medications.
- Research on Leontiasis Ossea aims to improve understanding and develop better treatments, including genetic studies and clinical trials for new medications and therapies.
What is Leontiasis Ossea?
Leontiasis Ossea, also known as lion face syndrome, is a rare medical condition characterized by the overgrowth of facial and cranial bones. This condition can lead to significant facial deformities and other complications. Here are some fascinating facts about this rare disorder.
-
Leontiasis Ossea gets its name from the Greek word "leon," meaning lion, due to the lion-like appearance of the face in affected individuals.
-
The condition is often associated with Paget's disease, a chronic disorder that can result in enlarged and misshapen bones.
-
Fibrous dysplasia, a bone disorder where scar-like tissue develops in place of normal bone, can also lead to Leontiasis Ossea.
-
Hyperparathyroidism, an overactivity of the parathyroid glands, is another condition that can cause this rare disorder.
-
The first documented case of Leontiasis Ossea was described by the German pathologist Rudolf Virchow in the 19th century.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and how Leontiasis Ossea is diagnosed can help in early detection and management.
-
Facial deformity is the most noticeable symptom, often leading to a lion-like appearance.
-
Nasal obstruction can occur due to the overgrowth of bones around the nasal passages.
-
Vision problems may arise if the bones around the eyes are affected, potentially leading to blindness.
-
Hearing loss is another common symptom, caused by the overgrowth of bones around the ears.
-
Headaches are frequent due to increased pressure within the skull.
-
Dental issues such as misaligned teeth and difficulty chewing can result from jawbone overgrowth.
-
CT scans and X-rays are commonly used to diagnose Leontiasis Ossea by revealing abnormal bone growth.
-
MRI scans can provide detailed images of the affected areas, helping to assess the extent of the condition.
-
Biopsies may be performed to rule out other conditions and confirm the diagnosis.
Causes and Risk Factors
Exploring the causes and risk factors can provide insight into why some people develop Leontiasis Ossea.
-
Genetic mutations are believed to play a role in the development of this condition.
-
Environmental factors such as exposure to certain chemicals or radiation may increase the risk.
-
Age is a significant risk factor, with most cases occurring in middle-aged and older adults.
-
Gender can influence the likelihood of developing Leontiasis Ossea, with men being more commonly affected than women.
-
Family history of bone disorders can increase the risk of developing this condition.
-
Nutritional deficiencies, particularly in calcium and vitamin D, may contribute to the development of bone abnormalities.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for Leontiasis Ossea, various treatments can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
Surgical intervention is often necessary to remove excess bone and relieve pressure on affected areas.
-
Medications such as bisphosphonates can help slow down bone growth and reduce symptoms.
-
Radiation therapy may be used in some cases to shrink abnormal bone tissue.
-
Pain management is crucial, with options including over-the-counter pain relievers and prescription medications.
-
Physical therapy can help improve mobility and function in affected individuals.
-
Occupational therapy may assist with daily activities and improve quality of life.
-
Support groups and counseling can provide emotional support and coping strategies for patients and their families.
Complications and Prognosis
Understanding the potential complications and long-term outlook can help patients and caregivers prepare for the future.
-
Respiratory issues can arise due to nasal obstruction and other airway complications.
-
Neurological problems such as seizures may occur if the brain is affected by increased pressure.
-
Infections are a risk, particularly in areas where bone overgrowth has caused tissue damage.
-
Malnutrition can result from difficulty chewing and swallowing.
-
Psychological impact is significant, with many patients experiencing depression and anxiety due to their appearance and symptoms.
-
Life expectancy can be affected, particularly if complications are severe and not managed effectively.
-
Regular monitoring by healthcare professionals is essential to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research is crucial for improving our understanding of Leontiasis Ossea and developing better treatments.
-
Genetic studies are being conducted to identify specific mutations associated with the condition.
-
Clinical trials are exploring new medications and therapies to manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
-
Stem cell research holds promise for regenerating healthy bone tissue and repairing damage.
-
Advanced imaging techniques are being developed to improve diagnosis and monitoring of the condition.
-
Patient registries are being established to collect data and improve our understanding of the condition.
-
Public awareness campaigns aim to educate people about Leontiasis Ossea and reduce stigma associated with the condition.
Final Thoughts on Leontiasis Ossea
Leontiasis ossea, a rare bone disorder, causes facial bones to overgrow, leading to a lion-like appearance. This condition, though uncommon, has fascinated medical professionals for years. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments can help those affected manage their condition better. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for improving quality of life. Treatments range from medications to surgery, depending on severity. While it can be challenging to live with, advancements in medical science offer hope. Awareness and education about leontiasis ossea can reduce stigma and support those living with it. Remember, knowledge is power. The more we learn about rare conditions like this, the better equipped we are to offer help and compassion. Stay informed, stay empathetic, and continue to support medical research.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
