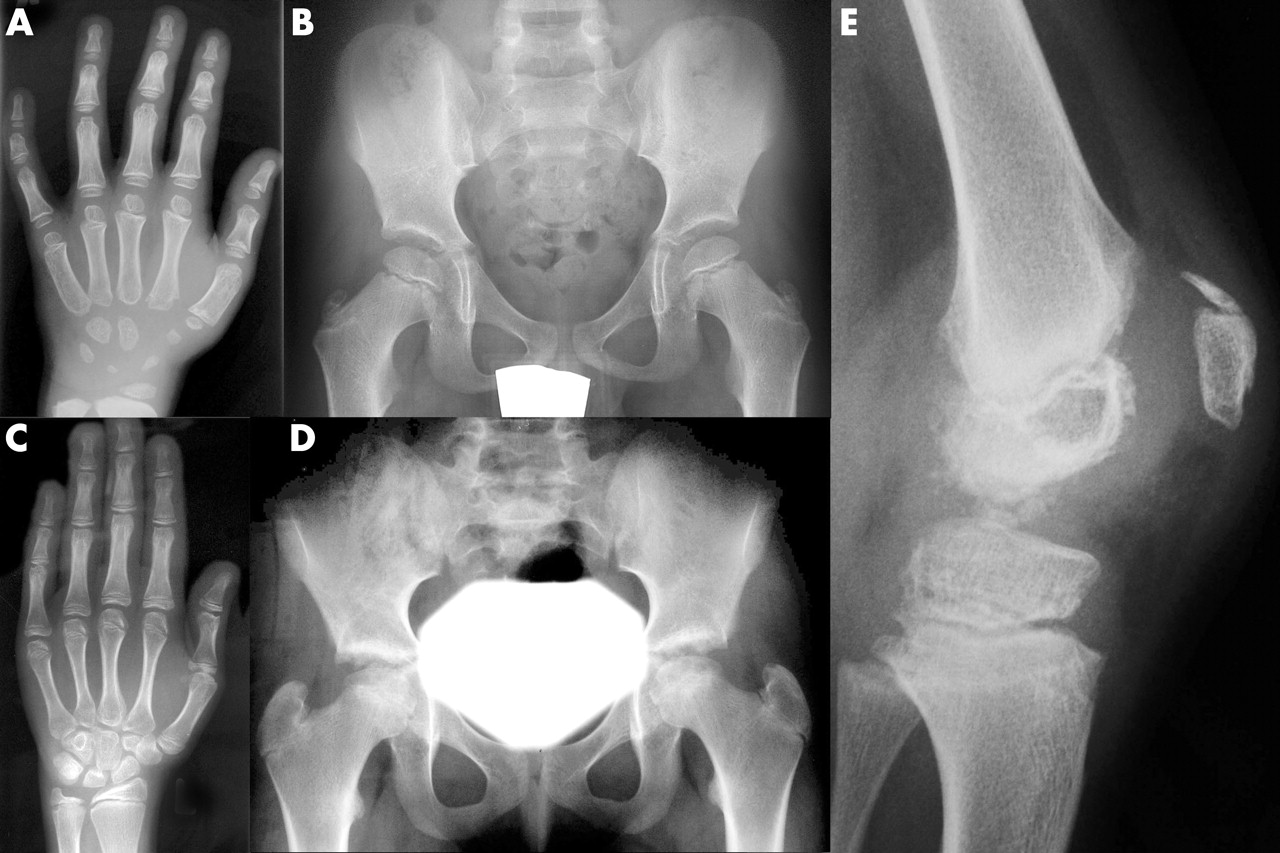
Epiphyseal Dysplasia is a rare genetic disorder affecting bone growth, particularly in the long bones and spine. This condition often leads to short stature, joint pain, and early-onset arthritis. Epiphyseal Dysplasia can manifest in various forms, each with unique characteristics and severity. Understanding this disorder is crucial for early diagnosis and management, which can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected. In this blog post, we will explore 40 intriguing facts about Epiphyseal Dysplasia, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Whether you're a medical professional, a student, or someone seeking knowledge, these facts will provide valuable insights into this complex condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Epiphyseal Dysplasia affects bone growth, causing joint pain and short stature. Early diagnosis and a multidisciplinary approach can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Living with Epiphyseal Dysplasia presents challenges, but early intervention, adaptive activities, and social support can help individuals lead fulfilling lives. Self-advocacy and mental health support are crucial.
What is Epiphyseal Dysplasia?
Epiphyseal Dysplasia is a group of disorders affecting the growth of bones, particularly at the ends where growth plates are located. These conditions can lead to short stature, joint pain, and other skeletal abnormalities. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this condition.
