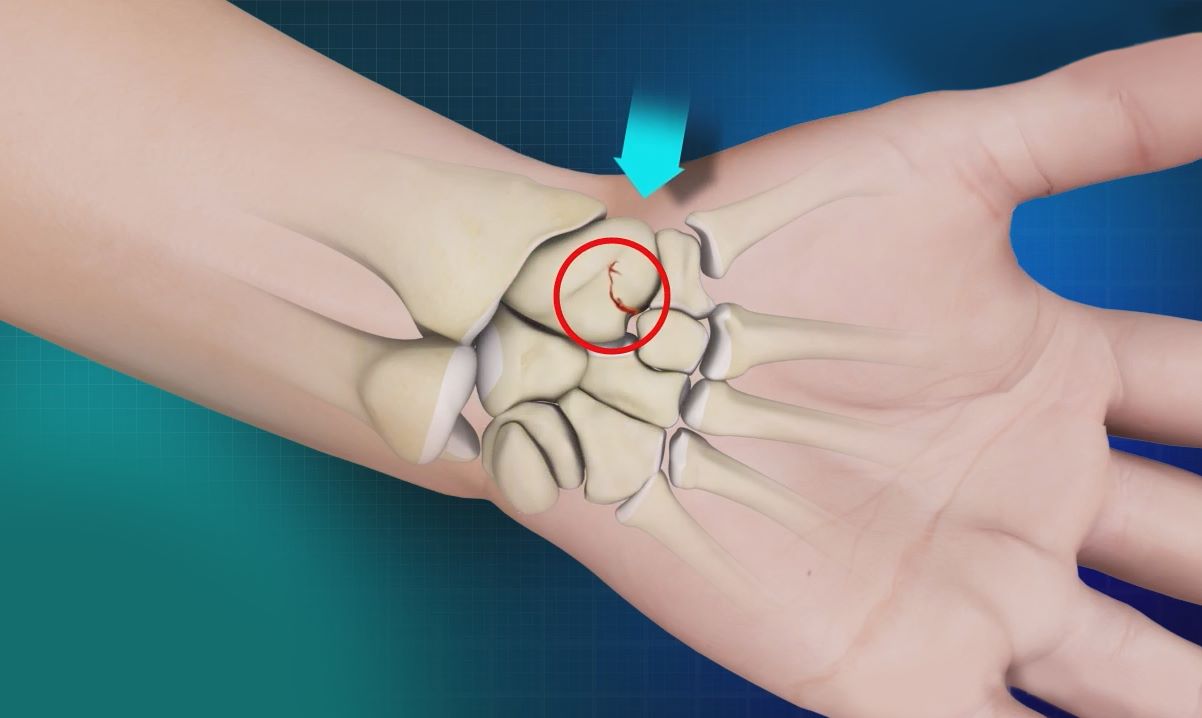
Herbert Classification is a system used to categorize fractures of the scaphoid bone in the wrist. Developed by Dr. Timothy Herbert, this classification helps doctors understand the severity and type of scaphoid fractures, which is crucial for proper treatment. Why is Herbert Classification important? It provides a standardized way to describe these fractures, ensuring consistent communication among healthcare professionals. This system divides fractures into stable and unstable categories, further breaking them down into subtypes based on specific characteristics. Understanding these categories can help predict healing times and potential complications. In this blog post, we'll explore 30 intriguing facts about Herbert Classification, shedding light on its significance in the medical field.
Key Takeaways:
- Herbert Classification categorizes wrist fractures into 4 types (A, B, C, D) to guide treatment. It helps doctors decide if surgery is needed and predicts healing time, improving communication and aiding in research.
- Recent advances in medical technology have improved scaphoid fracture treatment, making Herbert Classification even more relevant. Minimally invasive surgery, improved imaging, bone grafting, and biodegradable implants offer new options for patients.
Herbert Classification: An Overview
Herbert Classification is a system used to categorize fractures of the scaphoid bone in the wrist. This system helps medical professionals determine the severity of the fracture and the appropriate treatment plan. Here are some interesting facts about Herbert Classification.
-
Developed by Timothy Herbert
The classification was created by orthopedic surgeon Timothy Herbert in 1984. He aimed to provide a standardized method for assessing scaphoid fractures. -
Focuses on Scaphoid Fractures
This classification specifically addresses fractures of the scaphoid bone, one of the small bones in the wrist that is crucial for wrist movement. -
Divided into Four Main Types
Herbert Classification divides scaphoid fractures into four main types: A, B, C, and D. Each type has subcategories that provide more detailed information about the fracture.
Type A: Stable Fractures
Type A fractures are considered stable and usually heal without surgical intervention. Here are some key points about Type A fractures.
-
A1: Tubercle Fractures
A1 fractures involve the tubercle, a small bump on the scaphoid bone. These fractures are generally stable and heal well with immobilization. -
A2: Incomplete Fractures
A2 fractures are incomplete, meaning the bone is cracked but not completely broken. These fractures are also stable and typically heal with a cast.
