Tracheal agenesis is a rare congenital condition where the windpipe fails to develop. This anomaly can lead to severe breathing difficulties right after birth. Tracheal agenesis affects approximately 1 in 50,000 births, making it a critical topic for medical professionals and parents alike. Understanding this condition is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. In this blog post, we’ll explore 30 intriguing facts about tracheal agenesis, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and potential treatments. Whether you're a medical student, a concerned parent, or just curious, these facts will provide valuable insights into this rare but significant condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Tracheal agenesis is an extremely rare condition where the windpipe fails to develop, causing severe respiratory distress in newborns. Immediate intervention and ongoing research are crucial for improving survival rates and treatment options.
- Families facing tracheal agenesis experience significant emotional stress, but support groups and healthcare teams provide valuable support. Ongoing research aims to improve understanding and treatment through genetic research and stem cell advancements.
What is Tracheal Agenesis?
Tracheal agenesis is a rare congenital condition where the trachea, or windpipe, fails to develop. This condition is often diagnosed at birth due to severe respiratory distress. Let's explore some fascinating facts about this medical anomaly.
-
Tracheal agenesis occurs in approximately 1 in 50,000 births. This makes it an extremely rare condition, often surprising even seasoned medical professionals.
-
The condition was first described in 1900 by Payne. Despite its rarity, tracheal agenesis has been known to the medical community for over a century.
-
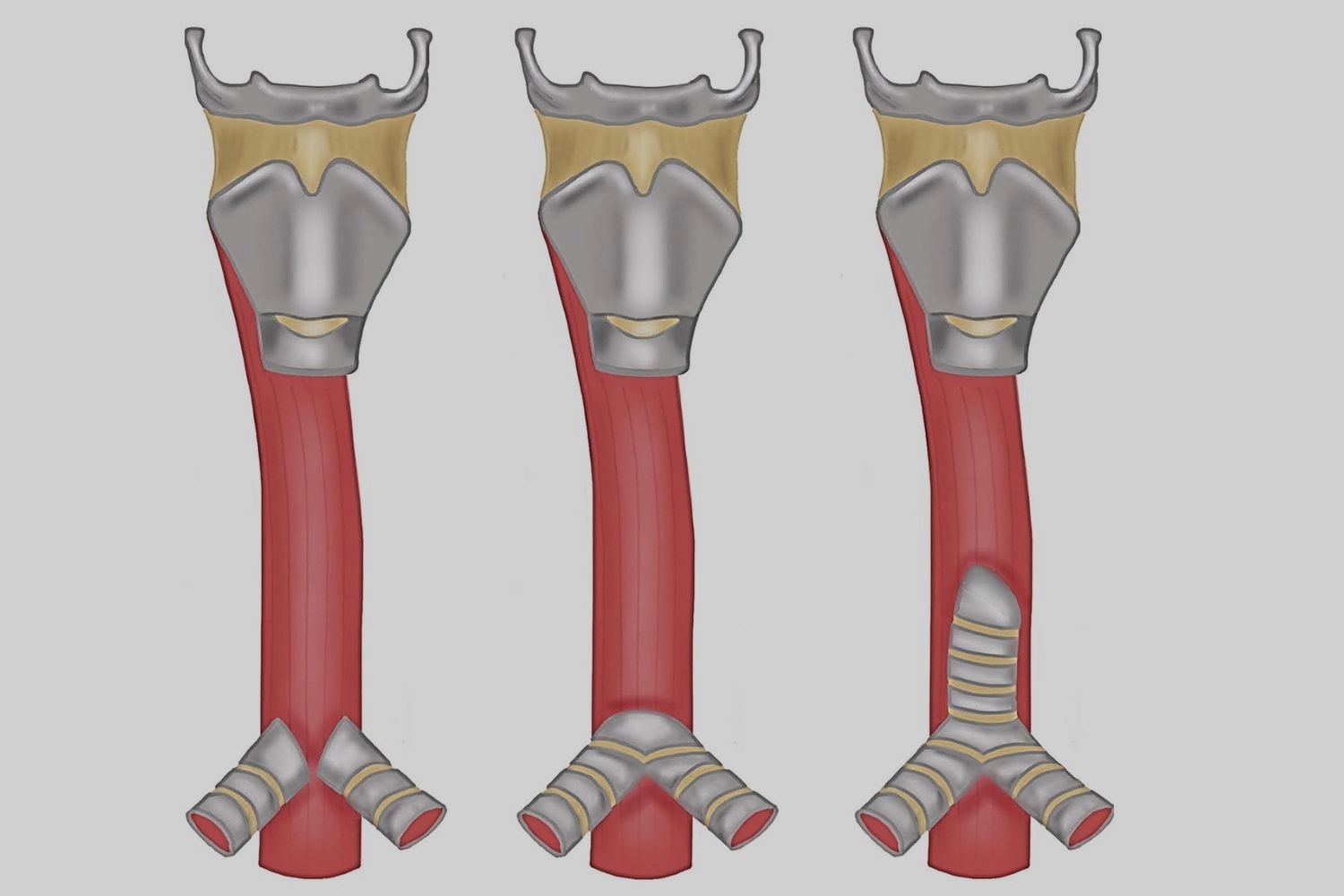
There are three types of tracheal agenesis. Type I involves a partial trachea, Type II has no trachea but a bronchi connection, and Type III lacks both trachea and bronchi.
