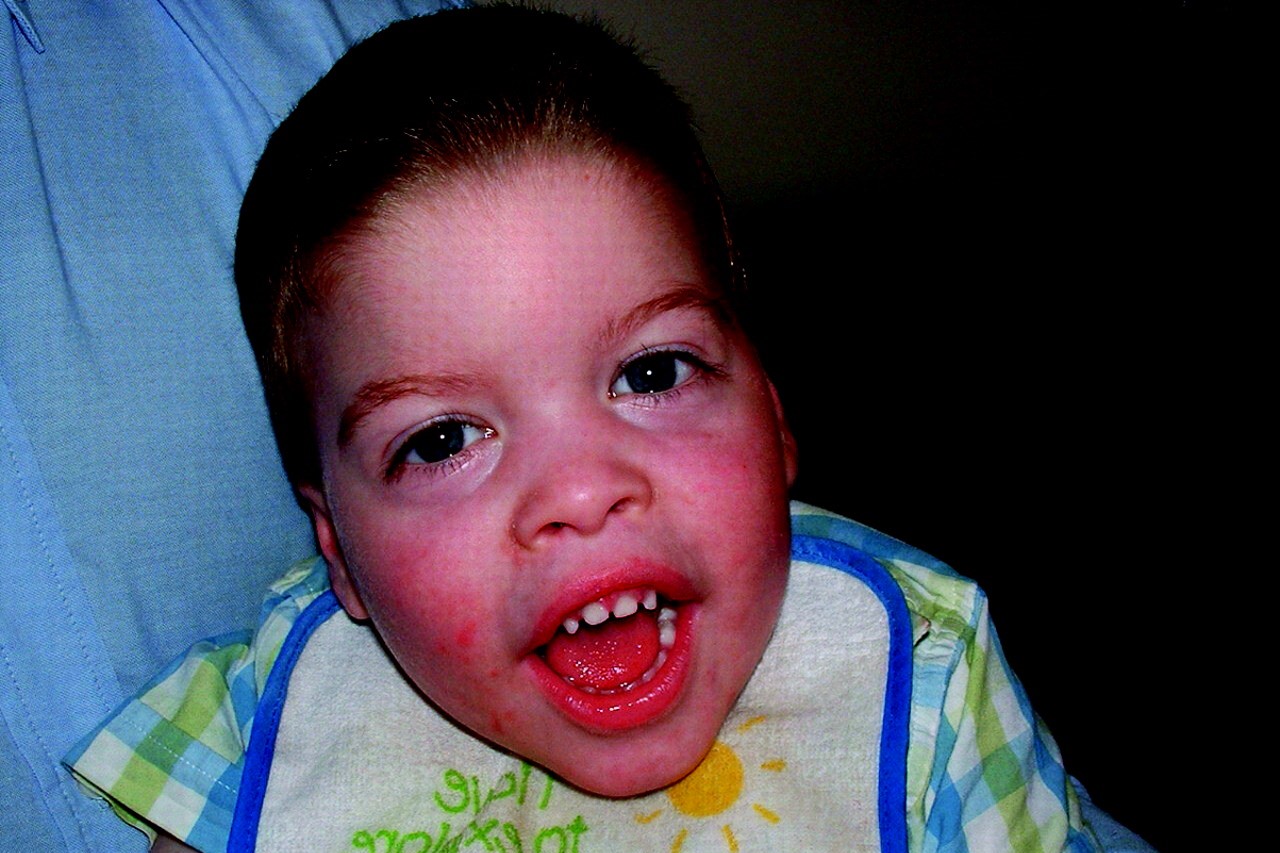
Smith-Fineman-Myers Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects various parts of the body. Caused by mutations in the UBE3A gene, this condition can lead to developmental delays, intellectual disabilities, and distinctive facial features. People with this syndrome often experience speech difficulties, behavioral challenges, and may have seizures. Understanding Smith-Fineman-Myers Syndrome is crucial for providing proper care and support to those affected. This article will delve into 30 essential facts about this condition, offering insights into its symptoms, diagnosis, and management. Whether you're a caregiver, medical professional, or simply curious, these facts will help you grasp the complexities of Smith-Fineman-Myers Syndrome.
