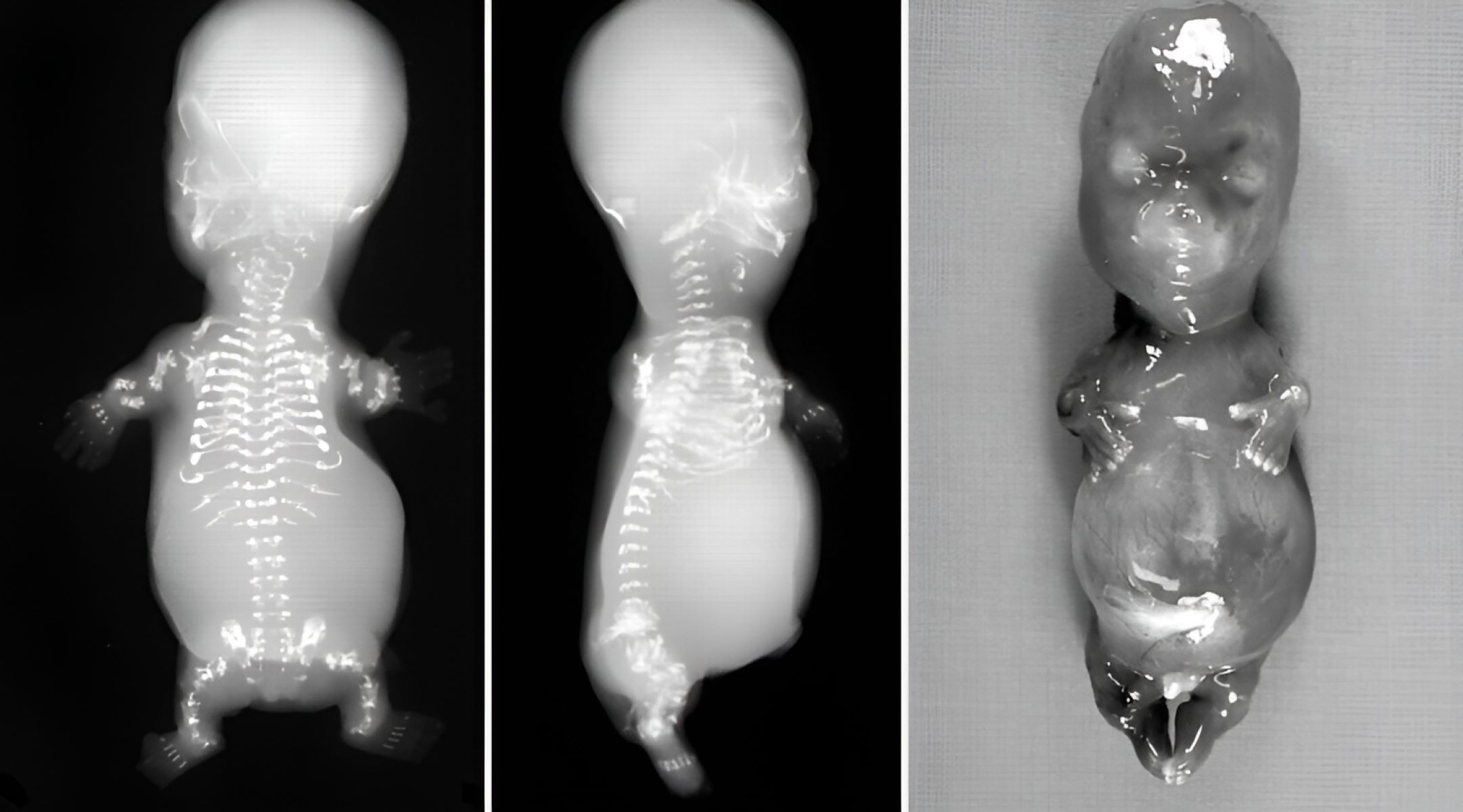
What is Greenberg Dysplasia? Greenberg Dysplasia, also known as Hydrops-Ectopic Calcification-Moth-Eaten Skeletal Dysplasia (HEM), is a rare genetic disorder. It affects bone development, leading to skeletal abnormalities. This condition is caused by mutations in the LBR gene, which plays a role in cholesterol metabolism and nuclear membrane structure. Babies with Greenberg Dysplasia often have severe skeletal malformations, including short limbs and abnormal bone formation. Sadly, this disorder is usually fatal before or shortly after birth. Why is it important to learn about Greenberg Dysplasia? Understanding this condition helps researchers and doctors improve genetic counseling and prenatal diagnosis. Although rare, studying such disorders can provide insights into bone development and genetic mutations. Families affected by Greenberg Dysplasia can benefit from support and resources tailored to their unique needs.
Key Takeaways:
- Greenberg Dysplasia is a rare genetic disorder causing severe skeletal abnormalities. It's typically lethal in the prenatal or neonatal period, impacting families emotionally and financially. Research and support networks offer hope and resources.
- Genetic counseling and family planning play a crucial role in helping families understand the risks and make informed decisions about Greenberg Dysplasia. Building a supportive community is essential for families facing this rare disorder.
What is Greenberg Dysplasia?
Greenberg Dysplasia is a rare genetic disorder that affects bone development. It's a condition that can lead to severe skeletal abnormalities. Understanding this disorder can help us appreciate the complexities of human genetics and the challenges faced by those affected.
-
Genetic Origin: Greenberg Dysplasia is caused by mutations in the LBR gene. This gene plays a crucial role in the development of the nuclear envelope, which is essential for proper cell function.
