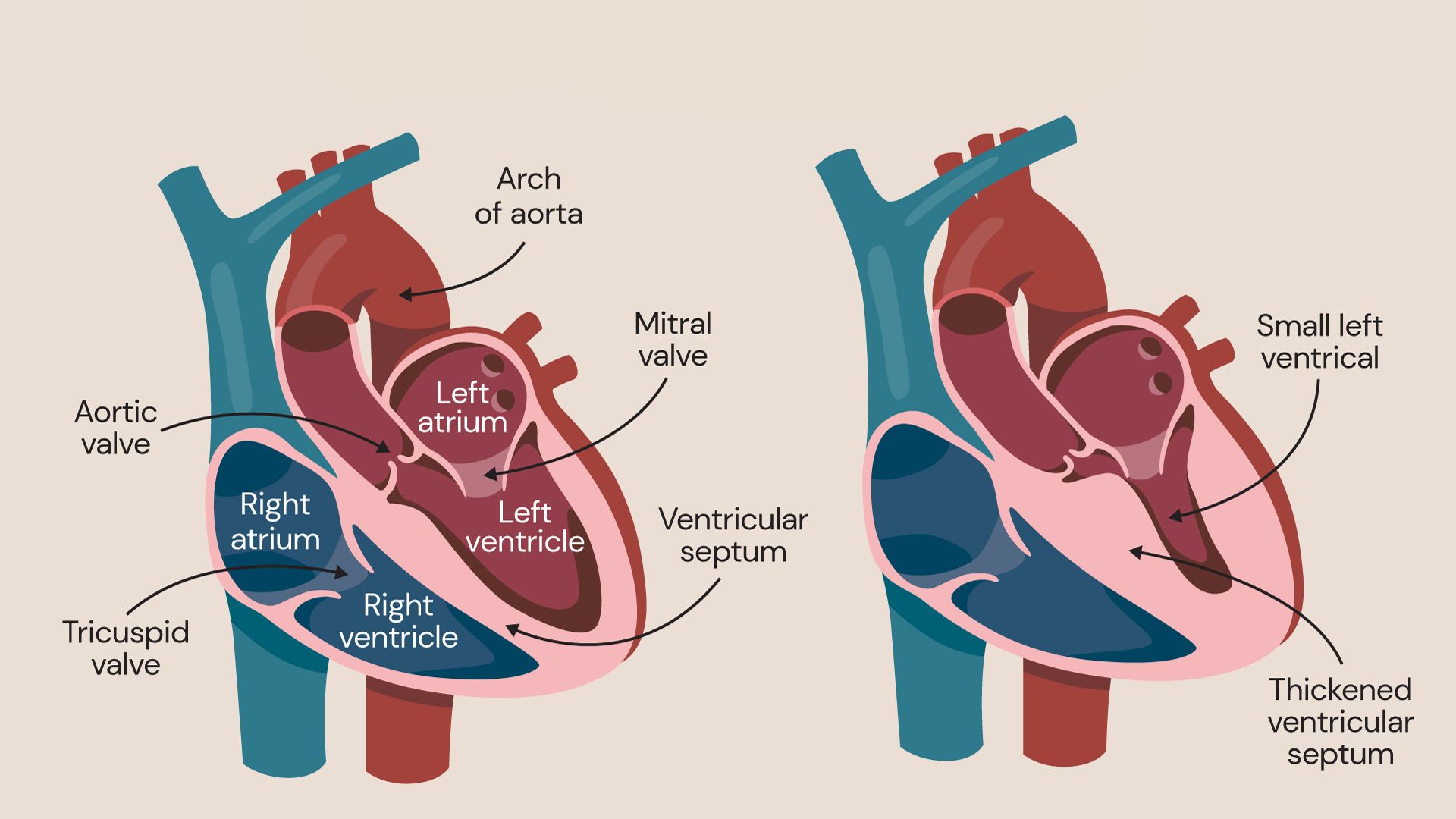
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a heart condition where the heart muscle becomes abnormally thick. This thickening can make it harder for the heart to pump blood. HCM often goes undiagnosed because many people with the disease have few, if any, symptoms. However, it can lead to serious complications like heart failure or sudden cardiac arrest. Genetics play a significant role, as the condition is often inherited. Symptoms can include chest pain, shortness of breath, and fainting, especially during exercise. Diagnosis usually involves imaging tests like an echocardiogram. Treatment options range from medications to surgical procedures. Understanding HCM is crucial for managing the condition and improving quality of life.
