Granulomatous Allergic Angiitis, also known as Churg-Strauss Syndrome, is a rare autoimmune disorder that affects small to medium-sized blood vessels. This condition primarily impacts individuals with a history of asthma or allergies. Symptoms can vary widely but often include asthma, sinusitis, skin rashes, and nerve pain. The exact cause remains unknown, but it is believed to involve an overactive immune response. Diagnosis typically involves blood tests, imaging studies, and sometimes a biopsy. Treatment usually includes corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs to control inflammation. Understanding this complex disease can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Key Takeaways:
- Granulomatous Allergic Angiitis, or Churg-Strauss Syndrome, is a rare autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation of blood vessels and can affect multiple organs. Early recognition of symptoms is crucial for better management.
- Treatment focuses on reducing inflammation and managing symptoms. Lifestyle adjustments, ongoing medical care, and support from healthcare providers and loved ones are essential for living with Granulomatous Allergic Angiitis.
What is Granulomatous Allergic Angiitis?
Granulomatous Allergic Angiitis, also known as Churg-Strauss Syndrome, is a rare autoimmune disorder. It causes inflammation of blood vessels, leading to restricted blood flow and damage to organs.
- Rare Disease: Only about 2-5 people per million are diagnosed with Granulomatous Allergic Angiitis each year.
- Autoimmune Disorder: The body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own blood vessels.
- Named After Doctors: The syndrome is named after Dr. Jacob Churg and Dr. Lotte Strauss, who first described it in 1951.
- Affects Multiple Organs: It can impact the lungs, skin, heart, kidneys, and nervous system.
- Three Phases: The disease progresses through allergic, eosinophilic, and vasculitic phases.
Symptoms of Granulomatous Allergic Angiitis
Symptoms vary widely but often include respiratory issues, skin rashes, and nerve pain. Recognizing these signs early can lead to better management.
- Asthma: Most patients develop asthma, often severe and difficult to control.
- Sinusitis: Chronic sinus infections are common.
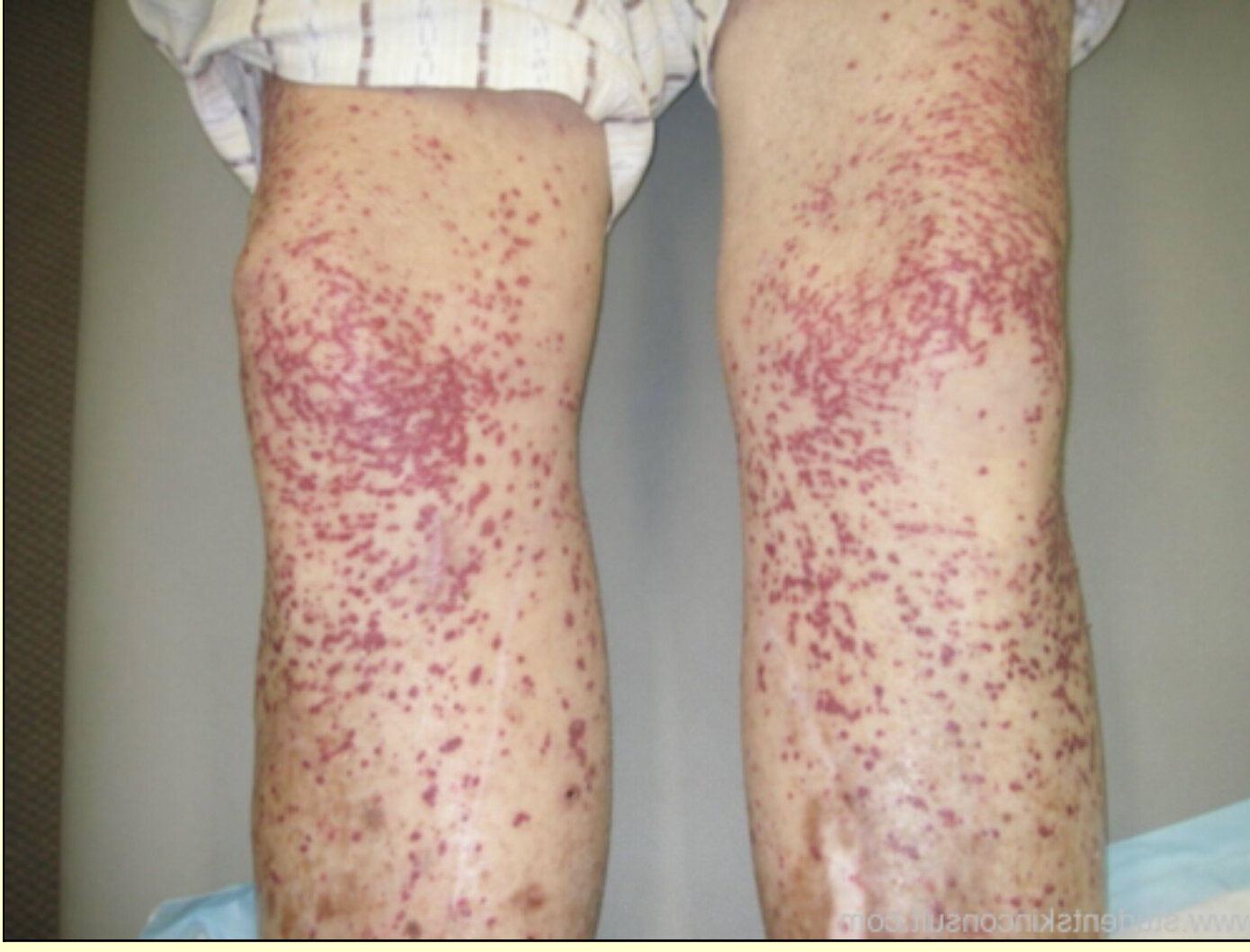
- Skin Rashes: Red or purplish spots, often on the legs, are a typical symptom.