Type B: Unstable Fractures
Type B fractures are unstable and often require surgical intervention to ensure proper healing. Let's explore the subcategories of Type B fractures.
-
B1: Distal Oblique Fractures
B1 fractures occur at the distal end of the scaphoid and are oblique in nature. These fractures are unstable and may need surgical fixation. -
B2: Complete Waist Fractures
B2 fractures involve a complete break at the waist of the scaphoid. These fractures are highly unstable and often require surgery. -
B3: Proximal Pole Fractures
B3 fractures occur at the proximal pole of the scaphoid. These fractures are unstable due to poor blood supply to the area, making healing difficult without surgery. -
B4: Trans-Scaphoid Perilunate Fracture-Dislocations
B4 fractures are complex and involve both the scaphoid and the lunate bone. These fractures are highly unstable and require surgical intervention. -
B5: Comminuted Fractures
B5 fractures are comminuted, meaning the bone is shattered into multiple pieces. These fractures are unstable and need surgical repair.
Type C: Delayed Union
Type C fractures are characterized by delayed union, meaning the bone takes longer to heal than usual. Here are some details about Type C fractures.
- C1: Delayed Union
C1 fractures show signs of healing but at a slower rate than expected. These fractures may require additional treatment to promote healing.
Type D: Non-Union
Type D fractures are non-union fractures, meaning the bone has not healed properly. These fractures often require surgical intervention to correct.
-
D1: Fibrous Non-Union
D1 fractures involve fibrous tissue forming between the broken bone ends instead of bone. These fractures need surgery to heal correctly. -
D2: Sclerotic Non-Union
D2 fractures are characterized by the formation of hard, sclerotic bone at the fracture site. These fractures are challenging to treat and often require surgery.
Importance of Herbert Classification
Understanding the importance of Herbert Classification helps medical professionals make informed decisions about treatment plans.
-
Guides Treatment Decisions
The classification system helps doctors decide whether a fracture can be treated with a cast or if surgery is necessary. -
Predicts Healing Time
By categorizing the fracture, doctors can estimate how long it will take for the bone to heal. -
Improves Communication
The standardized system allows for clear communication between medical professionals about the type and severity of the fracture. -
Aids in Research
Researchers use Herbert Classification to study scaphoid fractures and develop better treatment methods.
Challenges and Limitations
While Herbert Classification is widely used, it has some challenges and limitations that medical professionals should be aware of.
-
Subjectivity in Classification
The classification relies on the interpretation of X-rays, which can be subjective and lead to different diagnoses. -
Limited to Scaphoid Fractures
The system only applies to scaphoid fractures, limiting its use for other types of wrist injuries. -
Requires Expertise
Accurate classification requires a thorough understanding of wrist anatomy and fracture patterns, which may not be available in all medical settings.
Advances in Scaphoid Fracture Treatment
Recent advances in medical technology have improved the treatment of scaphoid fractures, making the Herbert Classification even more relevant.
-
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Advances in surgical techniques allow for minimally invasive procedures, reducing recovery time for patients with unstable fractures. -
Improved Imaging Techniques
Better imaging techniques, such as MRI and CT scans, provide more accurate assessments of scaphoid fractures, aiding in proper classification. -
Bone Grafting
Bone grafting techniques have improved, helping to treat non-union fractures more effectively. -
Biodegradable Implants
The development of biodegradable implants offers new options for surgical fixation, reducing the need for additional surgeries to remove hardware.
Interesting Facts About the Scaphoid Bone
The scaphoid bone itself has some fascinating characteristics that make it unique among the bones in the wrist.
-
Largest Carpal Bone
The scaphoid is the largest of the carpal bones, playing a crucial role in wrist movement and stability. -
Poor Blood Supply
The scaphoid has a limited blood supply, making it prone to non-union fractures and delayed healing. -
Named After a Boat
The name "scaphoid" comes from the Greek word "skaphe," meaning boat, due to its boat-like shape. -
Commonly Injured in Sports
Scaphoid fractures are common in sports, especially those involving falls on an outstretched hand, such as skateboarding and snowboarding. -
Difficult to Diagnose
Scaphoid fractures can be challenging to diagnose because they may not show up on initial X-rays, requiring advanced imaging techniques for accurate assessment. -
Vital for Wrist Function
The scaphoid plays a vital role in wrist function, connecting the two rows of carpal bones and allowing for smooth wrist movement.
Final Thoughts on Herbert Classification
Herbert Classification is a system used to categorize fractures of the scaphoid bone in the wrist. It helps doctors determine the severity of the fracture and decide the best treatment. This classification divides fractures into stable and unstable types, with further subcategories based on specific fracture patterns.
Understanding this system is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Stable fractures often heal with casting, while unstable ones might need surgery. Knowing the type of fracture can prevent complications and ensure a quicker recovery.
In short, Herbert Classification plays a vital role in orthopedic medicine. It guides healthcare professionals in making informed decisions, ultimately improving patient outcomes. Whether you're a medical student, a healthcare provider, or just curious, grasping these facts can enhance your knowledge about wrist fractures and their management.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
