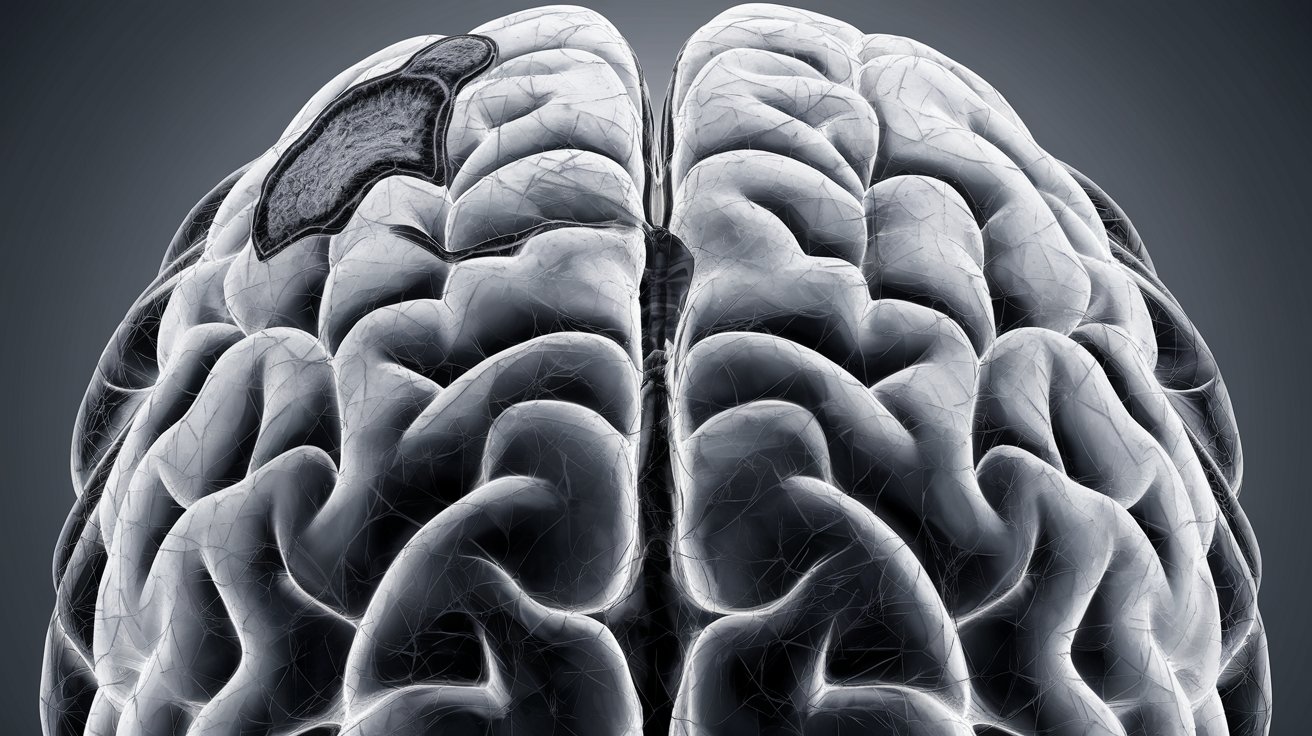
Focal Agyria Pachygyria might sound like a mouthful, but understanding it is crucial for those affected. This rare brain disorder involves abnormal brain development, leading to issues with motor skills, intellectual abilities, and sometimes seizures. Agyria means "without gyri," referring to the smooth brain surface, while Pachygyria means "thick gyri," indicating fewer and broader folds. These conditions fall under the umbrella of lissencephaly, which translates to "smooth brain." Knowing the facts about this condition can help in recognizing symptoms early, seeking appropriate medical advice, and understanding the challenges faced by those living with it. Let's dive into 30 essential facts about Focal Agyria Pachygyria to shed light on this complex condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Focal Agyria Pachygyria is a rare brain condition with fewer folds and grooves, causing seizures, developmental delays, and muscle weakness. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
- Research is ongoing to understand and treat Focal Agyria Pachygyria, including stem cell and gene therapy, clinical trials, and improved imaging technology. Support groups and educational accommodations help individuals and families navigate the challenges.
