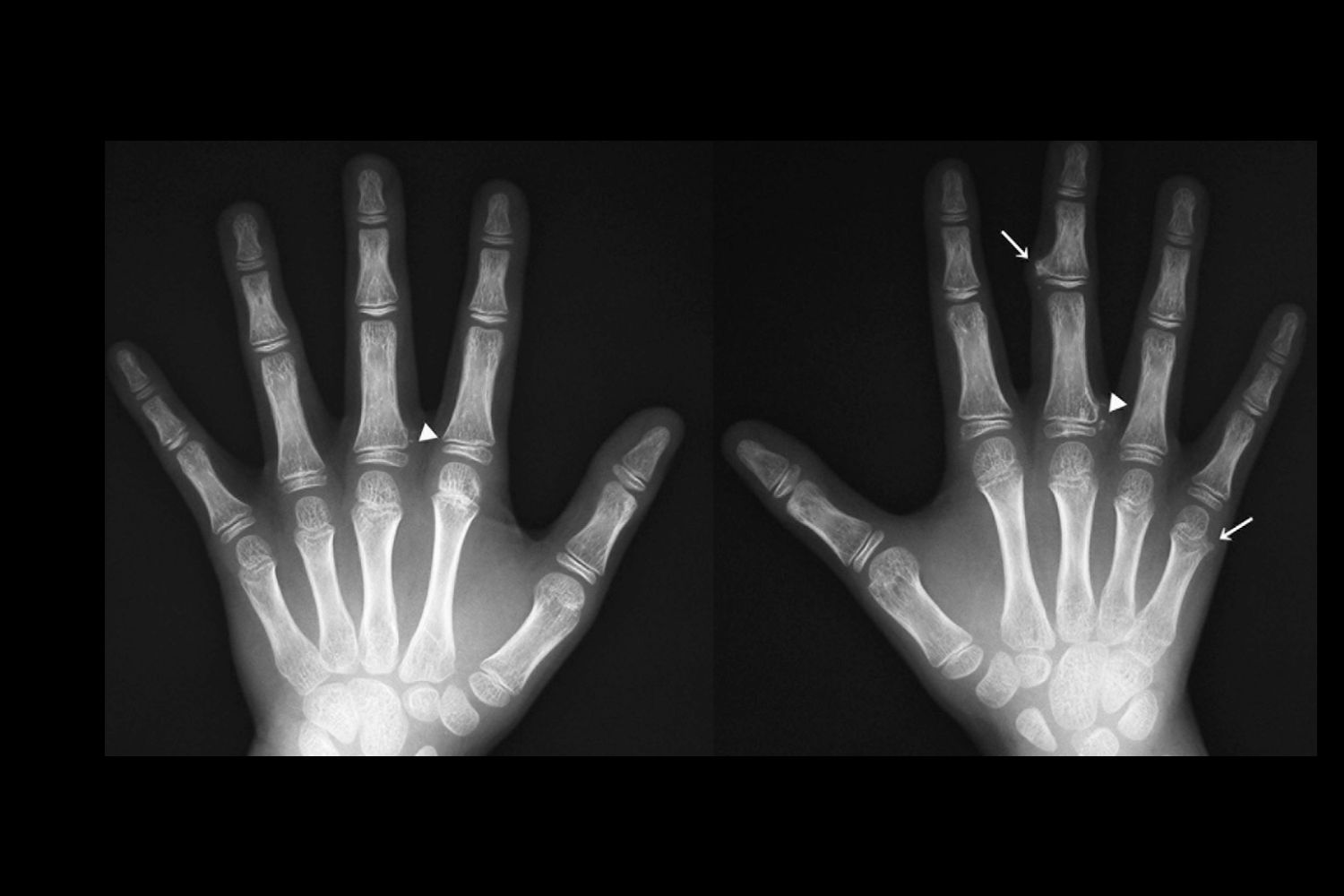
Metachondromatosis is a rare genetic disorder that affects the bones and cartilage. Characterized by the development of both enchondromas (benign cartilage tumors inside bones) and osteochondromas (bone growths covered by cartilage), this condition can lead to various complications. Symptoms often include bone pain, deformities, and fractures. Caused by mutations in the PTPN11 gene, metachondromatosis is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, meaning a single copy of the altered gene can cause the disorder. Diagnosis typically involves imaging studies like X-rays or MRIs, along with genetic testing. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and may include surgery to remove problematic growths. Understanding metachondromatosis is crucial for early detection and effective management.
Key Takeaways:
- Metachondromatosis is a rare genetic disorder causing bone and cartilage abnormalities. Early detection, pain management, and ongoing research offer hope for improved treatments and quality of life.