Key Takeaways:
- Smith-Fineman-Myers Syndrome (SFMS) is a rare genetic disorder causing intellectual disability and unique physical traits. Early diagnosis and tailored interventions can improve the quality of life for those affected.
- SFMS affects multiple systems in the body, leading to developmental, behavioral, and medical complications. While there is no cure, early intervention programs, special education services, and regular medical check-ups can make a positive difference.
What is Smith-Fineman-Myers Syndrome?
Smith-Fineman-Myers Syndrome (SFMS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects multiple systems in the body. It is characterized by intellectual disability, distinctive facial features, and various physical abnormalities. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
SFMS is caused by mutations in the PHF6 gene located on the X chromosome.
-
The syndrome primarily affects males due to its X-linked recessive inheritance pattern.
-
Females can be carriers of the mutation but usually do not show severe symptoms.
-
The disorder was first described by Dr. Smith, Dr. Fineman, and Dr. Myers in 1983.
-
Intellectual disability is a hallmark of SFMS, often ranging from moderate to severe.
Physical Characteristics of SFMS
Individuals with SFMS often exhibit unique physical traits that help in diagnosing the condition. These features can vary but are generally consistent among those affected.
-
Distinctive facial features include a broad forehead, widely spaced eyes, and a flat nasal bridge.
-
Dental anomalies such as widely spaced teeth and delayed tooth eruption are common.
-
Short stature is frequently observed in individuals with SFMS.
-
Microcephaly, or a smaller than average head size, is another characteristic.
-
Hypotonia, or low muscle tone, often affects motor skills and physical development.
Developmental and Behavioral Aspects
SFMS impacts not just physical appearance but also developmental and behavioral aspects of life. Understanding these can help in managing the condition better.
-
Delayed speech development is common, with many children experiencing significant language delays.
-
Behavioral issues such as hyperactivity and impulsivity are often reported.
-
Autistic-like behaviors may be present, including difficulties with social interactions and repetitive behaviors.
-
Seizures can occur in some individuals, although they are not a universal symptom.
-
Learning difficulties are prevalent, necessitating special education and support.
Medical Complications
SFMS can lead to various medical complications that require ongoing care and management. Awareness of these issues is crucial for improving quality of life.
-
Heart defects such as ventricular septal defects may be present at birth.
-
Hearing loss is another potential complication, often requiring hearing aids or other interventions.
-
Vision problems like strabismus (crossed eyes) and refractive errors are common.
-
Gastrointestinal issues such as constipation and feeding difficulties may occur.
-
Respiratory problems can arise, particularly in infancy, due to weak muscle tone.
Diagnosis and Genetic Testing
Accurate diagnosis of SFMS involves a combination of clinical evaluation and genetic testing. Early diagnosis can help in planning appropriate interventions.
-
Genetic testing is the definitive method for diagnosing SFMS, identifying mutations in the PHF6 gene.
-
Prenatal testing is available for families with a known history of the disorder.
-
Clinical evaluation includes a thorough physical examination and assessment of developmental milestones.
-
Family history is often reviewed to identify potential carriers of the gene mutation.
-
Molecular analysis can confirm the diagnosis and help in understanding the specific mutation involved.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for SFMS, various treatments and management strategies can improve the quality of life for those affected.
-
Early intervention programs focusing on speech, occupational, and physical therapy can be beneficial.
-
Special education services tailored to individual needs help in addressing learning difficulties.
-
Behavioral therapy can assist in managing hyperactivity and other behavioral issues.
-
Regular medical check-ups are essential for monitoring and addressing any arising complications.
-
Support groups and counseling can provide emotional support for families dealing with SFMS.
Understanding Smith-Fineman-Myers Syndrome
Smith-Fineman-Myers Syndrome (SFMS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects many parts of the body. Knowing the symptoms and causes can help in early diagnosis and better management. Common signs include developmental delays, distinct facial features, and intellectual disabilities. Genetic mutations, especially in the NLGN4 gene, play a significant role in this condition.
Early intervention and supportive therapies can improve the quality of life for those affected. Speech therapy, occupational therapy, and physical therapy are often beneficial. Families and caregivers should seek genetic counseling to understand the risks and implications.
Raising awareness about SFMS can lead to better resources and support networks. Sharing information and experiences can make a big difference. Remember, every bit of knowledge helps in managing and understanding this complex syndrome. Stay informed and connected for the best outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