What is Focal Agyria Pachygyria?
Focal Agyria Pachygyria is a rare brain malformation that affects the development of the cerebral cortex. This condition results in abnormal brain folds and grooves, leading to various neurological issues. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Focal Agyria Pachygyria is a type of lissencephaly, which means "smooth brain." The brain's surface appears smoother than usual due to fewer folds and grooves.
-
The term "Agyria" refers to the absence of gyri, the ridges on the brain's surface. "Pachygyria" means thickened gyri, indicating fewer but broader ridges.
-
This condition is usually diagnosed through MRI scans, which reveal the abnormal brain structure.
-
Focal Agyria Pachygyria can affect one or multiple areas of the brain, leading to varying degrees of severity in symptoms.
Causes and Genetic Factors
Understanding the causes and genetic factors behind Focal Agyria Pachygyria can provide insight into its development and potential treatments.
-
Genetic mutations are often responsible for this condition. Mutations in genes like LIS1, DCX, and TUBA1A have been linked to it.
-
Some cases are inherited in an autosomal dominant or recessive pattern, meaning they can be passed down from parents to children.
-
Prenatal infections or exposure to harmful substances during pregnancy can also contribute to the development of this brain malformation.
-
Environmental factors like maternal diabetes or malnutrition during pregnancy may increase the risk of Focal Agyria Pachygyria.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of Focal Agyria Pachygyria can vary widely, making diagnosis challenging. Here are some key points about its symptoms and how it is diagnosed.
-
Seizures are a common symptom, often starting in infancy or early childhood.
-
Developmental delays in motor skills, speech, and cognitive abilities are frequently observed.
-
Muscle weakness or stiffness, known as spasticity, can affect movement and coordination.
-
Feeding difficulties and poor growth may occur in infants with this condition.
-
MRI scans are the primary diagnostic tool, providing detailed images of the brain's structure.
-
Genetic testing can help identify specific mutations responsible for the condition.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for Focal Agyria Pachygyria, various treatments and management strategies can help improve the quality of life for those affected.
-
Antiepileptic medications are often prescribed to control seizures.
-
Physical therapy can help improve muscle strength and coordination.
-
Occupational therapy focuses on enhancing daily living skills and independence.
-
Speech therapy can assist with communication difficulties and language development.
-
Nutritional support may be necessary for those with feeding difficulties to ensure proper growth and development.
-
Regular monitoring by a team of healthcare professionals is essential to address the evolving needs of individuals with this condition.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand Focal Agyria Pachygyria and develop more effective treatments.
-
Stem cell research holds promise for repairing damaged brain tissue and improving neurological function.
-
Gene therapy is being explored as a potential treatment to correct genetic mutations causing the condition.
-
Clinical trials are ongoing to test new medications and therapies for managing symptoms.
-
Advances in imaging technology are improving the accuracy of diagnosis and understanding of brain malformations.
-
Collaborative research efforts between scientists, clinicians, and patient advocacy groups are driving progress in this field.
Living with Focal Agyria Pachygyria
Living with Focal Agyria Pachygyria presents unique challenges, but support and resources are available to help individuals and families.
-
Support groups provide a platform for sharing experiences and advice with others facing similar challenges.
-
Educational accommodations can help children with this condition succeed in school.
-
Assistive technology like communication devices and mobility aids can enhance independence.
-
Respite care services offer temporary relief for caregivers, allowing them to rest and recharge.
-
Awareness campaigns aim to educate the public and healthcare professionals about Focal Agyria Pachygyria, promoting early diagnosis and intervention.
Final Thoughts on Focal Agyria Pachygyria
Focal Agyria Pachygyria, though rare, presents a unique set of challenges and insights into brain development. Understanding this condition helps medical professionals provide better care and support for affected individuals. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve quality of life, offering hope to families navigating this complex journey.
Research continues to evolve, shedding light on potential treatments and therapies. Staying informed about the latest advancements is crucial for those impacted by this condition. By spreading awareness and fostering a supportive community, we can make a difference in the lives of those affected by Focal Agyria Pachygyria.
Remember, knowledge is power. The more we learn about this condition, the better equipped we are to support and advocate for those who need it most.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
