Hypodysfibrinogenemia might sound like a mouthful, but understanding it is crucial. This rare blood disorder affects the way your blood clots, leading to potential bleeding issues or even thrombosis. Hypodysfibrinogenemia occurs when the fibrinogen in your blood, a protein essential for clotting, is either dysfunctional or present in lower amounts. This condition can be inherited or acquired due to liver disease or other medical conditions. Symptoms vary widely, from mild to severe, and can include easy bruising, nosebleeds, or excessive bleeding after surgery. Diagnosing hypodysfibrinogenemia involves blood tests to measure fibrinogen levels and functionality. Treatment often requires managing symptoms and addressing underlying causes. Understanding this condition can help manage its impact on daily life.
Key Takeaways:
- Hypodysfibrinogenemia is a rare blood disorder causing both bleeding and clotting issues. It's diagnosed through blood tests, genetic testing, and family history evaluation. Treatment includes fibrinogen replacement therapy and lifestyle adjustments.
- Ongoing research for hypodysfibrinogenemia aims to improve treatment options, including gene therapy and new medications. Clinical trials and patient registries help advance knowledge, while personalized medicine and awareness campaigns offer hope for better management.
What is Hypodysfibrinogenemia?
Hypodysfibrinogenemia is a rare blood disorder affecting the fibrinogen protein, crucial for blood clotting. People with this condition have abnormal fibrinogen levels, leading to bleeding issues or thrombotic events. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Fibrinogen Role: Fibrinogen is a protein produced by the liver, essential for blood clot formation. It converts into fibrin during the clotting process.
-
Genetic Disorder: Hypodysfibrinogenemia is often inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, meaning one copy of the altered gene can cause the disorder.
-
Rare Condition: This disorder is extremely rare, with only a few hundred cases reported worldwide.
-
Bleeding and Clotting: Individuals may experience both excessive bleeding and abnormal clotting, making management challenging.
-
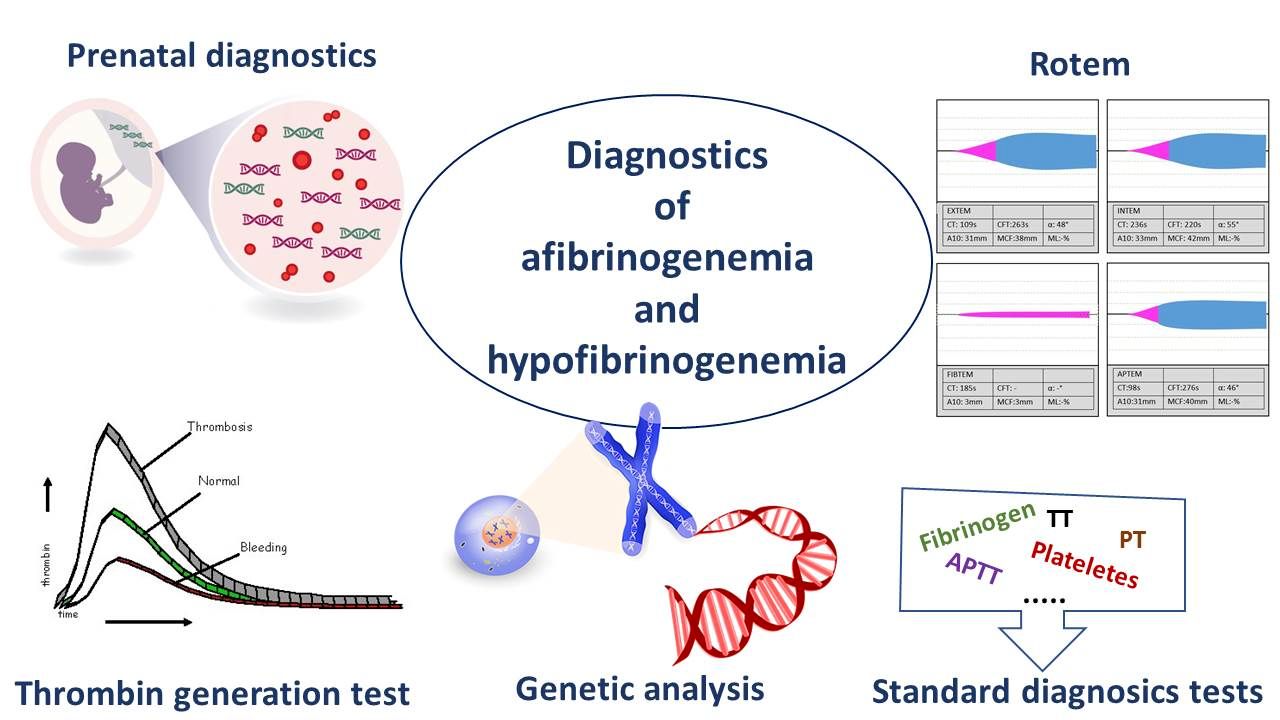
Diagnosis: Diagnosing hypodysfibrinogenemia involves blood tests measuring fibrinogen levels and functionality.