-
Epiphyseal Dysplasia primarily affects the growth plates, which are areas of developing cartilage tissue near the ends of long bones.
-
There are multiple types of Epiphyseal Dysplasia, including multiple epiphyseal dysplasia (MED) and spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia (SED).
-
MED is characterized by irregular growth of the epiphyses, leading to joint pain and early-onset arthritis.
-
SED affects both the spine and the epiphyses of long bones, often resulting in a shorter trunk and neck.
-
Genetic mutations are the primary cause of Epiphyseal Dysplasia, with different genes involved in different types.
-
Inheritance patterns can vary; some forms are inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, while others are autosomal recessive.
-
Symptoms often appear in early childhood, though the severity can vary widely among individuals.
-
Joint pain is a common symptom, often worsening with age due to early-onset osteoarthritis.
-
Short stature is another hallmark of the condition, with affected individuals often being significantly shorter than their peers.
-
X-rays are commonly used to diagnose Epiphyseal Dysplasia, revealing irregularities in the growth plates and bones.
How is Epiphyseal Dysplasia Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Epiphyseal Dysplasia involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and genetic testing. Here are some key facts about the diagnostic process.
-
Clinical evaluation includes a thorough physical examination and assessment of growth patterns.
-
Family history is crucial, as many forms of Epiphyseal Dysplasia are inherited.
-
X-rays can show characteristic changes in the bones, such as irregular epiphyses and shortened long bones.
-
MRI scans may be used to get a more detailed view of the cartilage and soft tissues.
-
Genetic testing can confirm the diagnosis by identifying mutations in specific genes associated with the condition.
-
Prenatal diagnosis is possible for some forms, allowing for early intervention and planning.
-
Differential diagnosis is important to rule out other conditions with similar symptoms, such as rickets or other skeletal dysplasias.
-
Growth charts are used to track the child's growth over time and identify any deviations from typical patterns.
-
Joint function assessments help determine the extent of joint involvement and guide treatment plans.
-
Multidisciplinary approach often involves pediatricians, geneticists, orthopedic surgeons, and physical therapists.
Treatment and Management of Epiphyseal Dysplasia
While there is no cure for Epiphyseal Dysplasia, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Here are some important facts about treatment and management.
-
Physical therapy is often recommended to maintain joint mobility and muscle strength.
-
Pain management strategies include medications, physical therapy, and sometimes surgical interventions.
-
Orthopedic surgery may be necessary to correct severe joint deformities or improve function.
-
Growth hormone therapy has been used in some cases to promote growth, though its effectiveness varies.
-
Assistive devices like braces or orthotics can help support joints and improve mobility.
-
Regular monitoring by healthcare professionals is essential to track the progression of the condition and adjust treatments as needed.
-
Nutritional support ensures that children with Epiphyseal Dysplasia receive adequate nutrients for bone health.
-
Psychosocial support helps children and families cope with the emotional and social challenges of living with a chronic condition.
-
Patient education empowers families with knowledge about the condition and its management.
-
Research is ongoing to better understand the genetic causes and develop new treatments for Epiphyseal Dysplasia.
Living with Epiphyseal Dysplasia
Living with Epiphyseal Dysplasia can present unique challenges, but with the right support and resources, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Here are some facts about daily life with this condition.
-
Early intervention can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life.
-
Adaptive sports and activities allow children to participate in physical activities safely.
-
Educational accommodations may be necessary to support learning and participation in school.
-
Social support from family, friends, and support groups can provide emotional and practical assistance.
-
Self-advocacy is important for individuals to communicate their needs and access appropriate resources.
-
Employment considerations may include finding jobs that accommodate physical limitations.
-
Independent living skills can be developed with the help of occupational therapists.
-
Mental health support is crucial, as chronic conditions can impact emotional well-being.
-
Community resources such as support groups and organizations can provide valuable information and connections.
-
Technological aids like mobility devices and communication tools can enhance independence and quality of life.
Final Thoughts on Epiphyseal Dysplasia
Epiphyseal dysplasia, a rare genetic disorder, affects bone growth and development. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments can help those affected manage their condition better. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and improving quality of life.
Medical advancements have made it possible to address many challenges associated with this disorder. Genetic counseling and regular check-ups play a significant role in managing the condition. Support from family, friends, and healthcare professionals is essential for those living with epiphyseal dysplasia.
Raising awareness about this condition can lead to better support systems and resources for affected individuals. Knowledge empowers people to make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
By staying informed and proactive, individuals with epiphyseal dysplasia can lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges they face. Let's continue to support and advocate for those affected by this rare disorder.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
