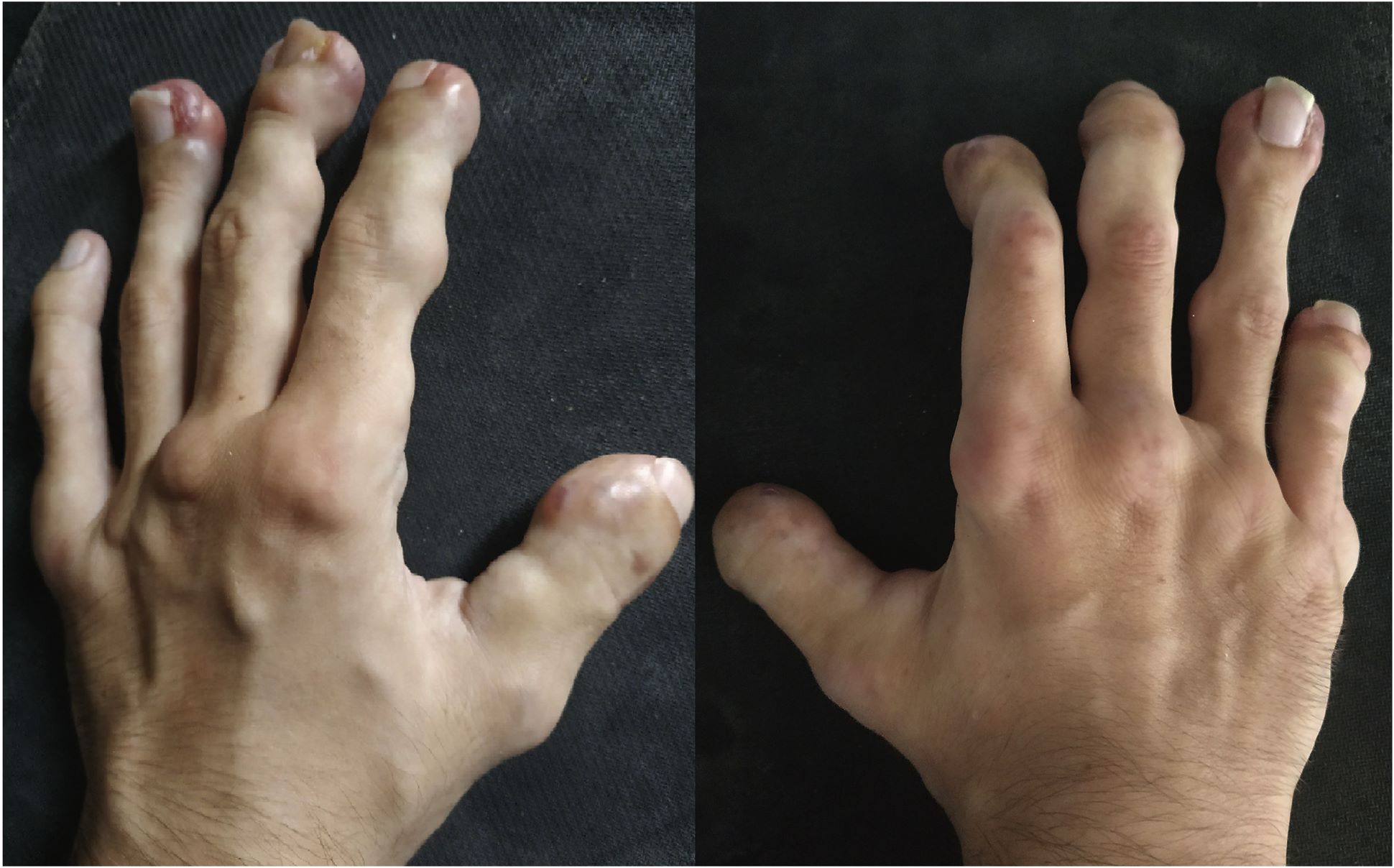
Juvenile Hyaline Fibromatosis (JHF) might sound like a mouthful, but it's a rare genetic condition that affects kids. What exactly is Juvenile Hyaline Fibromatosis? It's a disorder where small, firm lumps called nodules form under the skin, often around joints. These nodules can make moving painful and difficult. Kids with JHF might also have thickened skin, gum overgrowth, and joint stiffness. The condition is caused by changes in a specific gene, and it's something kids inherit from their parents. Though it's rare, understanding JHF is important for those affected. Treatments focus on managing symptoms, like pain relief and physical therapy, to help kids live more comfortably. While there's no cure yet, ongoing research offers hope for better treatments in the future.
Key Takeaways:
- Juvenile Hyaline Fibromatosis is a rare genetic disorder affecting connective tissues, causing skin nodules, joint contractures, and gum overgrowth. Early diagnosis and multidisciplinary care are crucial for managing symptoms.
- Living with Juvenile Hyaline Fibromatosis presents unique challenges, impacting mobility, social interactions, and family dynamics. However, with proper treatment and support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives despite physical limitations.
What is Juvenile Hyaline Fibromatosis?
Juvenile Hyaline Fibromatosis (JHF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects connective tissues. It usually appears in early childhood and can cause a variety of symptoms. Let's explore some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Genetic Roots: JHF is caused by mutations in the ANTXR2 gene. This gene plays a role in the development and maintenance of connective tissues.
-
Rare Occurrence: It's an extremely rare condition, with only about 70 cases reported worldwide. This rarity makes it challenging to study and understand fully.
