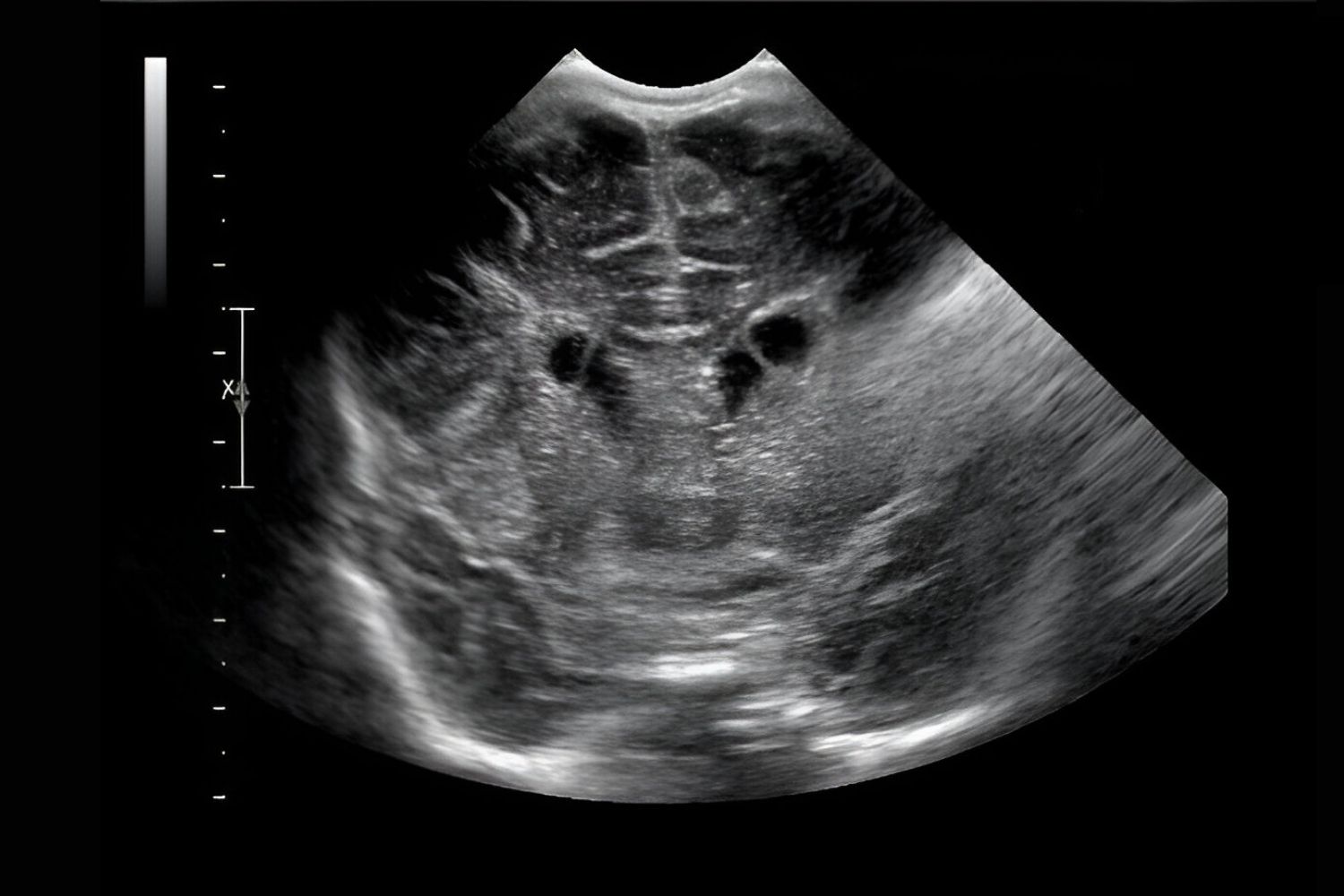
What is a frontal horn cyst? A frontal horn cyst is a fluid-filled sac located in the frontal horn of the brain's lateral ventricles. These cysts can vary in size and may be discovered during routine imaging tests like an MRI or CT scan. While some cysts are benign and cause no symptoms, others might lead to headaches, seizures, or other neurological issues. Understanding the nature of these cysts is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. In this blog post, we'll explore 30 intriguing facts about frontal horn cysts, shedding light on their causes, symptoms, and potential treatments. Get ready to learn more about this fascinating medical condition!