- Living with metachondromatosis can be challenging, but support groups, educational resources, and advocacy organizations provide valuable support and resources for patients and families.
What is Metachondromatosis?
Metachondromatosis is a rare genetic disorder affecting the bones and cartilage. It often presents in childhood and can lead to various skeletal abnormalities. Here are some fascinating facts about this condition.
-
Genetic Origin: Metachondromatosis is caused by mutations in the PTPN11 gene, which plays a crucial role in cell signaling.
-
Inheritance Pattern: This disorder follows an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern, meaning only one copy of the mutated gene is needed for the condition to manifest.
-
Bone Lesions: Individuals with metachondromatosis develop both enchondromas (benign cartilage tumors) and osteochondromas (bone growths).
-
Symptom Onset: Symptoms typically appear in early childhood, often between the ages of 2 and 10.
-
Affected Areas: The hands and feet are the most commonly affected areas, though other bones can be involved.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and how metachondromatosis is diagnosed can help in early detection and management.
-
Pain and Swelling: Affected individuals may experience pain and swelling in the areas where bone lesions are present.
-
Joint Deformities: Over time, the bone growths can lead to joint deformities and limited range of motion.
-
X-rays: X-rays are often used to identify the characteristic bone lesions associated with metachondromatosis.
-
MRI Scans: MRI scans can provide detailed images of the cartilage and bone, helping to differentiate between enchondromas and osteochondromas.
-
Genetic Testing: Genetic testing can confirm the diagnosis by identifying mutations in the PTPN11 gene.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for metachondromatosis, several treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
Surgical Removal: In some cases, surgical removal of bone lesions may be necessary to relieve pain or prevent complications.
-
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help maintain joint function and mobility.
-
Pain Management: Pain management strategies, including medications and lifestyle modifications, can help alleviate discomfort.
-
Regular Monitoring: Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider is essential to track the progression of the disease and adjust treatment as needed.
-
Orthopedic Interventions: Orthopedic interventions, such as braces or orthotics, may be used to support affected joints and improve function.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand metachondromatosis and develop more effective treatments.
-
Gene Therapy: Researchers are exploring the potential of gene therapy to correct the underlying genetic mutation.
-
Targeted Therapies: Targeted therapies that specifically address the abnormal cell signaling pathways in metachondromatosis are being investigated.
-
Clinical Trials: Clinical trials are essential for testing new treatments and improving patient outcomes.
-
Patient Registries: Patient registries help collect data on individuals with metachondromatosis, providing valuable insights into the condition.
-
Collaborative Research: Collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and patient advocacy groups is crucial for advancing our understanding of metachondromatosis.
Living with Metachondromatosis
Living with a rare genetic disorder like metachondromatosis can be challenging, but support and resources are available.
-
Support Groups: Joining a support group can provide emotional support and practical advice from others who understand the condition.
-
Educational Resources: Educational resources can help patients and families learn more about metachondromatosis and how to manage it.
-
Advocacy: Advocacy organizations work to raise awareness of metachondromatosis and support research efforts.
-
Mental Health: Addressing mental health is important, as living with a chronic condition can take an emotional toll.
-
Adaptive Strategies: Developing adaptive strategies can help individuals with metachondromatosis lead fulfilling lives.
Interesting Facts and Trivia
Here are some lesser-known facts and trivia about metachondromatosis that might surprise you.
-
Rare Condition: Metachondromatosis is extremely rare, with only a few hundred cases reported worldwide.
-
First Described: The condition was first described in medical literature in the early 20th century.
-
Named After: The name "metachondromatosis" comes from the Greek words "meta" (change) and "chondros" (cartilage).
-
Research Milestones: Significant research milestones include the identification of the PTPN11 gene mutation and the development of animal models for studying the disease.
-
Hope for the Future: Advances in genetics and molecular biology hold promise for better treatments and possibly a cure in the future.
Final Thoughts on Metachondromatosis
Metachondromatosis, a rare genetic disorder, affects cartilage and bone development. Understanding its symptoms, like bone deformities and cartilage growths, helps in early diagnosis. Genetic mutations, specifically in the PTPN11 gene, play a significant role. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms, often requiring a team of specialists. Regular monitoring and supportive therapies can improve quality of life.
Awareness is crucial for early intervention and better outcomes. If you or someone you know shows signs of metachondromatosis, consult a healthcare professional. Staying informed and proactive makes a big difference.
Remember, while rare, metachondromatosis is manageable with the right care and support. Keep learning and advocating for those affected. Knowledge empowers us to face challenges head-on.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
