Subependymal Nodular Heterotopia (SNH) might sound like a mouthful, but understanding it can be simpler than you think. SNH is a rare brain condition where nerve cells, or neurons, don't migrate to their proper places during brain development. Instead, they form clumps or nodules along the brain's ventricles. These misplaced neurons can lead to seizures, learning difficulties, or other neurological issues. Why does this happen? Often, it's due to genetic mutations, though sometimes the cause remains unknown. Knowing more about SNH can help in recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate medical advice. Ready to learn some intriguing facts about this condition? Let's dive in!
Key Takeaways:
- Subependymal Nodular Heterotopia (SNH) is a rare brain condition causing seizures and learning difficulties. Early diagnosis and supportive therapies can improve the lives of those affected.
- Genetic mutations play a crucial role in SNH, affecting brain development. Research and advocacy efforts are essential for better treatments and support systems.
What is Subependymal Nodular Heterotopia?
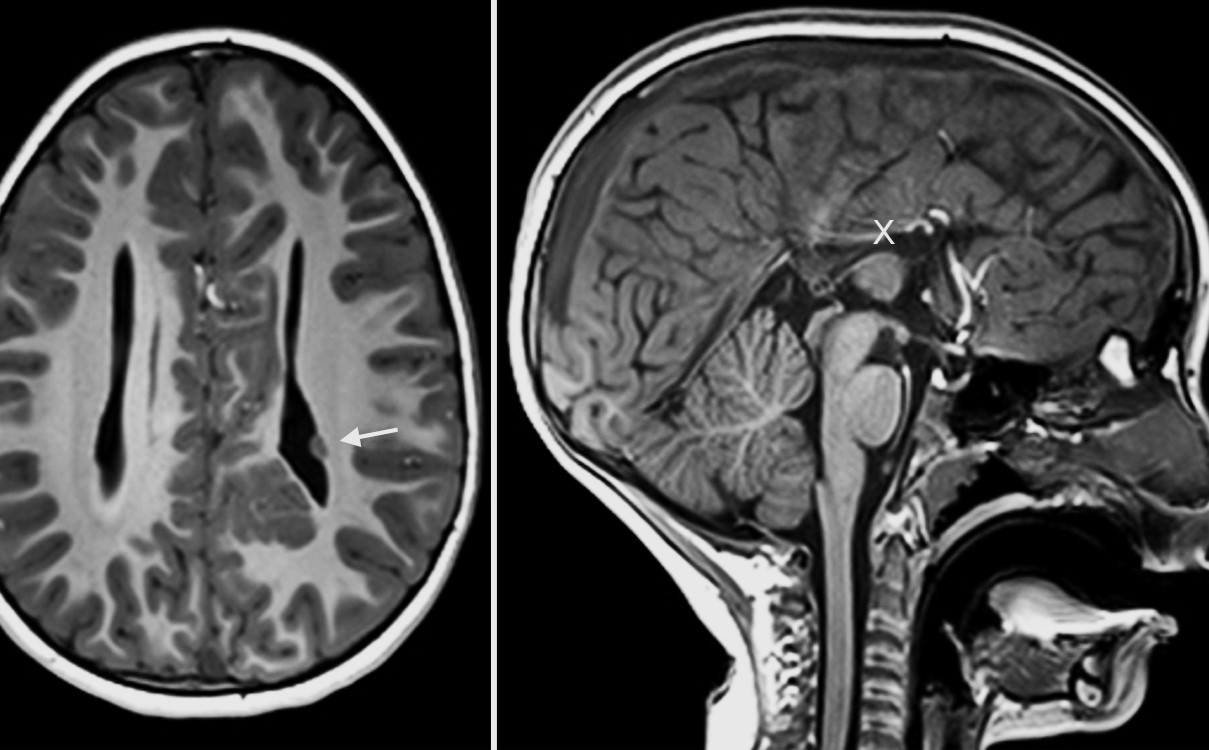
Subependymal Nodular Heterotopia (SNH) is a rare brain malformation where neurons fail to migrate to their proper positions during brain development. This condition can lead to various neurological symptoms and is often associated with epilepsy.
-
SNH is a congenital condition, meaning it is present at birth. It results from genetic mutations affecting neuronal migration.
-
The neurons in SNH form nodules along the walls of the brain's ventricles instead of reaching the cerebral cortex.
-
SNH is often diagnosed through MRI scans, which reveal the characteristic nodules.
-
The condition can be inherited in an X-linked dominant pattern, primarily affecting females.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
SNH presents a range of symptoms, often making diagnosis challenging. Understanding these symptoms can help in early detection and management.
-
Epilepsy is a common symptom, with seizures often beginning in childhood or adolescence.
-
Cognitive impairment varies, with some individuals having normal intelligence while others experience learning difficulties.
-
SNH can cause headaches, often due to increased intracranial pressure.
-
MRI is the gold standard for diagnosis, revealing nodules that are not visible on CT scans.
Genetic Factors
Genetics play a crucial role in SNH, with several genes implicated in its development.
-
Mutations in the FLNA gene are the most common cause of SNH, affecting the filamin A protein involved in cell structure.
-
FLNA mutations are X-linked, explaining why the condition is more prevalent in females.
-
Other genes like ARFGEF2 have also been associated with SNH, though less commonly.
-
Genetic testing can confirm diagnosis, especially in families with a history of the condition.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for SNH, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) are commonly prescribed to control seizures.
-
Surgical options may be considered for severe cases, particularly if seizures are not controlled by medication.
-
Regular monitoring is essential, as symptoms can evolve over time.
-
Supportive therapies, such as physical and occupational therapy, can help manage motor and cognitive impairments.
Impact on Daily Life
Living with SNH can be challenging, but understanding its impact can help individuals and families cope better.
-
Educational support is crucial, as learning difficulties are common.
-
Social and emotional support can help individuals deal with the psychological impact of the condition.
-
Regular medical check-ups are important to monitor and manage symptoms effectively.
-
Awareness and advocacy can improve understanding and support for those affected by SNH.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand SNH and develop more effective treatments.
-
Stem cell research holds promise, potentially offering new ways to repair neuronal migration defects.
-
Gene therapy is being explored, aiming to correct the underlying genetic mutations.
-
Animal models are used in research, helping scientists study the condition and test new treatments.
-
Clinical trials are ongoing, with new drugs and therapies being tested for efficacy and safety.
Real-Life Stories
Hearing from those living with SNH can provide valuable insights and inspiration.
-
Personal stories highlight resilience, showing how individuals overcome challenges associated with SNH.
-
Support groups offer a sense of community, providing a platform for sharing experiences and advice.
-
Advocacy efforts by affected families have led to increased awareness and research funding.
-
Educational initiatives help schools and communities better support students with SNH.
Conclusion
Subependymal Nodular Heterotopia is a complex condition with a wide range of symptoms and challenges. Understanding its genetic basis, symptoms, and management options can help improve the lives of those affected.
-
Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve outcomes for individuals with SNH.
-
Continued research and advocacy are essential for developing better treatments and support systems for those living with this condition.
Final Thoughts on Subependymal Nodular Heterotopia
Subependymal Nodular Heterotopia (SNH) is a rare brain condition where nerve cells don't migrate properly during development. This can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, including seizures and learning difficulties. Understanding SNH helps in managing the condition better and providing appropriate care.
Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Genetic testing and imaging techniques like MRI play a significant role in identifying SNH. While there's no cure, medications and therapies can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Raising awareness about SNH can lead to better support and resources for those affected. If you or someone you know shows symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance. Knowledge is power when it comes to rare conditions like SNH. Stay informed and proactive in seeking the best care possible.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