-
Inheritance Pattern: The disorder follows an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern. This means both parents must carry a copy of the mutated gene for a child to be affected.
-
Skeletal Abnormalities: Individuals with this condition often have severe skeletal abnormalities, including short limbs and a small chest.
-
Prenatal Diagnosis: It can be diagnosed prenatally through ultrasound and genetic testing. This allows families to prepare and make informed decisions.
-
Lethality: Unfortunately, Greenberg Dysplasia is typically lethal in the prenatal or neonatal period. Most affected infants do not survive long after birth.
Symptoms and Characteristics
The symptoms of Greenberg Dysplasia are profound and can be identified early in development. These characteristics are crucial for diagnosis and understanding the severity of the condition.
-
Hydrops Fetalis: A common symptom is hydrops fetalis, a condition where fluid accumulates in the fetus, leading to swelling.
-
Distinctive Facial Features: Affected individuals may have distinctive facial features, including a flat face and a small jaw.
-
Underdeveloped Lungs: Lung development is often severely affected, contributing to the high mortality rate.
-
Shortened Long Bones: The long bones in the arms and legs are significantly shortened, a hallmark of the disorder.
-
Abnormal Rib Cage: The rib cage is often underdeveloped, which can lead to respiratory issues.
Diagnosis and Testing
Diagnosing Greenberg Dysplasia involves a combination of imaging and genetic testing. Early detection is key for managing expectations and planning.
-
Ultrasound Imaging: Ultrasound can reveal skeletal abnormalities and other signs of the disorder during pregnancy.
-
Genetic Testing: Confirmatory genetic testing can identify mutations in the LBR gene, providing a definitive diagnosis.
-
Family History: A detailed family history can help assess the risk of recurrence in future pregnancies.
-
Amniocentesis: This procedure can be used to obtain fetal cells for genetic analysis.
-
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS): CVS is another method to obtain fetal tissue for genetic testing early in pregnancy.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for Greenberg Dysplasia, understanding treatment options can help manage symptoms and provide support to families.
-
Supportive Care: Palliative care focuses on providing comfort and support to affected infants and their families.
-
Genetic Counseling: Families can benefit from genetic counseling to understand the risks and implications of the disorder.
-
Research and Trials: Ongoing research aims to better understand the disorder and explore potential treatments.
-
Psychological Support: Families may require psychological support to cope with the emotional impact of the diagnosis.
-
Community Resources: Connecting with support groups and communities can provide valuable resources and support.
Research and Future Directions
Research into Greenberg Dysplasia is ongoing, with scientists striving to uncover more about its genetic basis and potential interventions.
-
Gene Therapy Potential: While still in early stages, gene therapy holds potential for future treatment options.
-
Animal Models: Researchers use animal models to study the disorder and test potential therapies.
-
Understanding LBR Gene: Further research into the LBR gene may reveal insights into other related conditions.
-
Collaborative Efforts: International collaborations are crucial for advancing research and sharing knowledge.
-
Raising Awareness: Increasing awareness about Greenberg Dysplasia can lead to better support and funding for research.
Impact on Families
The impact of Greenberg Dysplasia extends beyond the affected individual, deeply affecting families and communities.
-
Emotional Toll: The diagnosis can be emotionally challenging for families, requiring strong support systems.
-
Financial Strain: Medical expenses and care can place a significant financial burden on families.
-
Advocacy and Awareness: Families often become advocates, raising awareness and supporting research efforts.
-
Community Support: Building a network of support can help families navigate the challenges of the disorder.
-
Educational Resources: Access to educational resources can empower families to make informed decisions.
Genetic Counseling and Family Planning
Genetic counseling plays a vital role in helping families understand the risks and make informed decisions about family planning.
-
Risk Assessment: Genetic counselors assess the risk of recurrence in future pregnancies.
-
Carrier Testing: Testing for carrier status can help identify individuals at risk of passing on the disorder.
-
Reproductive Options: Families can explore reproductive options, such as IVF with genetic screening, to reduce the risk of recurrence.
-
Informed Decision-Making: Counseling provides families with the information needed to make informed decisions about family planning.
-
Supportive Environment: Genetic counselors create a supportive environment for discussing sensitive topics.
Community and Support Networks
Building a strong community and support network is essential for families affected by Greenberg Dysplasia.
-
Online Communities: Online forums and social media groups provide a platform for sharing experiences and support.
-
Support Groups: Local support groups offer in-person connections and resources.
-
Educational Workshops: Workshops and seminars provide valuable information and resources for families.
-
Advocacy Organizations: Organizations dedicated to rare genetic disorders can offer support and advocacy.
-
Peer Support: Connecting with other families facing similar challenges can provide comfort and understanding.
Final Thoughts on Greenberg Dysplasia
Greenberg Dysplasia, a rare genetic disorder, presents unique challenges for those affected. Understanding its genetic basis is crucial for developing potential treatments. This condition, caused by mutations in the LAMIN B receptor gene, leads to severe skeletal abnormalities and often results in prenatal lethality. While research is ongoing, advancements in genetic testing offer hope for early diagnosis and better management strategies.
Families dealing with this disorder face emotional and medical hurdles, making support networks and genetic counseling essential. Raising awareness can drive further research and support for affected individuals and their families. Though the journey is tough, each step forward in understanding and managing Greenberg Dysplasia brings us closer to improving lives. By fostering collaboration among scientists, healthcare providers, and families, we can continue to make strides in addressing the challenges posed by this rare condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