-
Symptoms Vary: Symptoms can range from mild to severe, including easy bruising, nosebleeds, and prolonged bleeding after injury.
-
Liver Connection: Since fibrinogen is produced in the liver, liver diseases can exacerbate hypodysfibrinogenemia symptoms.
-
Thrombotic Events: Despite low fibrinogen levels, some patients may develop blood clots, leading to conditions like deep vein thrombosis.
-
Pregnancy Risks: Pregnant women with hypodysfibrinogenemia face higher risks of miscarriage and postpartum hemorrhage.
-
Treatment Options: Treatment may include fibrinogen replacement therapy, antifibrinolytic agents, or blood transfusions.
How is Hypodysfibrinogenemia Diagnosed?
Diagnosing hypodysfibrinogenemia requires a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests. Here are some key facts about the diagnostic process.
-
Blood Tests: Initial blood tests measure fibrinogen levels and assess clotting function.
-
Genetic Testing: Genetic tests can identify mutations in the FGA, FGB, or FGG genes responsible for the disorder.
-
Family History: A detailed family history helps determine if the condition is inherited.
-
Liver Function Tests: Assessing liver function is crucial since liver health impacts fibrinogen production.
-
Coagulation Studies: Additional tests like thrombin time and reptilase time help evaluate fibrinogen functionality.
-
Differential Diagnosis: Doctors rule out other bleeding disorders with similar symptoms, such as hemophilia or von Willebrand disease.
Treatment and Management of Hypodysfibrinogenemia
Managing hypodysfibrinogenemia involves addressing both bleeding and clotting risks. Here are some important facts about treatment and management.
-
Fibrinogen Concentrates: Fibrinogen replacement therapy involves administering fibrinogen concentrates to maintain adequate levels.
-
Antifibrinolytic Agents: Medications like tranexamic acid help prevent excessive bleeding by inhibiting fibrin breakdown.
-
Blood Transfusions: In severe cases, blood transfusions may be necessary to manage bleeding episodes.
-
Regular Monitoring: Patients require regular monitoring of fibrinogen levels and clotting function to adjust treatment as needed.
-
Lifestyle Adjustments: Avoiding activities that increase bleeding risk, like contact sports, is crucial for managing the condition.
-
Pregnancy Management: Pregnant women need specialized care to manage bleeding risks during pregnancy and childbirth.
-
Thrombosis Prevention: Preventive measures, such as anticoagulants, may be necessary for patients prone to blood clots.
-
Emergency Preparedness: Patients should carry medical alert information and have an emergency plan in place for bleeding episodes.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to improve understanding and treatment of hypodysfibrinogenemia. Here are some exciting developments in the field.
-
Gene Therapy: Researchers are exploring gene therapy as a potential cure by correcting the genetic mutations causing the disorder.
-
New Medications: Development of new antifibrinolytic agents and clotting factors offers hope for better management options.
-
Clinical Trials: Participation in clinical trials helps advance knowledge and treatment of hypodysfibrinogenemia.
-
Patient Registries: Establishing patient registries aids in collecting data to improve understanding of the condition's prevalence and impact.
-
Personalized Medicine: Advances in personalized medicine allow for tailored treatment plans based on individual genetic profiles.
-
Awareness Campaigns: Increasing awareness about hypodysfibrinogenemia helps improve diagnosis, treatment, and support for affected individuals.
Final Thoughts on Hypodysfibrinogenemia
Hypodysfibrinogenemia, a rare blood disorder, affects the body's ability to clot properly. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments can help manage the condition better. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment, which often includes medication and sometimes surgery. Regular check-ups and staying informed about the latest medical advancements can make a significant difference.
Living with hypodysfibrinogenemia requires a proactive approach to health. Patients should maintain open communication with healthcare providers and adhere to prescribed treatments. Support from family and friends also plays a vital role in managing the emotional and physical challenges of the disorder.
Knowledge is power. By staying educated about hypodysfibrinogenemia, patients and caregivers can navigate this condition more effectively, improving quality of life. Remember, you're not alone—many resources and communities are available to offer support and information.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
