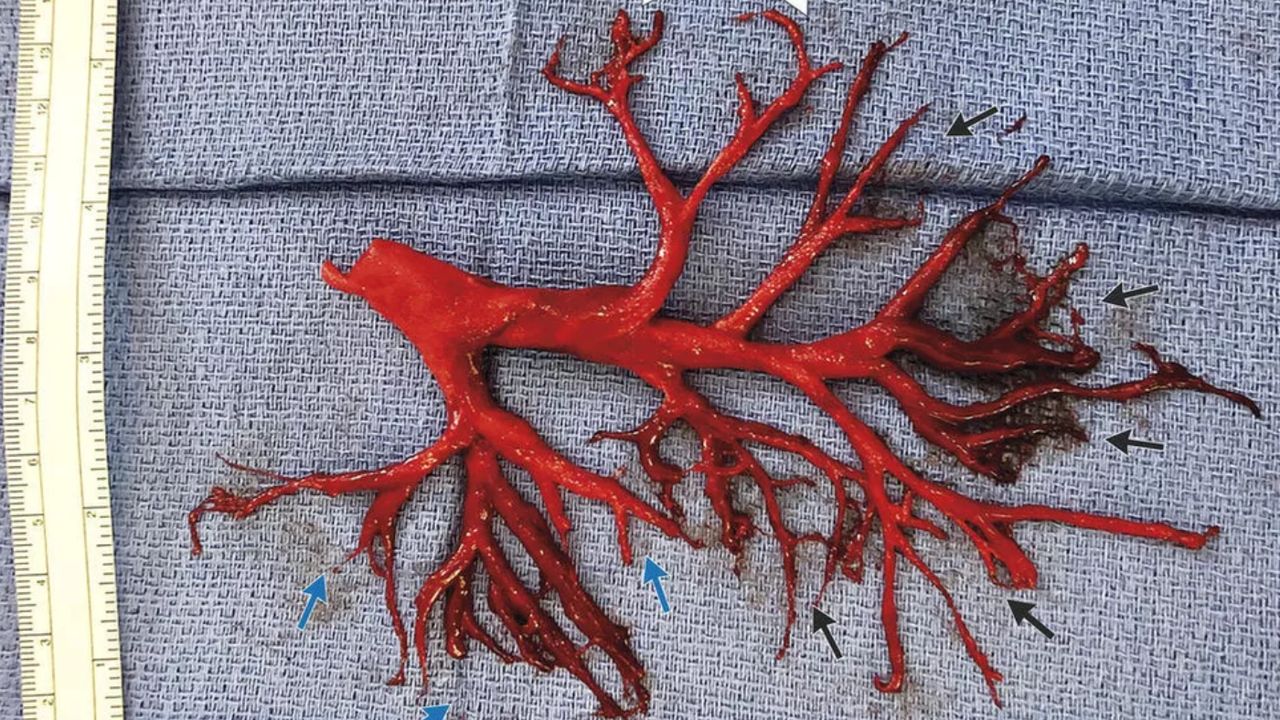
What is a bronchial tree blood clot? A bronchial tree blood clot is a blockage in the network of airways within the lungs. These airways, known as the bronchial tree, branch out like a tree from the trachea into smaller bronchi and bronchioles. When a blood clot forms in these passages, it can obstruct airflow, leading to serious health issues. Symptoms might include shortness of breath, chest pain, and coughing up blood. Causes range from trauma to underlying medical conditions like deep vein thrombosis. Understanding these clots is crucial for timely treatment and preventing complications. Let's dive into 37 essential facts about bronchial tree blood clots.
Key Takeaways:
- Blood clots in the bronchial tree can cause breathing problems and chest pain. They can be diagnosed through CT scans and treated with blood thinners or surgery.
- Lifestyle changes like regular exercise and staying hydrated can help prevent blood clots. Early detection and treatment are crucial for a better prognosis.
Understanding the Bronchial Tree
The bronchial tree is a vital part of the respiratory system. It consists of the bronchi and bronchioles, which carry air to the lungs. Blood clots in this area can be serious and require immediate attention.
- The bronchial tree starts at the trachea and branches into the left and right bronchi.