-
Early Onset: Symptoms typically begin in infancy or early childhood, often before the age of two. Early diagnosis is crucial for managing the condition.
-
Connective Tissue Impact: The disorder primarily affects the skin, bones, and joints. This can lead to a range of physical symptoms and complications.
-
Skin Nodules: One of the hallmark signs is the development of skin nodules. These are firm, painless lumps that can appear on various parts of the body.
-
Joint Contractures: Many individuals with JHF experience joint contractures, which limit movement and flexibility. This can significantly impact mobility.
-
Gum Overgrowth: Gingival hypertrophy, or gum overgrowth, is another common symptom. This can lead to dental issues and discomfort.
-
Bone Lesions: Some patients develop bone lesions, which can cause pain and affect bone growth and development.
-
Growth Delays: Children with JHF often experience growth delays, resulting in shorter stature compared to their peers.
-
Pain Management: Chronic pain is a common issue for those with JHF, requiring ongoing pain management strategies.
How is Juvenile Hyaline Fibromatosis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing JHF can be complex due to its rarity and the overlap of symptoms with other conditions. Here are some key facts about the diagnostic process.
-
Clinical Evaluation: Diagnosis often begins with a thorough clinical evaluation, including a review of symptoms and medical history.
-
Genetic Testing: Confirming the diagnosis usually involves genetic testing to identify mutations in the ANTXR2 gene.
-
Biopsy: A skin biopsy may be performed to examine the nodules and confirm the presence of hyaline material.
-
Radiographic Imaging: X-rays or other imaging techniques can help identify bone lesions and assess joint involvement.
-
Differential Diagnosis: Doctors must rule out other conditions with similar symptoms, such as infantile systemic hyalinosis.
-
Family History: A detailed family history can provide clues, as JHF is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern.
-
Multidisciplinary Approach: Diagnosis often involves a team of specialists, including dermatologists, geneticists, and orthopedic surgeons.
What are the Treatment Options for Juvenile Hyaline Fibromatosis?
While there is no cure for JHF, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Let's look at some treatment strategies.
-
Pain Relief: Pain management is a priority, often involving medications like NSAIDs or stronger pain relievers.
-
Physical Therapy: Regular physical therapy can help maintain joint mobility and prevent contractures.
-
Surgical Interventions: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove nodules or correct joint deformities.
-
Dental Care: Regular dental check-ups and treatments are important to manage gum overgrowth and maintain oral health.
-
Nutritional Support: Ensuring proper nutrition can support growth and overall health, especially in children with growth delays.
-
Psychological Support: Counseling or therapy can help patients and families cope with the emotional challenges of living with a chronic condition.
-
Regular Monitoring: Ongoing medical monitoring is essential to track the progression of symptoms and adjust treatment plans as needed.
-
Customized Care Plans: Treatment plans are highly individualized, tailored to each patient's specific symptoms and needs.
What is the Prognosis for Juvenile Hyaline Fibromatosis?
Understanding the long-term outlook for JHF can help families prepare and plan for the future. Here are some insights into the prognosis.
-
Variable Outcomes: Prognosis can vary widely depending on the severity of symptoms and the effectiveness of treatment.
-
Chronic Condition: JHF is a lifelong condition, requiring ongoing management and care.
-
Quality of Life: With appropriate treatment, many individuals can lead fulfilling lives, although they may face physical limitations.
-
Potential Complications: Complications such as infections or severe joint deformities can impact prognosis.
-
Research and Advances: Ongoing research may lead to new treatments and improved outcomes in the future.
-
Support Networks: Connecting with support groups and other families affected by JHF can provide valuable resources and encouragement.
-
Importance of Early Intervention: Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve the long-term outlook for children with JHF.
How Does Juvenile Hyaline Fibromatosis Affect Daily Life?
Living with JHF presents unique challenges. Here are some ways it can impact daily life and strategies for coping.
-
Mobility Challenges: Joint contractures and pain can make movement difficult, requiring adaptive devices or assistance.
-
Social Impact: Physical differences and limitations can affect social interactions and self-esteem, especially in children.
-
Educational Needs: Some children may require special accommodations at school to support their learning and participation.
-
Family Dynamics: Caring for a child with JHF can affect family dynamics, requiring adjustments and support.
-
Financial Considerations: Medical expenses and the need for specialized care can pose financial challenges for families.
-
Advocacy and Awareness: Raising awareness about JHF can help improve understanding and support for affected individuals.
-
Resilience and Strength: Many families and individuals with JHF demonstrate remarkable resilience and strength in facing challenges.
-
Hope for the Future: Advances in research and treatment offer hope for improved outcomes and quality of life for those with JHF.
Final Thoughts on Juvenile Hyaline Fibromatosis
Juvenile Hyaline Fibromatosis (JHF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects children, causing skin lesions, joint contractures, and bone deformities. Understanding this condition is crucial for early diagnosis and management. Genetic mutations in the ANTXR2 gene lead to JHF, and symptoms often appear in infancy or early childhood. While there's no cure, treatments focus on managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Physical therapy, pain management, and sometimes surgery can help alleviate discomfort and improve mobility. Support groups and counseling can provide emotional support for families dealing with JHF. Raising awareness about this condition can lead to better resources and support for affected individuals. By staying informed and advocating for research, we can hope for advancements in treatment options. Remember, knowledge is power, and understanding JHF can make a significant difference in the lives of those affected.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
