Non-Lissencephalic Cortical Dysplasia might sound like a mouthful, but understanding it can be simpler than you think. This condition affects the brain's development, leading to a variety of symptoms that can impact daily life. Non-Lissencephalic Cortical Dysplasia isn't as rare as you might assume, and knowing more about it can help in recognizing and managing the condition. From its causes to its effects on the brain, there’s a lot to learn. Whether you're a student, a parent, or just curious, these 30 facts will give you a clearer picture of what Non-Lissencephalic Cortical Dysplasia is all about.
Key Takeaways:
- Non-Lissencephalic Cortical Dysplasia (NLCD) is a brain disorder affecting children, causing seizures and developmental delays. Genetic factors play a significant role, and treatment involves managing symptoms with medication, therapy, and surgery.
- Research on NLCD is ongoing, exploring stem cell therapy, genetic targeted therapies, and new medications. Collaboration between experts is crucial for advancing our understanding and treatment of this complex condition.
Understanding Non-Lissencephalic Cortical Dysplasia
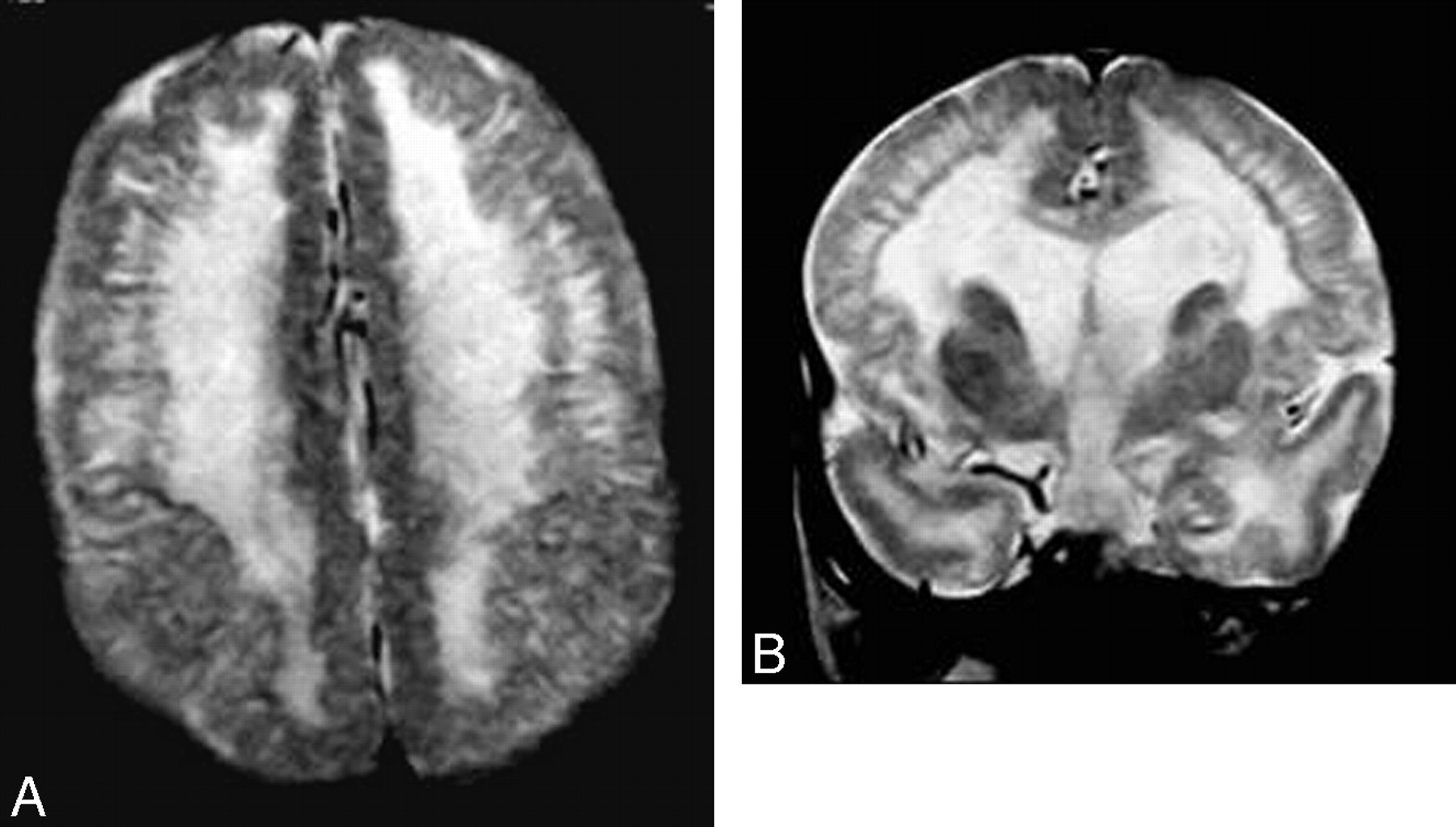
Non-Lissencephalic Cortical Dysplasia (NLCD) is a complex brain disorder. It affects the structure and function of the cerebral cortex. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
NLCD is a type of cortical dysplasia where the brain's surface appears relatively normal, unlike lissencephaly, which means "smooth brain."
