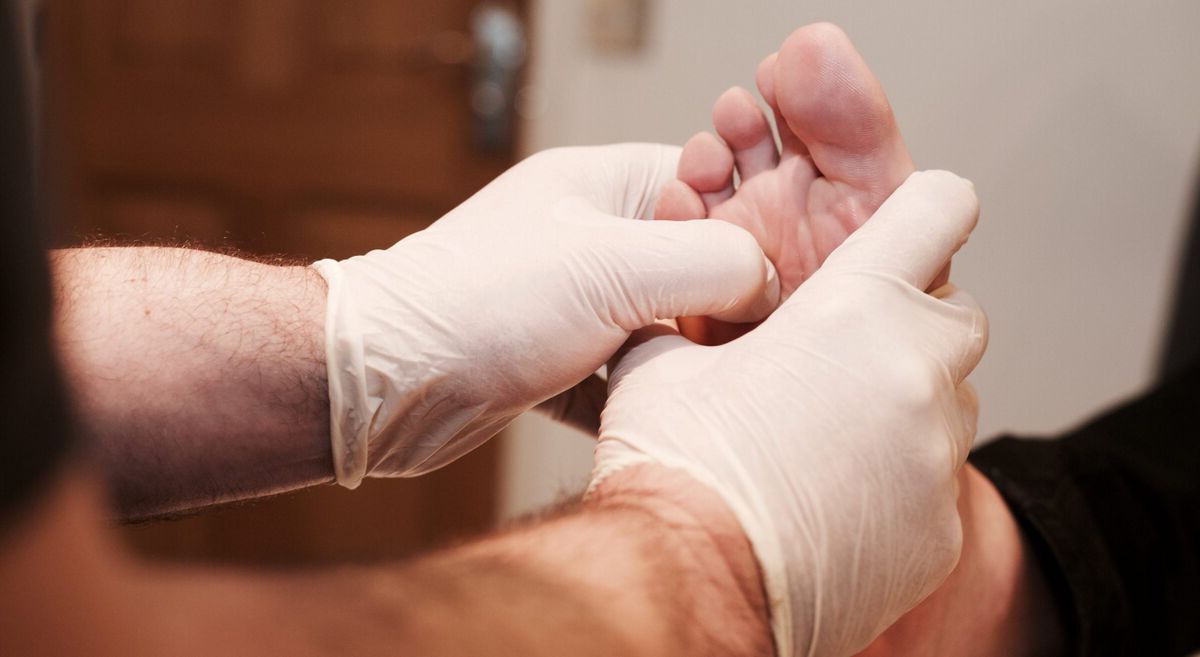
Mulder's Sign is a clinical test used to diagnose Morton's neuroma, a painful condition affecting the ball of the foot. But what exactly is Mulder's Sign? In simple terms, it's a physical maneuver where a doctor squeezes the foot to elicit a clicking sound or sensation, indicating the presence of a neuroma. This test helps pinpoint the source of foot pain, guiding effective treatment. Understanding Mulder's Sign can be crucial for anyone experiencing unexplained foot discomfort. Let's dive into 35 fascinating facts about this diagnostic tool, its history, and its role in modern medicine.
Key Takeaways:
- Mulder's Sign is a test for foot pain. It helps diagnose Morton's neuroma by pressing on the foot to find clicking sounds or pain. It's quick, reliable, and can save costs.
- If you have foot pain, Mulder's Sign can help diagnose Morton's neuroma. Treatment options include orthotics, footwear changes, physical therapy, medications, and surgery. Recovery varies, but most patients experience significant pain relief.
What is Mulder's Sign?
Mulder's Sign is a clinical test used to diagnose Morton's neuroma, a painful condition affecting the ball of the foot. This test is named after the Dutch physician who first described it. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about Mulder's Sign.
-
Origin: Named after Jacob Mulder, a Dutch physician who first described the test in the early 20th century.
-
Purpose: Used primarily to diagnose Morton's neuroma, a condition where a nerve in the foot becomes thickened.
-
Procedure: Involves squeezing the foot while pressing on the affected area to elicit a clicking sound or pain.
-
Clicking Sound: The clicking sound, known as Mulder's click, is a key indicator of Morton's neuroma.