- Nerve Pain: Tingling, numbness, or pain in the hands and feet can occur.
- Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss is a frequent symptom.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause remains unknown, but several factors may increase the risk of developing this condition.
- Genetic Factors: A family history of autoimmune diseases can increase risk.
- Environmental Triggers: Exposure to certain allergens or infections might trigger the disease.
- Medications: Some asthma medications have been linked to the onset of Granulomatous Allergic Angiitis.
- Age: Most commonly diagnosed in adults aged 30-50.
- Gender: Slightly more common in males than females.
Diagnosis of Granulomatous Allergic Angiitis
Diagnosing this condition can be challenging due to its rarity and varied symptoms. Multiple tests are often required.
- Blood Tests: Elevated levels of eosinophils, a type of white blood cell, are a key indicator.
- Biopsy: Tissue samples from affected organs can confirm the diagnosis.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs help identify organ damage.
- Pulmonary Function Tests: Assess lung function and detect asthma.
- Nerve Conduction Studies: Evaluate nerve damage and function.
Treatment Options
Treatment focuses on reducing inflammation and managing symptoms. Early intervention can improve outcomes.
- Corticosteroids: Prednisone is commonly used to reduce inflammation.
- Immunosuppressants: Medications like cyclophosphamide help control the immune system.
- Biologics: Drugs like mepolizumab target specific immune cells.
- Physical Therapy: Helps manage nerve pain and improve mobility.
- Regular Monitoring: Frequent check-ups are essential to adjust treatment plans.
Complications of Granulomatous Allergic Angiitis
Without proper treatment, this condition can lead to severe complications affecting various organs.
- Heart Disease: Inflammation can lead to heart attacks or heart failure.
- Kidney Damage: Reduced blood flow can cause kidney failure.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Inflammation can lead to abdominal pain, bleeding, or perforation.
- Peripheral Neuropathy: Severe nerve damage can result in permanent loss of sensation or movement.
- Lung Damage: Chronic asthma and lung inflammation can cause long-term respiratory issues.
Living with Granulomatous Allergic Angiitis
Managing this condition requires lifestyle adjustments and ongoing medical care. Support from healthcare providers and loved ones is crucial.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet can help manage symptoms and improve overall health.
- Exercise: Regular, low-impact exercise can enhance physical and mental well-being.
- Stress Management: Techniques like meditation or yoga can reduce stress and improve quality of life.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others facing similar challenges can provide emotional support.
- Medication Adherence: Taking medications as prescribed is vital for controlling the disease.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand this condition and develop more effective treatments.
- Genetic Studies: Researchers are exploring genetic factors that may contribute to the disease.
- New Medications: Clinical trials are testing new drugs to improve treatment outcomes.
- Biomarkers: Identifying biomarkers can help diagnose the disease earlier and more accurately.
- Patient Registries: Collecting data from patients worldwide helps researchers track the disease's progression and response to treatments.
- Public Awareness: Increasing awareness can lead to earlier diagnosis and better support for those affected.
Final Thoughts on Granulomatous Allergic Angiitis
Granulomatous Allergic Angiitis, also known as Churg-Strauss Syndrome, is a rare but serious condition. It causes inflammation of blood vessels, leading to various symptoms like asthma, sinusitis, and nerve damage. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing this disease effectively. Treatments often include corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs to reduce inflammation and control symptoms. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers help monitor the condition and adjust treatments as needed. Understanding the symptoms and seeking medical advice early can make a significant difference in outcomes. Stay informed, consult specialists, and don't ignore persistent symptoms. Knowledge and proactive healthcare can improve quality of life for those affected by this condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