Key Takeaways:
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy is a genetic condition that thickens the heart muscle, affecting 1 in 500 people globally. It can lead to symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, and fainting, especially during exercise.
- Early diagnosis and proper treatment, including regular check-ups, moderate exercise, and a heart-healthy diet, can improve the quality of life for those living with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Support groups and emergency plans are also crucial for managing this condition.
What is Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy?
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a condition where the heart muscle becomes abnormally thick. This thickening can make it harder for the heart to pump blood. Here are some fascinating facts about this condition:
-
Genetic Condition: HCM is often inherited. About 60-70% of cases are linked to genetic mutations.
-
Prevalence: It affects approximately 1 in 500 people globally.
-
Symptoms: Common symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, and fainting, especially during exercise.
-
Silent Killer: Many people with HCM may not show symptoms, making it a silent threat.
-
Sudden Cardiac Arrest: HCM is a leading cause of sudden cardiac arrest in young athletes.
-
Diagnosis: It can be diagnosed using an echocardiogram, which uses sound waves to create images of the heart.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors can help in managing HCM better. Here are some key points:
-
Genetic Mutations: Mutations in genes that encode proteins in the heart muscle are the primary cause.
-
Family History: Having a family member with HCM increases your risk.
-
Age: Although it can occur at any age, symptoms often appear in adolescence or early adulthood.
-
Gender: Men and women are equally affected, but men may show symptoms earlier.
-
High Blood Pressure: Chronic high blood pressure can contribute to the thickening of the heart muscle.
Symptoms and Complications
Recognizing symptoms early can lead to better management of HCM. Here are some symptoms and potential complications:
-
Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity, is common.
-
Chest Pain: Often mistaken for angina, this pain occurs due to reduced blood flow to the heart.
-
Palpitations: Irregular heartbeats or a fluttering sensation in the chest.
-
Fainting: Sudden loss of consciousness, particularly during or after exercise.
-
Heart Failure: The heart's inability to pump blood effectively can lead to heart failure.
-
Atrial Fibrillation: Irregular and often rapid heart rate that can increase the risk of stroke.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and proper treatment can improve the quality of life for those with HCM. Here’s how it’s done:
-
Echocardiogram: The most common test to diagnose HCM.
-
MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging provides detailed images of the heart.
-
Genetic Testing: Identifies specific mutations responsible for HCM.
-
Medications: Beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers can help manage symptoms.
-
Surgery: Procedures like septal myectomy can remove part of the thickened heart muscle.
-
Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD): A device that helps prevent sudden cardiac arrest.
Living with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Managing HCM involves lifestyle changes and regular medical check-ups. Here are some tips:
-
Regular Check-ups: Frequent visits to a cardiologist are essential.
-
Exercise: Moderate exercise is beneficial, but intense activities should be avoided.
-
Diet: A heart-healthy diet low in salt and saturated fats can help.
-
Avoid Stimulants: Caffeine and other stimulants can exacerbate symptoms.
-
Medication Adherence: Taking prescribed medications regularly is crucial.
-
Support Groups: Joining a support group can provide emotional and practical support.
-
Emergency Plan: Always have a plan in place for medical emergencies, including knowing the nearest hospital.
Final Thoughts on Hypertrophic Myocardiopathy
Hypertrophic Myocardiopathy (HCM) remains a significant heart condition affecting many worldwide. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments can help manage this disease better. Regular check-ups, genetic testing, and lifestyle changes play crucial roles in managing HCM. Awareness and education about HCM can lead to early diagnosis and improved quality of life.
Medical advancements continue to offer hope, with new treatments and technologies emerging. Staying informed and proactive about heart health can make a big difference. Remember, knowledge is power when dealing with HCM.
If you or a loved one shows symptoms, seek medical advice promptly. Early intervention can save lives. Keep learning, stay vigilant, and prioritize heart health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