-
Pain: Patients often report sharp, burning pain during the test, which helps in diagnosis.
How is Mulder's Sign Performed?
Performing Mulder's Sign is straightforward but requires precision. Here are the steps involved in the procedure:
-
Patient Position: The patient lies down or sits with the foot relaxed.
-
Foot Squeeze: The examiner squeezes the foot from the sides, compressing the metatarsal heads.
-
Palpation: The examiner uses the other hand to press on the space between the metatarsal heads.
-
Click Detection: A clicking sound or palpable click indicates a positive Mulder's Sign.
-
Pain Assessment: The patient's pain response is noted to confirm the diagnosis.
Why is Mulder's Sign Important?
Mulder's Sign plays a crucial role in diagnosing foot conditions. Here are some reasons why it is important:
-
Early Diagnosis: Helps in the early detection of Morton's neuroma, leading to timely treatment.
-
Non-Invasive: A non-invasive test that can be performed in a clinical setting without any special equipment.
-
Cost-Effective: Saves costs associated with more expensive diagnostic tools like MRI or ultrasound.
-
Quick: The test takes only a few minutes, making it efficient for busy clinics.
-
Reliable: Provides reliable results when performed correctly, aiding in accurate diagnosis.
Symptoms Indicating Mulder's Sign
Certain symptoms can indicate the need for Mulder's Sign. Here are some common ones:
-
Foot Pain: Persistent pain in the ball of the foot, especially between the third and fourth toes.
-
Numbness: Numbness or tingling in the toes, often worsening with activity.
-
Swelling: Swelling in the affected area, sometimes visible.
-
Burning Sensation: A burning sensation in the ball of the foot, often described as "walking on a pebble."
-
Toe Cramping: Cramping or curling of the toes, particularly during physical activity.
Treatment Options After a Positive Mulder's Sign
Once Mulder's Sign is positive, several treatment options are available. Here are some common ones:
-
Orthotics: Custom orthotic devices to relieve pressure on the affected nerve.
-
Footwear Changes: Switching to shoes with a wider toe box and better arch support.
-
Physical Therapy: Exercises and stretches to alleviate symptoms and improve foot mechanics.
-
Medications: Anti-inflammatory medications to reduce pain and swelling.
-
Injections: Corticosteroid injections to provide temporary relief from pain.
Surgical Interventions for Morton's Neuroma
In severe cases, surgery might be necessary. Here are some surgical options:
-
Neurectomy: Surgical removal of the affected nerve to eliminate pain.
-
Decompression: Surgical decompression to relieve pressure on the nerve.
-
Cryosurgery: Freezing the nerve to reduce pain and inflammation.
-
Radiofrequency Ablation: Using radiofrequency energy to destroy the affected nerve tissue.
-
Endoscopic Surgery: Minimally invasive surgery using an endoscope to remove or decompress the nerve.
Recovery and Prognosis
Recovery from Morton's neuroma varies. Here are some key points about recovery and prognosis:
-
Recovery Time: Recovery time can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on the treatment.
-
Physical Therapy: Post-surgical physical therapy can aid in faster recovery and prevent recurrence.
-
Success Rate: Surgical treatments have a high success rate, with most patients experiencing significant pain relief.
-
Recurrence: Recurrence of symptoms is possible, especially if underlying issues like poor footwear are not addressed.
-
Lifestyle Changes: Long-term lifestyle changes, including proper footwear and regular foot exercises, are essential for preventing recurrence.
The Final Word on Mulder's Sign
Mulder's Sign is a key indicator for diagnosing Morton's Neuroma, a condition causing pain in the ball of the foot. This sign involves a clicking sensation when squeezing the foot, pointing to nerve compression. Understanding this sign helps in early detection, leading to better treatment outcomes.
Morton's Neuroma often affects those who wear tight shoes or engage in high-impact activities. Recognizing symptoms like tingling, burning, or numbness between the toes can prompt timely medical advice. Treatments range from footwear changes to surgical options, depending on severity.
Being aware of Mulder's Sign and its implications can make a significant difference in managing foot health. If you experience persistent foot pain, consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. Your feet will thank you!
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