-
Most infants with tracheal agenesis also have other congenital anomalies. These can include heart defects, gastrointestinal malformations, and limb abnormalities.
-
The exact cause of tracheal agenesis is unknown. Researchers believe it may involve genetic and environmental factors, but no definitive cause has been identified.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms and diagnosing tracheal agenesis can be challenging due to its rarity. Here are some key points to consider.
-
Newborns with tracheal agenesis exhibit severe respiratory distress immediately after birth. This is often the first sign that something is wrong.
-
Cyanosis, or a bluish tint to the skin, is common in affected infants. This occurs due to a lack of oxygen.
-
Diagnosis usually involves imaging techniques like X-rays and MRIs. These help visualize the absence of the trachea and any associated anomalies.
-
Prenatal diagnosis is rare but possible with advanced imaging techniques. Ultrasounds and MRIs can sometimes detect the condition before birth.
-
A definitive diagnosis often requires direct visualization during surgery. This allows doctors to confirm the absence of the trachea and plan for immediate intervention.
Treatment Options
Treating tracheal agenesis is complex and requires a multidisciplinary approach. Here are some treatment facts.
-
Immediate intervention is crucial for survival. Without a trachea, the infant cannot breathe, requiring emergency measures.
-
A tracheostomy is often performed to create an airway. This involves surgically creating an opening in the neck to insert a breathing tube.
-
Long-term treatment may involve reconstructive surgery. Surgeons attempt to create a functional airway using tissue grafts or synthetic materials.
-
Mechanical ventilation is often necessary. This helps maintain adequate oxygen levels while other treatments are being planned.
-
Nutritional support is critical. Many infants with tracheal agenesis have difficulty feeding and require specialized nutritional plans.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Understanding the prognosis and survival rates for tracheal agenesis can provide insight into the challenges faced by affected families.
-
The prognosis for tracheal agenesis is generally poor. Many infants do not survive the initial respiratory distress.
-
Survival rates have improved with advances in medical technology. Early diagnosis and immediate intervention have increased the chances of survival.
-
Long-term outcomes depend on the severity of the condition and associated anomalies. Some children may have ongoing respiratory and developmental issues.
-
Supportive care is essential for improving quality of life. This includes respiratory therapy, nutritional support, and developmental interventions.
-
Research is ongoing to improve treatment options and outcomes. Scientists are exploring new surgical techniques and genetic therapies.
Emotional and Social Impact
The emotional and social impact of tracheal agenesis on families is profound. Here are some important considerations.
-
Parents often experience significant emotional stress. The diagnosis and treatment of tracheal agenesis can be overwhelming.
-
Support groups can provide valuable emotional support. Connecting with other families facing similar challenges can be comforting.
-
Healthcare teams often include social workers and psychologists. These professionals help families navigate the emotional and social aspects of the condition.
-
Educational support is crucial for affected children. Many children with tracheal agenesis require special education services.
-
Awareness campaigns can help reduce stigma. Educating the public about tracheal agenesis can foster understanding and support.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to improve our understanding and treatment of tracheal agenesis. Here are some exciting developments.
-
Genetic research is exploring potential causes. Identifying genetic factors could lead to better prevention and treatment strategies.
-
Stem cell research holds promise for airway reconstruction. Scientists are investigating the use of stem cells to create functional tracheal tissue.
-
Advances in imaging technology are improving diagnosis. New techniques allow for earlier and more accurate detection of tracheal agenesis.
-
Collaborative research efforts are essential. Researchers from various fields are working together to find solutions.
-
Patient registries are helping track outcomes. Collecting data on affected individuals can provide valuable insights into the condition.
Final Thoughts on Tracheal Agenesis
Tracheal agenesis, a rare congenital condition, presents significant challenges for affected infants and their families. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for early diagnosis and intervention. Advances in medical technology and surgical techniques have improved outcomes, but the condition remains life-threatening. Awareness and research are key to better support and treatment.
Parents and caregivers need comprehensive information and support networks to navigate this complex condition. Medical professionals play a vital role in providing accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans. Continued research and collaboration among healthcare providers will enhance our understanding and management of tracheal agenesis.
By staying informed and advocating for further research, we can hope for better outcomes and support for those affected by this rare condition. Knowledge empowers us to make informed decisions and offer the best possible care for these vulnerable infants.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
