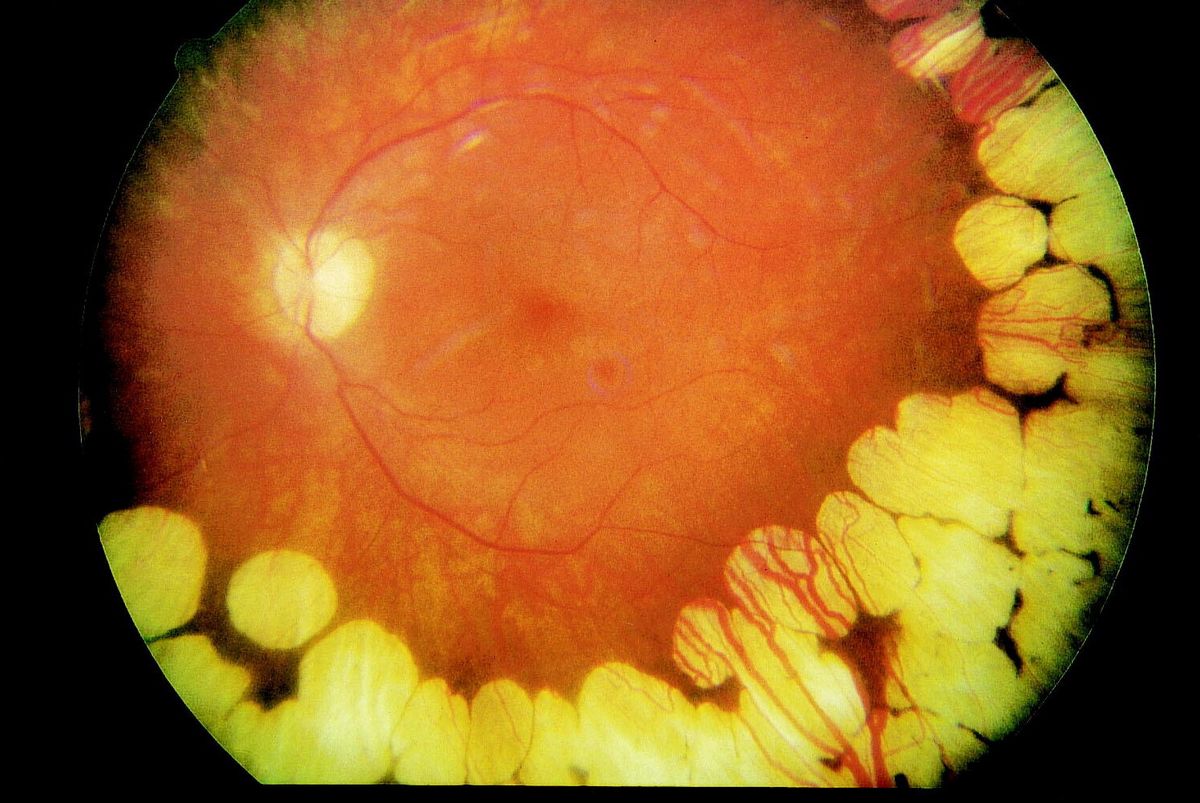
Gyrate Atrophy of the Choroid and Retina is a rare genetic disorder that affects vision. This condition causes progressive degeneration of the choroid and retina, leading to severe vision impairment over time. Symptoms often start in childhood, with night blindness being one of the first signs. As the disease progresses, peripheral vision narrows, eventually leading to tunnel vision. Caused by mutations in the OAT gene, this disorder affects the body's ability to break down an amino acid called ornithine. Treatment options are limited but may include dietary restrictions and vitamin B6 supplements to slow progression. Understanding this condition can help those affected manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Key Takeaways:
- Gyrate Atrophy of the Choroid and Retina is a rare genetic disorder causing vision loss. Early diagnosis and management can help preserve vision for as long as possible.
- While there is no cure for Gyrate Atrophy, treatments like vitamin B6 supplementation and low-protein diets can slow disease progression. Support groups and personalized aids can help individuals lead fulfilling lives.
What is Gyrate Atrophy of the Choroid and Retina?
Gyrate Atrophy of the Choroid and Retina is a rare genetic disorder affecting the eyes. This condition leads to progressive vision loss due to the degeneration of the choroid and retina, crucial parts of the eye responsible for vision.
- Gyrate Atrophy is caused by mutations in the OAT gene, which is responsible for producing the enzyme ornithine aminotransferase.