- Each bronchus further divides into smaller bronchioles, resembling a tree's branches.
- The primary function of the bronchial tree is to distribute air to the lungs.
- Bronchi are lined with cilia and mucus to trap and expel foreign particles.
- Bronchioles lack cartilage, making them more flexible but also more prone to collapse.
What is a Blood Clot?
A blood clot is a mass of blood that changes from a liquid to a gel-like state. While clots are essential for stopping bleeding, they can be dangerous when they form inappropriately.
- Blood clots can form in veins or arteries, blocking blood flow.
- Clots in the bronchial tree can obstruct airways, causing breathing difficulties.
- Symptoms of a blood clot in the bronchial tree include shortness of breath, chest pain, and coughing up blood.
- Risk factors for blood clots include smoking, obesity, and prolonged immobility.
- Blood clots can travel from other parts of the body to the bronchial tree, a condition known as pulmonary embolism.
Causes of Bronchial Tree Blood Clots
Understanding the causes can help in prevention and early detection. Various factors contribute to the formation of blood clots in the bronchial tree.
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can lead to clots that travel to the lungs.
- Certain medical conditions, like cancer and heart disease, increase clot risk.
- Surgery, especially on the legs or abdomen, can trigger clot formation.
- Hormonal changes, such as those during pregnancy or from birth control pills, can elevate clot risk.
- Genetic disorders like Factor V Leiden make individuals more prone to clotting.
Diagnosing Blood Clots in the Bronchial Tree
Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Various methods are used to detect blood clots in the bronchial tree.
- A CT scan is often the first step in diagnosing a blood clot.
- Pulmonary angiography provides detailed images of the blood vessels in the lungs.
- D-dimer tests measure a substance released when a blood clot breaks up.
- Ultrasound can detect clots in the legs, which might travel to the lungs.
- MRI scans offer detailed images without radiation exposure.
Treatment Options
Once diagnosed, several treatment options are available. The choice depends on the clot's size, location, and the patient's overall health.
- Anticoagulants, or blood thinners, prevent new clots from forming.
- Thrombolytics dissolve existing clots quickly but carry a higher risk of bleeding.
- Surgical removal of the clot, known as thrombectomy, is an option in severe cases.
- Inferior vena cava (IVC) filters can prevent clots from reaching the lungs.
- Oxygen therapy helps manage symptoms and improve breathing.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing blood clots in the bronchial tree involves lifestyle changes and medical interventions. Awareness and proactive measures can significantly reduce risk.
- Regular exercise improves circulation and reduces clot risk.
- Staying hydrated helps maintain blood flow and prevent clotting.
- Avoiding prolonged immobility, such as during long flights, is crucial.
- Compression stockings can improve blood flow in the legs.
- Medications like aspirin may be prescribed for those at high risk.
Complications and Prognosis
Blood clots in the bronchial tree can lead to serious complications. Understanding potential outcomes helps in managing expectations and treatment plans.
- Pulmonary embolism is a life-threatening condition resulting from clots in the lungs.
- Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) can develop from unresolved clots.
- Recurrent blood clots may indicate an underlying health issue.
- Long-term anticoagulant therapy may be necessary to prevent future clots.
- Early detection and treatment significantly improve prognosis.
Interesting Facts
Here are some lesser-known facts about blood clots in the bronchial tree. These tidbits offer a deeper understanding of this medical condition.
- Blood clots can form in as little as a few minutes.
- The body naturally dissolves small clots, but larger ones require medical intervention.
Final Thoughts on Bronchial Tree Blood Clots
Understanding bronchial tree blood clots can save lives. These clots block airways, causing serious health issues. Recognizing symptoms like shortness of breath, chest pain, and coughing up blood is crucial. Immediate medical attention is vital for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Preventive measures include staying active, avoiding smoking, and managing chronic conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes. Treatments range from blood thinners to surgical interventions.
Awareness and education about bronchial tree blood clots can lead to early detection and better outcomes. Share this knowledge with friends and family to help them stay informed.
Stay proactive about your health. If you experience any symptoms, consult a healthcare professional immediately. Your health is your wealth, so take care of it.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
