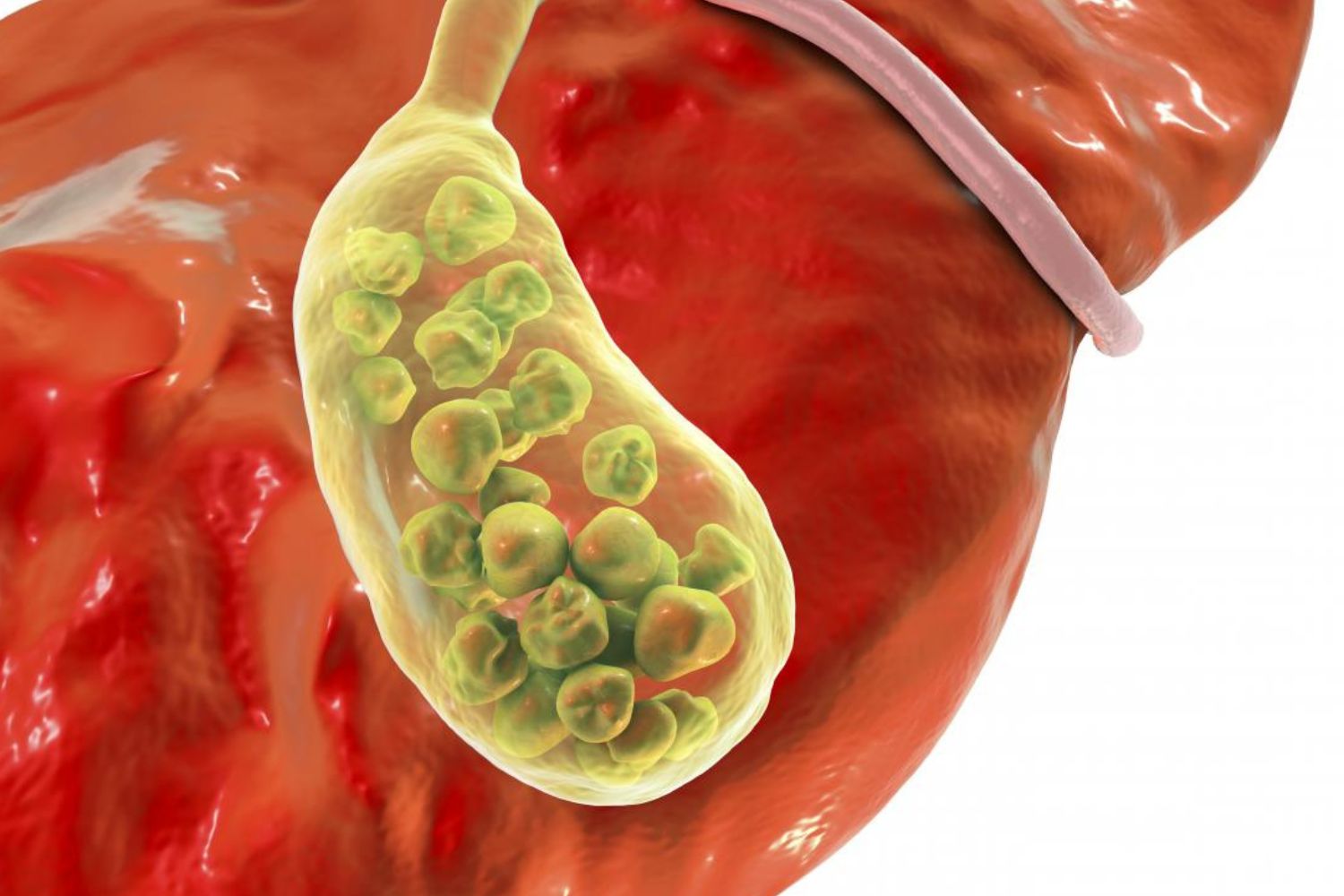
Courvoisier's Law is a fascinating principle in medicine that helps doctors diagnose the cause of jaundice. Named after the Swiss surgeon Ludwig Courvoisier, this law states that if a patient has jaundice and a palpable gallbladder, the cause is unlikely to be gallstones. Instead, it suggests a different underlying issue, often a tumor. This principle has guided countless medical professionals in their diagnostic processes, making it a cornerstone in the field of hepatobiliary medicine. Understanding Courvoisier's Law can provide valuable insights into the complexities of diagnosing jaundice and highlight the importance of thorough physical examinations.
Key Takeaways:
- Courvoisier's Law helps doctors diagnose jaundice by feeling the patient's gallbladder. If it's swollen and the patient has jaundice, it's likely not gallstones causing the issue. Instead, it could be something else like a tumor.
- While Courvoisier's Law is a helpful tool for diagnosing jaundice, it's not foolproof. Doctors need to use it alongside other tests and their experience to make accurate diagnoses and treatment decisions.