- The disorder is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, meaning both parents must carry the mutated gene for a child to be affected.
- Symptoms typically begin in childhood, often between the ages of 10 and 20.
- Early signs include difficulty seeing in low light or night blindness.
- As the condition progresses, peripheral vision loss occurs, leading to tunnel vision.
- Eventually, central vision may also be affected, resulting in significant visual impairment.
- The rate of progression can vary widely among individuals.
- Gyrate Atrophy is more common in certain populations, such as Finnish people, due to a higher prevalence of the gene mutation.
Diagnosis and Symptoms
Diagnosing Gyrate Atrophy involves a combination of clinical evaluation, genetic testing, and imaging studies. Recognizing the symptoms early can help manage the condition more effectively.
- An eye exam can reveal characteristic changes in the retina, such as areas of atrophy or thinning.
- Electroretinography (ERG) measures the electrical responses of the retina to light, helping to assess retinal function.
- Genetic testing can confirm the presence of mutations in the OAT gene.
- Blood tests may show elevated levels of ornithine, an amino acid that accumulates due to the enzyme deficiency.
- Visual field testing can help determine the extent of peripheral vision loss.
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT) provides detailed images of the retina, revealing structural changes.
- Fluorescein angiography involves injecting a dye into the bloodstream to highlight blood vessels in the retina.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for Gyrate Atrophy, various treatments can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression. Early intervention is key to preserving vision for as long as possible.
- Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) supplementation can reduce ornithine levels in some patients, slowing retinal degeneration.
- A low-protein diet may help lower ornithine levels, though it requires careful monitoring by a healthcare professional.
- Regular eye exams are essential to monitor disease progression and adjust treatment as needed.
- Visual aids, such as magnifiers or special glasses, can help individuals with vision loss maintain independence.
- Occupational therapy can teach adaptive techniques for daily living activities.
- Genetic counseling is recommended for affected individuals and their families to understand the inheritance pattern and risks for future children.
- Research is ongoing to explore potential gene therapies and other treatments for Gyrate Atrophy.
Living with Gyrate Atrophy
Living with Gyrate Atrophy presents unique challenges, but with the right support and resources, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Awareness and education are crucial for managing this condition.
- Support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice for individuals and families affected by Gyrate Atrophy.
- Low vision specialists can offer personalized recommendations for visual aids and adaptive devices.
- Schools and workplaces may need to make accommodations to support individuals with vision loss.
- Mobility training can help individuals navigate their environment safely and confidently.
- Mental health support is important, as vision loss can impact emotional well-being.
- Staying informed about the latest research and treatment options can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their care.
- Advocacy for accessibility and inclusion can help improve the quality of life for those with Gyrate Atrophy.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand Gyrate Atrophy and develop new treatments. Advances in genetics and ophthalmology hold promise for the future.
- Scientists are investigating the potential of gene therapy to correct the underlying genetic defect in Gyrate Atrophy.
- Stem cell research may offer new avenues for regenerating damaged retinal tissue.
- Clinical trials are testing new drugs and treatments to slow or halt disease progression.
- Advances in imaging technology are improving our ability to diagnose and monitor retinal diseases.
- Collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and patient advocacy groups is essential for advancing our understanding of Gyrate Atrophy.
- Public awareness campaigns can help increase funding and support for research efforts.
- Personalized medicine approaches are being explored to tailor treatments to individual genetic profiles.
- International registries and databases are being developed to track cases of Gyrate Atrophy and facilitate research.
- Patient participation in research studies is crucial for advancing knowledge and developing new treatments.
- Advances in genetic testing are making it easier to identify carriers of the OAT gene mutation.
- Continued investment in research and innovation is essential for improving outcomes for individuals with Gyrate Atrophy.
Final Thoughts on Gyrate Atrophy
Gyrate Atrophy of the Choroid and Retina is a rare genetic disorder that affects vision. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments can help those affected manage their condition better. Early diagnosis is crucial for slowing progression and preserving vision. Regular eye exams and a low-protein diet can make a significant difference. Genetic counseling is also recommended for families with a history of this condition.
While there's no cure yet, ongoing research offers hope for future treatments. Staying informed and proactive can improve quality of life for those living with Gyrate Atrophy. Remember, knowledge is power. The more you know about this condition, the better equipped you'll be to handle its challenges. Keep an eye on new developments and consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
