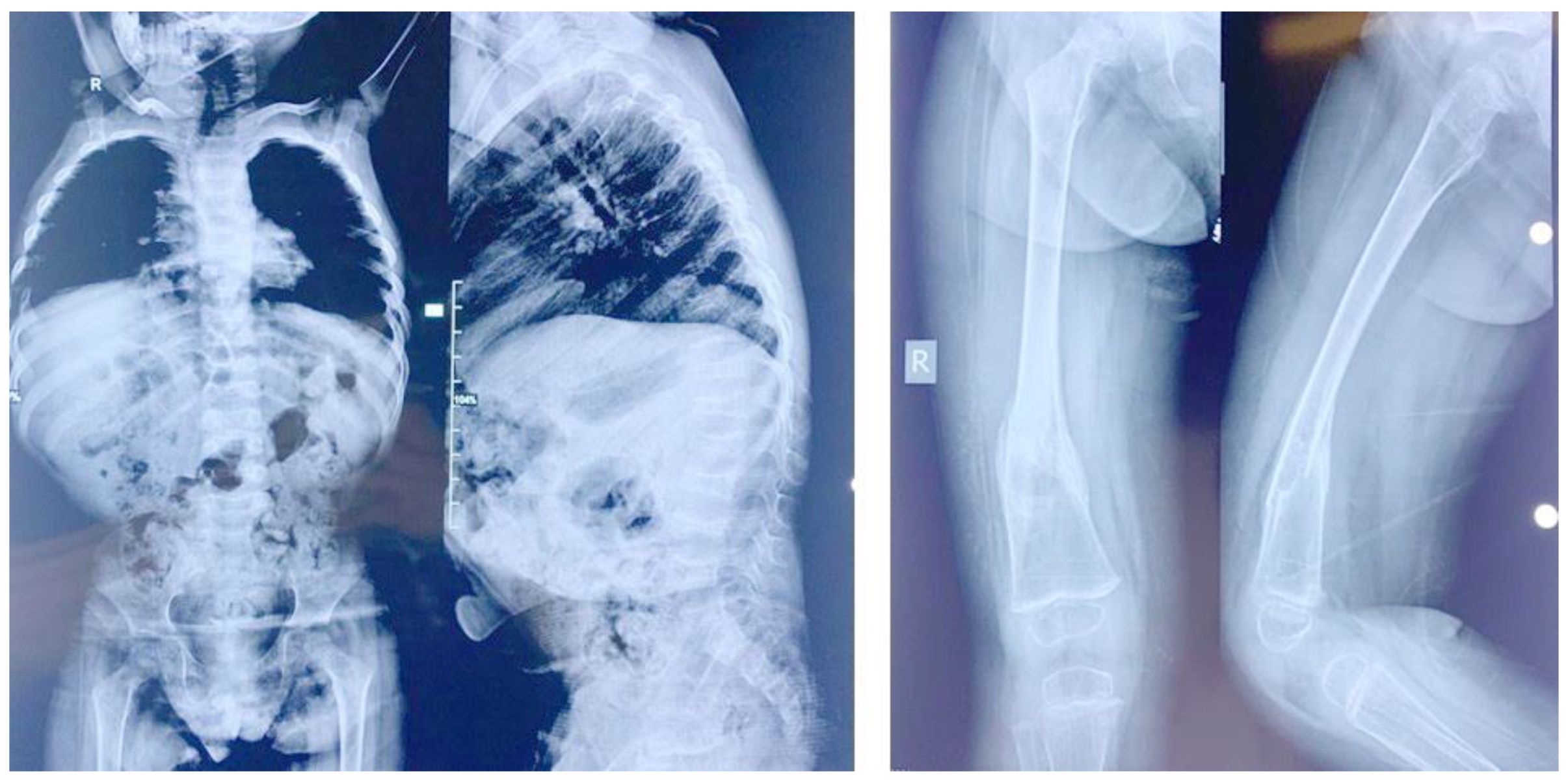
Spondylo-Ocular Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects both the spine and eyes. What causes Spondylo-Ocular Syndrome? This condition is primarily caused by mutations in the XYLT2 gene, which plays a crucial role in the production of a protein involved in the formation of connective tissues. People with this syndrome often experience a combination of skeletal abnormalities, such as scoliosis or kyphosis, and eye problems, including cataracts or retinal detachment. Understanding this syndrome can help in managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Let's dive into 30 fascinating facts about Spondylo-Ocular Syndrome that will shed light on its complexities and how it impacts those affected.
Key Takeaways:
- Spondylo-Ocular Syndrome (SOS) is a rare genetic disorder affecting the spine and eyes, leading to spinal and ocular symptoms. Early diagnosis and management strategies can help individuals lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges.