Key Takeaways:
- Frontal horn cysts are fluid-filled sacs in the brain's lateral ventricles. They can be asymptomatic or cause symptoms like headaches, seizures, and vision problems. Early detection and appropriate treatment are crucial for better outcomes.
- Genetic mutations, infections during pregnancy, trauma, and brain tumors are some causes of frontal horn cysts. Understanding these factors can help in early detection and management of these cysts.
What is a Frontal Horn Cyst?
A frontal horn cyst is a fluid-filled sac located in the frontal horn of the brain's lateral ventricles. These cysts can be congenital or acquired and vary in size and impact. Understanding them can help in recognizing symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment.
- Frontal horn cysts are often detected during prenatal ultrasounds.
- These cysts can be asymptomatic, meaning they might not cause any noticeable symptoms.
- Congenital cysts are present at birth, while acquired cysts develop later in life.
- The frontal horn is part of the brain's lateral ventricles, which produce cerebrospinal fluid.
- Cerebrospinal fluid helps cushion the brain and spinal cord from injury.
Causes of Frontal Horn Cysts
Understanding the causes of frontal horn cysts can help in early detection and management. These cysts can arise from various factors, including genetic and environmental influences.
- Genetic mutations can lead to the development of frontal horn cysts.
- Infections during pregnancy, such as cytomegalovirus, can cause these cysts.
- Trauma to the head can result in the formation of acquired cysts.
- Brain tumors might lead to cyst formation as a secondary effect.
- Vascular malformations in the brain can also be a contributing factor.
Symptoms of Frontal Horn Cysts
While some cysts are asymptomatic, others can cause a range of symptoms depending on their size and location. Recognizing these symptoms can prompt timely medical intervention.
- Headaches are a common symptom associated with larger cysts.
- Seizures might occur if the cysts affect brain function.
- Developmental delays in children can be a sign of congenital cysts.
- Vision problems may arise if the cysts press on optic pathways.
- Balance issues can occur if the cysts impact motor control areas.
Diagnosis of Frontal Horn Cysts
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective management. Various imaging techniques and tests help in identifying these cysts.
- Ultrasound is often used for prenatal detection of cysts.
- MRI scans provide detailed images of the brain, helping in cyst identification.
- CT scans can also be used to detect and monitor cysts.
- Neurological exams assess the impact of cysts on brain function.
- Genetic testing might be recommended if a hereditary condition is suspected.
Treatment Options for Frontal Horn Cysts
Treatment depends on the size and symptoms of the cysts. Options range from monitoring to surgical intervention.
- Observation is often recommended for asymptomatic cysts.
- Medication can help manage symptoms like headaches and seizures.
- Surgical drainage might be necessary for larger cysts causing pressure.
- Endoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive option for cyst removal.
- Shunt placement can help drain excess fluid from the cysts.
Prognosis and Long-term Outlook
The long-term outlook for individuals with frontal horn cysts varies. Early detection and appropriate treatment can improve outcomes.
- Prognosis is generally good for asymptomatic cysts.
- Regular monitoring is essential to detect any changes in cyst size or symptoms.
- Early intervention can prevent complications in symptomatic cases.
- Rehabilitation therapy might be needed for those with developmental delays.
- Support groups can provide emotional support and resources for affected families.
Final Thoughts on Frontal Horn Cysts
Frontal horn cysts, though often alarming, are usually benign and manageable. Understanding their nature, causes, and potential treatments can ease many concerns. Regular check-ups and open communication with healthcare providers ensure any changes are monitored closely. Knowledge empowers patients and their families to make informed decisions.
While most cysts don't cause significant issues, staying informed about symptoms and treatment options is crucial. Advances in medical imaging and research continue to improve diagnosis and management. If you or a loved one is dealing with a frontal horn cyst, remember that medical professionals are there to guide you through every step.
Stay proactive about your health, ask questions, and seek second opinions if needed. With the right information and support, navigating the complexities of frontal horn cysts becomes much more manageable.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