What is Courvoisier's Law?
Courvoisier's Law is a principle in medicine that helps doctors diagnose the cause of jaundice. Named after the Swiss surgeon Ludwig Courvoisier, it states that if a patient has jaundice and a palpable gallbladder, the cause is unlikely to be gallstones. Instead, it suggests a different underlying issue.
- Origin: Courvoisier's Law was first described by Ludwig Courvoisier in 1890.
- Jaundice: This condition causes yellowing of the skin and eyes due to high bilirubin levels.
- Palpable Gallbladder: A gallbladder that can be felt through the skin is considered palpable.
- Gallstones: These are hardened deposits of digestive fluid that can form in the gallbladder.
- Diagnosis Aid: Courvoisier's Law helps differentiate between causes of jaundice.
- Non-Gallstone Causes: Conditions like tumors or strictures are often the culprits if the gallbladder is palpable.
How Does Courvoisier's Law Work?
Understanding how Courvoisier's Law works can help medical professionals make more accurate diagnoses. It relies on the relationship between the gallbladder and bile ducts.
- Bile Ducts: These tubes carry bile from the liver and gallbladder to the small intestine.
- Bile Flow: When bile flow is blocked, it can cause jaundice.
- Gallbladder Enlargement: If the blockage is gradual, the gallbladder can enlarge without pain.
- Painful Gallstones: Gallstones usually cause pain and do not lead to a palpable gallbladder.
- Tumors: Tumors can block bile ducts slowly, causing the gallbladder to enlarge.
- Strictures: Narrowing of the bile ducts can also lead to a palpable gallbladder.
Clinical Significance of Courvoisier's Law
Courvoisier's Law is significant in clinical settings, guiding doctors in their diagnostic process. It helps narrow down potential causes of jaundice.
- Diagnostic Tool: It serves as a tool for diagnosing jaundice causes.
- Non-Invasive: The law relies on physical examination, making it non-invasive.
- Early Detection: Helps in the early detection of serious conditions like tumors.
- Surgical Decisions: Influences decisions regarding the need for surgery.
- Patient History: Combined with patient history, it provides a clearer diagnostic picture.
- Imaging Tests: Often followed by imaging tests like ultrasound or CT scans.
Limitations of Courvoisier's Law
While useful, Courvoisier's Law has its limitations. It is not foolproof and should be used in conjunction with other diagnostic methods.
- Exceptions: There are exceptions where gallstones can cause a palpable gallbladder.
- False Positives: Conditions like chronic cholecystitis can lead to false positives.
- False Negatives: Some tumors may not cause a palpable gallbladder.
- Complementary Tests: Should be used alongside other tests for accurate diagnosis.
- Experience: Requires clinical experience to interpret correctly.
- Not Absolute: It is a guideline, not an absolute rule.
Historical Context of Courvoisier's Law
Understanding the historical context of Courvoisier's Law provides insight into its development and application in modern medicine.
- Ludwig Courvoisier: A Swiss surgeon who first described the law in the late 19th century.
- Medical Advances: Reflects the medical knowledge and practices of the time.
- Evolution: The law has evolved with advancements in medical imaging and diagnostics.
- Historical Cases: Early cases helped establish the validity of the law.
- Medical Education: Taught in medical schools as part of diagnostic training.
- Continued Relevance: Remains relevant despite advancements in medical technology.
Practical Applications of Courvoisier's Law
In practice, Courvoisier's Law is applied in various clinical scenarios to aid in the diagnosis and treatment of patients with jaundice.
- Physical Examination: Used during the physical examination of patients with jaundice.
- Differential Diagnosis: Helps differentiate between gallstones and other causes.
- Treatment Planning: Influences treatment plans and surgical decisions.
- Patient Management: Aids in the overall management of patients with jaundice.
- Case Studies: Numerous case studies highlight its practical applications.
- Medical Protocols: Incorporated into medical protocols and guidelines.
Modern Perspectives on Courvoisier's Law
Modern medicine continues to use Courvoisier's Law, but with a more nuanced understanding and advanced diagnostic tools.
- Imaging Technology: Modern imaging technology complements the law.
- Multidisciplinary Approach: Used alongside a multidisciplinary approach to diagnosis.
- Research: Ongoing research continues to refine its application.
- Patient Outcomes: Contributes to improved patient outcomes through accurate diagnosis.
The Final Sip
Courvoisier's Law isn't just a quirky name; it's a fascinating principle that explains how light behaves. Named after the French physicist, this law helps us understand why light bends when it passes through different materials. It's used in everything from designing lenses to creating optical illusions. Knowing these 40 facts about Courvoisier's Law gives you a deeper appreciation for the science behind everyday phenomena. Whether you're a student, a teacher, or just curious, these insights can make you see the world in a new light. So next time you look through a glass of water or put on a pair of glasses, remember the science that makes it all possible. Cheers to learning something new!
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