- Research and ongoing efforts offer hope for better understanding and treatment of SOS. Gene therapy, clinical trials, patient registries, and support groups are paving the way for improved care and possibly a cure in the future.
What is Spondylo-Ocular Syndrome?
Spondylo-Ocular Syndrome (SOS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects both the spine and eyes. This condition can lead to a variety of symptoms and complications. Here are some intriguing facts about SOS.
-
Genetic Origin: SOS is caused by mutations in the XYLT2 gene, which plays a role in the production of enzymes necessary for the development of connective tissues.
-
Inheritance Pattern: This syndrome follows an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern, meaning both parents must carry the mutated gene for a child to be affected.
-
Spinal Abnormalities: Individuals with SOS often have spinal issues such as scoliosis or kyphosis, which are abnormal curvatures of the spine.
-
Eye Problems: Common ocular symptoms include cataracts, which cause clouding of the eye lens, and microcornea, where the cornea is smaller than usual.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and how SOS is diagnosed can help in managing the condition effectively.
-
Early Onset: Symptoms usually appear in early childhood, making early diagnosis crucial for better management.
-
Growth Delays: Children with SOS often experience growth delays, leading to shorter stature compared to their peers.
-
Hearing Loss: Some individuals may suffer from hearing loss, which can range from mild to severe.
-
Joint Issues: Joint pain and stiffness are common, often leading to arthritis at a young age.
-
Diagnostic Tests: Genetic testing is the most definitive way to diagnose SOS, confirming the presence of mutations in the XYLT2 gene.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for SOS, various treatments can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
Surgical Interventions: Surgery may be necessary to correct severe spinal deformities or cataracts.
-
Physical Therapy: Regular physical therapy can help maintain mobility and reduce joint pain.
-
Vision Aids: Glasses or contact lenses can improve vision for those with cataracts or other eye issues.
-
Hearing Aids: For those with hearing loss, hearing aids can significantly enhance their ability to communicate.
-
Pain Management: Medications and other therapies can help manage chronic pain associated with joint and spinal issues.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand SOS and develop more effective treatments.
-
Gene Therapy: Scientists are exploring gene therapy as a potential treatment, aiming to correct the underlying genetic mutations.
-
Clinical Trials: Various clinical trials are underway to test new medications and therapies for managing SOS symptoms.
-
Patient Registries: Patient registries help researchers gather data on SOS, leading to better understanding and treatment options.
-
Support Groups: Joining support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice for managing the condition.
Living with Spondylo-Ocular Syndrome
Living with SOS can be challenging, but with the right support and management strategies, individuals can lead fulfilling lives.
-
Educational Support: Children with SOS may need special educational support to help them succeed in school.
-
Adaptive Equipment: Using adaptive equipment can make daily tasks easier and improve independence.
-
Regular Monitoring: Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are essential to monitor the progression of the condition and adjust treatments as needed.
-
Mental Health: Addressing mental health is crucial, as living with a chronic condition can be emotionally taxing.
-
Family Support: Family members play a vital role in providing support and care for individuals with SOS.
Interesting Facts
Here are some lesser-known facts about SOS that highlight the uniqueness of this condition.
-
Rare Condition: SOS is extremely rare, with only a few hundred cases reported worldwide.
-
First Described: The syndrome was first described in medical literature in the early 2000s.
-
Multisystem Disorder: SOS affects multiple systems in the body, making it a complex condition to manage.
-
Research Advances: Advances in genetic research have significantly improved our understanding of SOS in recent years.
-
Awareness Efforts: Efforts to raise awareness about SOS are ongoing, helping to improve diagnosis and treatment.
-
Patient Advocacy: Patient advocacy groups work tirelessly to support those affected by SOS and their families.
-
Hope for the Future: With continued research and advancements in medical science, there is hope for better treatments and possibly a cure for SOS in the future.
Final Thoughts on Spondylo-Ocular Syndrome
Spondylo-Ocular Syndrome, a rare genetic disorder, affects both the spine and eyes. Understanding its symptoms, like joint pain and vision issues, can lead to early diagnosis and better management. Genetic testing plays a crucial role in identifying this condition, helping families prepare and seek appropriate treatments.
Living with Spondylo-Ocular Syndrome involves regular check-ups, physical therapy, and sometimes surgery. Support from healthcare professionals and patient communities can make a significant difference. Staying informed about the latest research and treatment options empowers patients and their families.
Raising awareness about this syndrome is essential. By sharing knowledge, we can support those affected and contribute to ongoing research efforts. Remember, early detection and proactive care are key to improving quality of life for individuals with Spondylo-Ocular Syndrome.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