-
The condition is often diagnosed in childhood, typically when children present with seizures or developmental delays.
-
NLCD can be focal, affecting a small area of the brain, or diffuse, impacting larger regions.
-
The exact cause of NLCD is not always known, but it can be linked to genetic mutations or prenatal brain injuries.
-
MRI scans are crucial for diagnosing NLCD, as they can reveal subtle abnormalities in brain structure.
-
Symptoms of NLCD vary widely but often include epilepsy, intellectual disability, and motor dysfunction.
-
Treatment for NLCD usually involves managing symptoms, particularly seizures, with medication or surgery.
-
Some children with NLCD may benefit from physical, occupational, and speech therapy to improve their developmental outcomes.
Genetic Factors and NLCD
Genetics play a significant role in many cases of NLCD. Understanding these factors can help in diagnosing and managing the condition.
-
Mutations in genes such as TSC1, TSC2, and MTOR have been associated with NLCD.
-
NLCD can be part of a broader genetic syndrome, such as tuberous sclerosis complex or focal cortical dysplasia type II.
-
Genetic testing can sometimes identify mutations responsible for NLCD, aiding in diagnosis and family planning.
-
In some cases, NLCD may be inherited in an autosomal dominant or recessive pattern.
-
Prenatal genetic testing can sometimes detect NLCD, especially if there is a known family history.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the diagnostic process is essential for managing NLCD effectively.
-
Seizures are the most common symptom of NLCD, often starting in early childhood.
-
Developmental delays, particularly in speech and motor skills, are frequently observed in children with NLCD.
-
Behavioral issues, such as hyperactivity or aggression, can also be present in individuals with NLCD.
-
An EEG (electroencephalogram) can help detect abnormal brain activity associated with NLCD.
-
Advanced imaging techniques, like functional MRI and PET scans, can provide more detailed information about brain function in NLCD patients.
-
A comprehensive neurological examination is crucial for diagnosing NLCD and ruling out other conditions.
Treatment and Management
Managing NLCD involves a multidisciplinary approach to address the various symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
Anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs) are commonly prescribed to control seizures in NLCD patients.
-
In cases where medication is ineffective, surgical options like resective surgery or laser ablation may be considered.
-
Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is another treatment option for controlling seizures in NLCD patients.
-
Ketogenic diets have shown promise in reducing seizure frequency in some individuals with NLCD.
-
Regular follow-up with a neurologist is essential for monitoring and adjusting treatment plans.
-
Early intervention programs can help children with NLCD achieve better developmental outcomes.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research is crucial for improving our understanding and treatment of NLCD.
-
Scientists are exploring the role of stem cell therapy in repairing brain damage caused by NLCD.
-
Advances in genetic research may lead to targeted therapies for specific mutations associated with NLCD.
-
Clinical trials are investigating new medications and treatment approaches for managing seizures in NLCD patients.
-
Improved imaging techniques are helping researchers better understand the structural abnormalities in NLCD.
-
Collaboration between neurologists, geneticists, and researchers is key to advancing our knowledge and treatment of NLCD.
Final Thoughts on Non-Lissencephalic Cortical Dysplasia
Non-Lissencephalic Cortical Dysplasia (NLCD) is a complex brain disorder that affects many people worldwide. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments can help those affected lead better lives. NLCD often presents with seizures, developmental delays, and cognitive impairments. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for managing these symptoms effectively.
Research continues to uncover more about this condition, offering hope for improved treatments and outcomes. Genetic factors play a significant role, but environmental influences can also contribute. Treatment typically involves a combination of medication, therapy, and sometimes surgery.
Awareness and education about NLCD are essential for early detection and support. By staying informed and advocating for those affected, we can make a difference in their lives. Keep learning, stay curious, and support ongoing research to help those living with NLCD.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
